Guide to Resin 3D Printing[+Cost Calculator]

Discover resin 3D printing: its precision, materials, and applications. Learn costs, tips, and get a free quote with Unionfab’s cost calculator!
Introduction
Originating in the early 20th century, resin materials have evolved into critical industrial enablers—earning the title "the lifeblood of industry."
In 1986, Chuck Hull pioneered SLA (stereolithography) technology, marking the birth of resin 3D printing. Today, no longer confined to prototyping, the technology now enables high-precision production in dentistry, jewelry, filming, and beyond, transforming the way we manufacture.
This guide is crafted for professionals and creators exploring resin 3D printing as a prototyping solution. We will walk you through its core aspects: technology, workflow, materials, benefits, challenges, and best practices.
By the end, you’ll understand how resin 3D printing can accelerate your design iteration process, reduce time to market, and bring your ideas to life with unparalleled detail.
What is Resin 3D Printing?

Resin 3D printing, also known as vat photopolymerization, is an additive manufacturing process that uses UV light to cure liquid photopolymer resins layer by layer.
Key technologies include SLA (stereolithography), DLP (digital light processing), LCD, or MSLA (masked stereolithography), and Polyjet which differ in light source and curing methods but share the core principle of selective resin solidification.
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
High Detail and Precision
Resin printers, especially SLA and DLP types, produce parts with incredibly fine details and smooth surfaces—ideal for intricate prototypes or components requiring tight tolerances.
Excellent Surface Finish
Compared to FDM printing, resin prints require less post-processing. The smooth, professional finish is perfect for visual prototypes, display models, or client-ready presentations.
Wide Range of Material Properties
From flexible and tough to high-temperature and castable resins, there’s a wide variety to suit different prototyping needs—from functional testing to mold-making.
Ideal for Small Parts
Resin printers are perfect for creating small, highly detailed parts such as dental aligners, jewelry masters, or mechanical components for fit testing.
Faster for Small Batches
For short runs of small parts, resin printing can be faster and more cost-effective than traditional manufacturing or other types of 3D printing.
Applications of Resin 3D Printing
Resin 3D printing’s precision and versatility make it a go-to technology across various fields. Here are some key applications:
Jewelry: Crafters use castable resins to create intricate molds for rings, pendants, and earrings, streamlining custom designs.
Miniatures: Hobbyists print highly detailed figurines for tabletop gaming or collectibles with smooth, paint-ready surfaces.
Dental and Medical: Dentists produce accurate dental molds, aligners, and surgical guides, while biocompatible resins enable custom prosthetics.
Prototyping: Engineers craft small, detailed prototypes for product testing, benefiting from resin’s fine resolution.
Art and Design: Artists sculpt unique pieces or replicate complex textures, pushing creative boundaries.
Engineering: Tough resins support functional parts like gears or housings for small-scale production.
How Does Resin 3D Printing Work?
Resin 3D printing begins with a digital 3D model, sliced into thin layers by software. A resin printer then builds the object layer by layer: liquid resin in a tank is selectively hardened by UV light, guided by the model’s design. Once printing is complete, the object is removed, cleaned, and cured for strength.
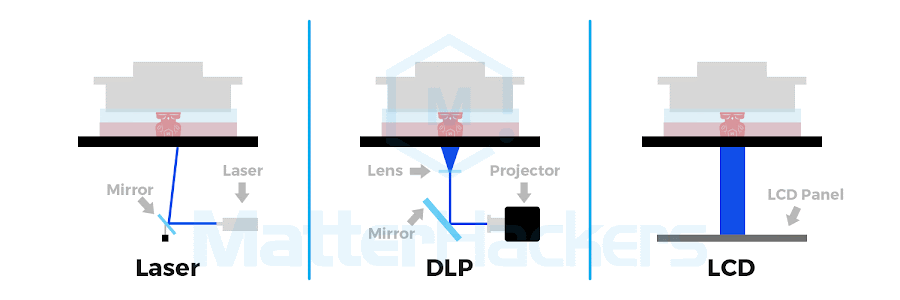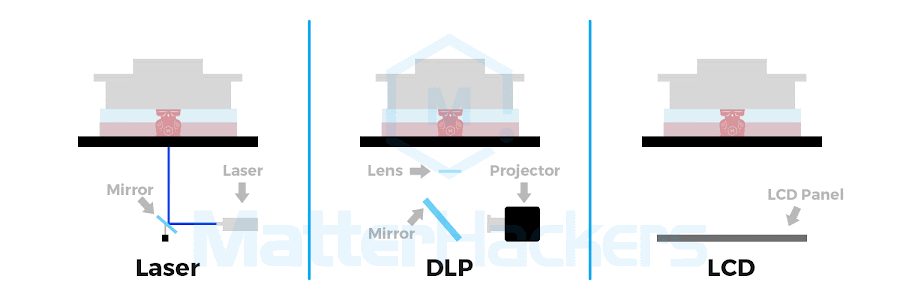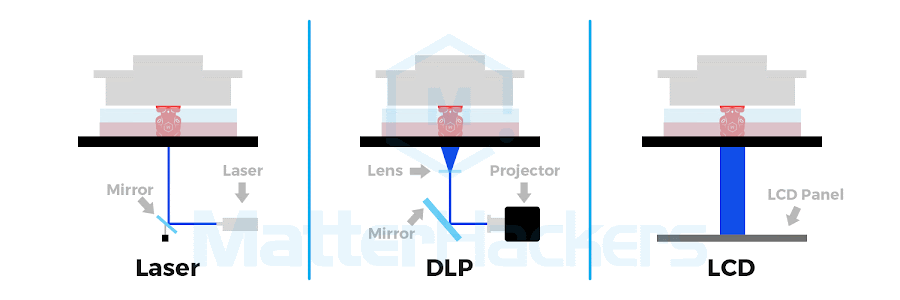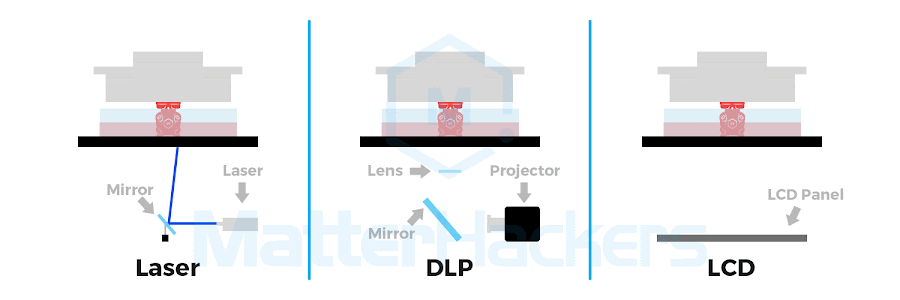
Source: matterhackers.com

Source: makeagif.com
SLA vs. DLP vs. LCD (MSLA) vs. Polyjet
The 4 key technologies for resin 3d printing are Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), Liquid Crystal Display (LCD, or Masked SLA, MSLA), and Polyjet. Each method uses light to solidify resin, differing mainly in speed and how the light is delivered.
SLA | DLP | LCD, or MSLA | Polyjet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Process | A laser precisely cures resin point by point. | A projector cures an entire layer at once with a flashed image. | An LCD screen shapes UV light to cure full layers, similar to DLP. | Inkjet-style print heads jet and cure layers of resin. |
Print Accuracy & Surface Quality | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
Print Speed | ⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
Price | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️ | ⭐️ |
Printable Size | Medium to large (varies by machine) | Small to medium (projector limits) | Small to medium (screen size limits) | Small to medium |
Best For | Precision work (jewelry, dental) | Small detailed batches (miniatures) | Budget prints with solid detail | High-end prototypes, visual models |
In summary:
SLA produces the finest details but is pricier.
DLP balances speed and detail, ideal for miniatures.
LCD is the most budget-friendly, with lower surface quality.
Polyjet offers the best finish and multi-materials, but at the highest cost.

Post-Processing Resin Prints
After printing, the object is removed from the build plate, still sticky with uncured resin. It’s washed—usually in isopropyl alcohol (IPA)—to remove excess resin, then cured under UV light (via a curing station or sunlight) to harden fully.
For unique surface effects, like transparency or color, optional techniques like sanding, dyeing, and painting can help. Btw, if you’re interested in clear resin 3d printing, you might as well read our previous article: Guide to Clear Resin 3D Printing.
Tips for Resin 3D Printing
Match Printing Settings Use the recommended print settings for each resin type. Run an exposure test if needed.
Resin Handling Tips Don’t mix different resins without testing—some may not be compatible. Filter old resin before reuse to remove dust or cured bits.
Cleaning & Maintenance Clean the build plate and resin vat after every print. Leftover resin can cause failures.
Model Repair If prints warp in hot weather, soak in 40–60°C warm water to reshape.
Types of Resin for 3D Printing

Resins can be sorted into three broad categories based on their properties and uses: General-Purpose Resins for everyday printing, Engineering Resins for tougher, functional parts, and Specialty Resins for unique, niche applications.
The breakdown below makes it easier to match a resin to your specific needs, whether you’re crafting a simple model or a complex prototype.
General-purpose Resin
Resin Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|
Standard Resin | Figurines, simple prototypes |
Translucent Resin | Semi-transparent objects like light diffusers, artistic pieces |
Transparent/Clear Resin | Clear parts like lenses, display models, or fluid containers |
High Detail Resin | tabletop game pieces, architectural models |
Ultra Detail Resin | miniature sculptures, intricate prototypes, or fine-scale models |
Engineering Resin
Resin Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|
High-Temp Resin | Heat-resistant parts like injection molds, engine components |
Tough Resin | Durable, functional parts like tool handles, casings, or brackets t |
Rigid Resin | Stiff, structural components like frames, mounts, or load-bearing prototypes |
Nylon-like Resin | Tough, slightly flexible parts like hinges, snap-fits, or wear-resistant engineering prototypes |
Rubber-like Resin | Soft, bendable items like gaskets, grips, shoe soles, or flexible prototypes |
Speciality Resin
Resin Type | Common Uses |
|---|---|
Casting Resin | Jewelry molds, dental frameworks, or small metal parts |
Biocompatible Resin | Medical items like dental aligners, hearing aids, or surgical guides |
Flame-Retardant Resin | Fire-safe parts like electronics housings, aerospace components, or safety equipment. |

3D Printing Resin vs Filament
In 3D printing, resin and filament are two of the main material players, each tied to different tech and results. Here’s how they compare:
Resin (SLA/DLP/LCD) | Filament (FDM) | |
|---|---|---|
How It Works | Liquid resin hardens under UV light, layer by layer | Plastic filament melts through a nozzle, building layers |
Pros | High detail (10-50 microns), smooth surfaces, versatile types (tough, flexible) | Cheaper materials, larger prints, simpler process |
Cons | Messy (needs washing, curing), more expensive, smaller print sizes | Visible layer lines, less detail (100-300 microns), limited variety |
Best For | Intricate minis, jewelry, or dental parts needing precision | Big prototypes, budget builds, or sturdy parts |
Quick Take
Detail: Resin beats filament for fine details and smoothness.
Cost: Filament wins on price and ease—no messy cleanup.
Size: Filament handles bigger objects; resin’s capped by tank size.
How Much Does Resin 3D Printing Cost?
When it comes to the question: How Much Does Resin 3D Printing Cost, the answer depends on you are planning to self-print via buying a 3d printer or simply outsource this job.
Here, we will break the question down to help you make decisions.
Self Printing
The cost of self-printing is more than the cost of equipment and materials. There are many potential costs. The table below has included the potential cost composition of self-printing.
Category | Item | Description |
|---|---|---|
Equipment Cost | 3D Printer (SLA/DLP/LCD) | Main printing device |
Wash & Cure Machine | Used to clean and post-cure printed models | |
Material Cost | Resin (Standard or Special Types) | Printing material sold by the kilogram |
Consumables | Gloves, Masks, Alcohol | For safe operation and cleaning |
FEP Film | Replace every 1–3 months | |
Funnel / Resin Filter | To remove debris from reused resin | |
Energy Cost | Electricity | For printer and curing machine |
Cleaning & Maintenance | IPA / Cleaning Solution | For washing uncured resin |
Tools & Maintenance Supplies | Scrapers, screwdrivers, etc. | |
Software Cost | Slicer Software (e.g., Chitubox Pro) | Free basic version; Pro version may require subscription |
Other | Failed Prints / Wasted Resin | Due to errors, support failure, etc. |
Test Prints (Support / Exposure) | Calibration towers, support tests, etc. |
Outsourcing
Although outsourcing is more convenient and hassle-free, it’s worth understanding how service providers calculate resin 3D printing costs. The formula is as follows:
Total 3DP Cost = Printing Cost (Material Unit Price * Material Volume) + Post-processing Fee + Packaging Fee + Shipping Fee + Taxes
Notes:
Some default post-processing (like cleaning and support removal) is free.
Extra fees apply for oversized prints or fragile items needing special packaging like wooden or air-freight boxes—standard packaging (corrugated box with bubble wrap or foam padding) is included at no cost.
Taxes typically range from 5% to 20% of the total, depending on the country’s customs policies.
For a deeper dive into 3D printing costs, check out our previous article: How Much Does It Cost to 3D Print Something?
Curious about the cost to print your model? Feel free to use Unionfab’s free online 3D printing cost calculator below:

Resin 3D Printing Service Provider Comparison
To help you find the most suitable resin 3d printing service provider, we have compared som of the key players around the world in the table below.

Takeaways
On a Budget? Prioritize Cost
✅ Unionfab: Lowest sample cost at $2.
✅ PCBWay: Also affordable, sample cost at $4.98.
Need Large Build Volume?
✅ Unionfab / PCBWay / Materialise: Offer up to 2100 x 800 x 700 mm, ideal for large models.
Tight on Time? Need Fast Turnaround?
✅ Xometry: As fast as 2 business days.
✅ Unionfab / PCBWay: Standard 3 business days, cost-effective choices.
Achieve Superior Detail with Resin 3D Printing at Unionfab
Unionfab is a subsidiary of Uniontech, which, being China's leading 3D printing company, dominates 60% of China's resin 3d printing market share. Unionfab excels in providing comprehensive 3d printing services, highlighted by four key strengths: experience, certification, shipping, and cost.
Experience: With 100 3D printers and 20+ years' experience in 3D printing.
Quality Assurance: Certified to the strict ISO 9001 quality management standards.
Fast Shipping: Air shipments in 3-5 days via DHL Express and FedEx.
Competitive Pricing: 70% cheaper than European and American competitors without compromising on quality.
To give you a better understanding of our resin 3D printing capabilities, we’ve prepared a VR video for a virtual factory tour. Click the GIF below to start now!
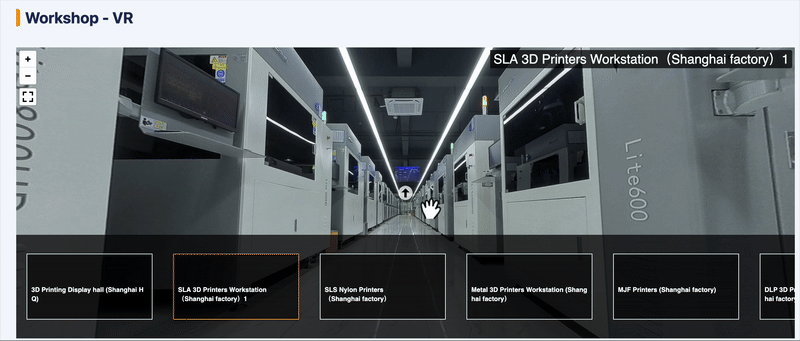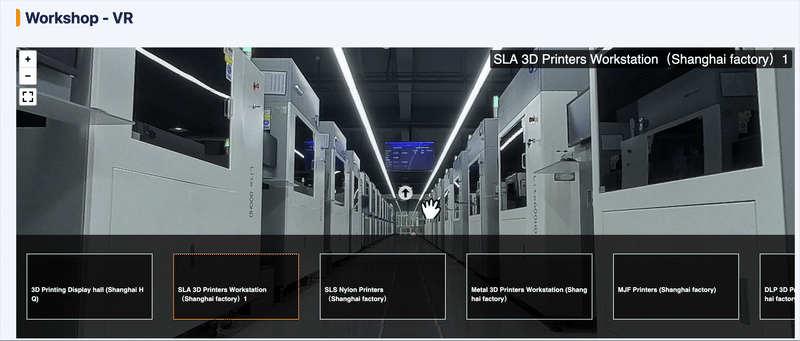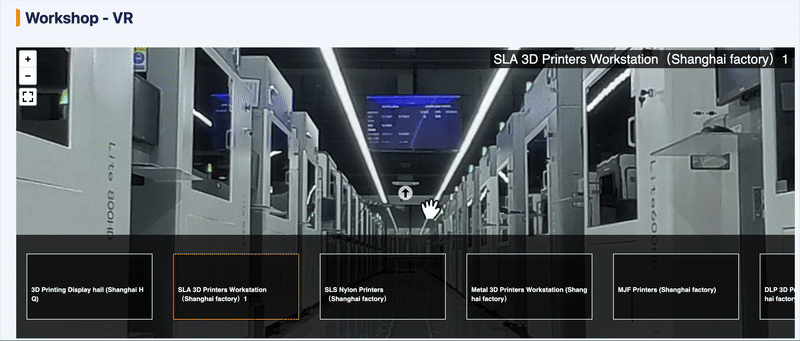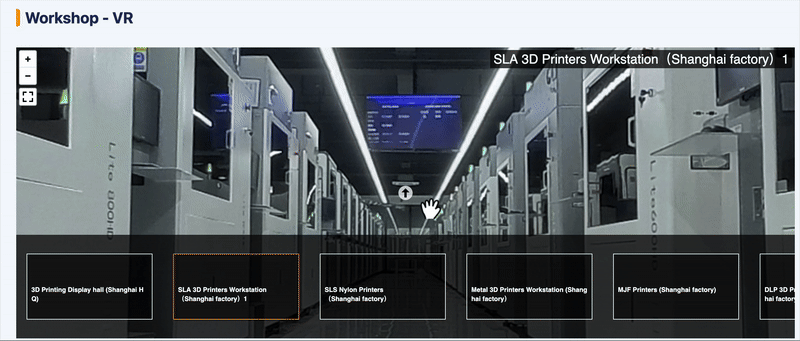
Unionfab’s Resin 3D Printing Service
Here are the details of Unionfab’s resin 3d printing service.
SLA | DLP | Polyjet | |
|---|---|---|---|
Equipment | Uniontech (500+) | Uniontech | Stratasys |
Materials | High-temp-150D/220D Resin | Ultra Detail Resin | Multi Color Resin |
Max Part Size | 2100 x 700 x 800 mm | 300 x 140 x 240 mm | 500 x 400 x 200mm |
Layer Thickness | 0.1mm | 0.1mm | 14μm |
Tolerance | ±0.3% | ±0.3% | ±0.3% |
Min. Feature Size | Normal Resolution: X-Y: 0.254mm Z: 0.406mm | Normal Resolution: X-Y: 0.254mm Z: 0.406mm | / |
Min. Wall Thickness | 0.7 mm | 0.7 mm | 0.06mm |
Min. Reference Unit Price of Materials | Standard Resin (White): $0.14/g | Standard Resin (White): $0.14/g | |
Pass Rate | 99.5% | 99.5% | 99.5% |
On-time Delivery Rate |
|
|
|
*The actual unit price is subject to real-time inquiry.
If you haven’t used Unionfab’s 3d printing service before, sign up to get 10% discount for your first order.

Post-processings for Resin 3D Printing
Except for different resin 3d printing services, we can also finish your parts as required. The followings are some of our finished prints.

| 
|
|---|---|

| 
|

| 
|

| 
|
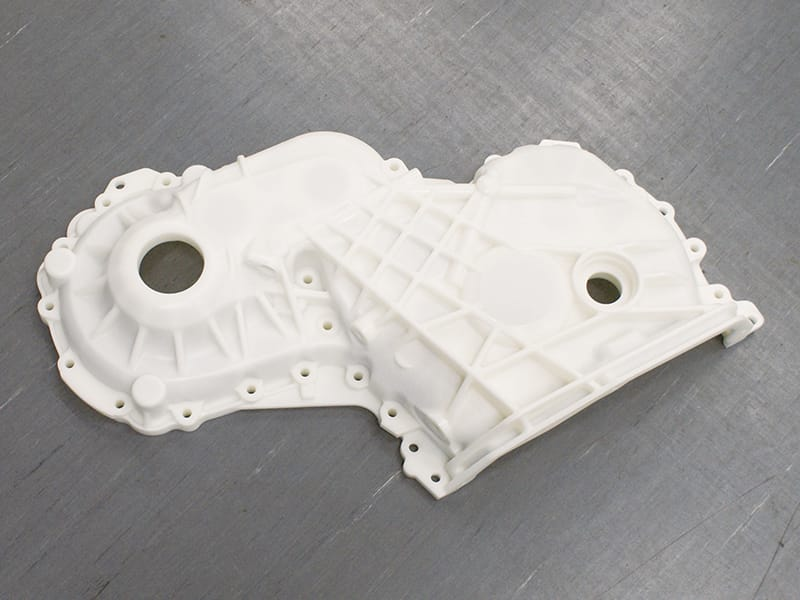
Resin 3D Printing Case Displays
The followings are some resin 3d prints made by Unionfab.

| 
High-detail Resin |
|---|---|

Ultra-detail Resin | 
|

| 
|
FAQs
How long do resin 3d prints last?
Resin 3D prints can last years if kept away from direct sunlight, moisture, and heat. However, they may become brittle or yellow over time, especially if not fully cured or if stored improperly.
Is resin or filament better for 3d printing?
It depends on your needs:
Resin offers higher detail and smooth surfaces, ideal for miniatures, jewelry, and detailed prototypes.
Filament (FDM/PLA/ABS) is stronger, cheaper, less messy, and better for larger or functional parts.
What to do when 3d print is slowly falling resin?
If a resin print is slumping, bending, or falling apart, check:
Insufficient curing → re-cure with UV light.
Thin walls or unsupported structure → add supports or increase wall thickness.
Overheating or poor material → store in a cooler place, or use higher-quality resin.
What are the best resin and the strongest resin for 3d printing?
Best quality resin: Siraya Tech, Anycubic, Elegoo ABS-like resins.
Strongest resin: Engineering-grade resins like Siraya Tech Blu, Phrozen Onyx Rigid Pro410, or Formlabs Tough/ Durable Resin.
How to paint resin 3d prints?
Post-cure and clean the print.
Sand the surface if needed.
Apply a primer (usually spray primer).
Use acrylic paints for color.
Seal with a clear coat to protect.
Is 3d print resin toxic?
Yes, uncured resin is toxic and can irritate skin, eyes, and lungs. Always wear gloves and a mask, and work in a well-ventilated area. Once fully cured, prints are generally safe to handle.
Is resin 3D printing better than PLA?
For fine details and surface finish, resin is better.
For strength, ease of use, and safety, PLA (filament) is better. Choose based on your project’s priorities.
What are the disadvantages of resin 3D printing?
Toxic and messy: Requires gloves, cleaning, and careful disposal.
More expensive: Printers, resin, and post-processing tools cost more.
Post-processing: Requires washing and curing.
Brittle parts: Less flexible and durable than filament prints.

