5 Common Metal Casting Types: A Comprehensive Guide [+ Comparison Table]
Explore metal casting types and compare precision, cost, and finish with our easy comparison table. Find the best process for your project!
Introduction
Choosing the right metal casting method can be challenging, but understanding these key factors will help you make an informed decision:
Design complexity: Which method suits intricate designs?
Material compatibility: What materials work best for each casting type?
Production volume: How does scale affect your choice?
Precision and finish: What level of detail do you need?
Cost efficiency: Which method offers the best balance of cost and quality?
This guide will help you make informed decisions. Stay tuned for expert tips on how to evaluate each factor and choose the right process for your project!
5 Common Types of Metal Casting
Sand Casting
Process
Sand casting involves creating a mold from sand mixed with a bonding agent, such as clay or resin. The mold consists of two halves, which are joined together to form a cavity where molten metal is poured. Once the metal cools and solidifies, the sand mold is broken to extract the finished part.
Key Steps in Sand Casting
Pattern Making: A pattern of the desired part is created, typically from wood, metal, or plastic.
Mold Preparation: Sand is packed around the pattern to form the mold cavity. Gating and risers are added to guide molten metal and release gases.
Pouring: Molten metal is poured into the cavity and left to cool.
Breaking the Mold: Once solidified, the sand mold is broken, and the part is removed.
Finishing: The part undergoes post-processing, such as trimming, grinding, and machining.
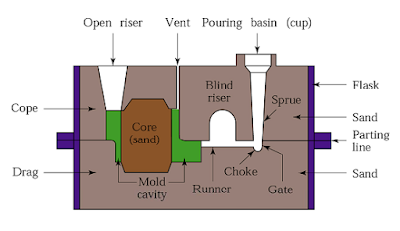
Sand casting Process
Source: bernierinc.com

Common Materials for Sand Casting
Metals:
Steel
Cast iron
Aluminum
Brass
Non-metals (for patterns):
Wood
Plastic
Metal
Advantages of Sand Casting
Cost-effective for small-batch and large-part production.
Handles complex geometries and large components.
Compatible with a wide range of materials.
Challenges
Surface finish is rough and may require additional machining.
Dimensional accuracy is lower compared to investment or die casting.
Real-World Applications
Engine blocks and cylinder heads
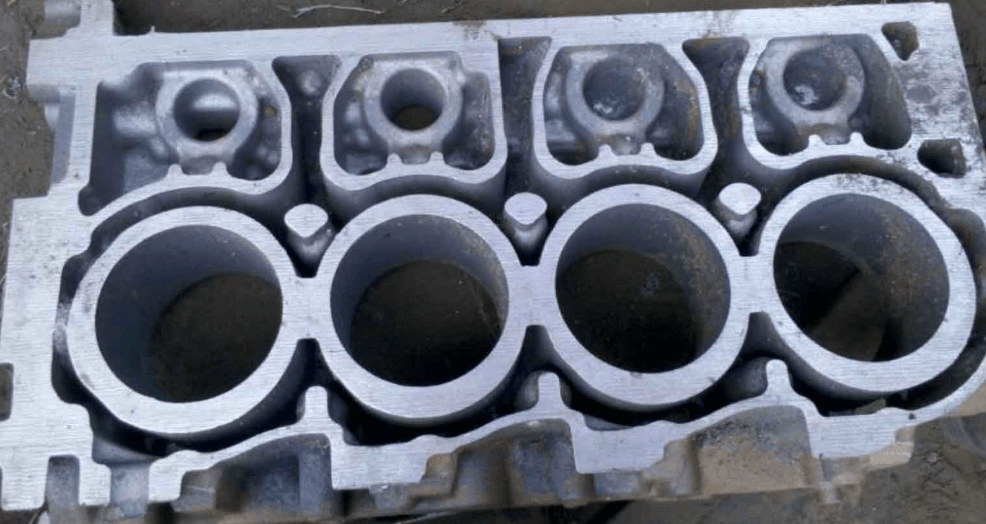

Source: zhycasting.com

Pump housings and gearboxes
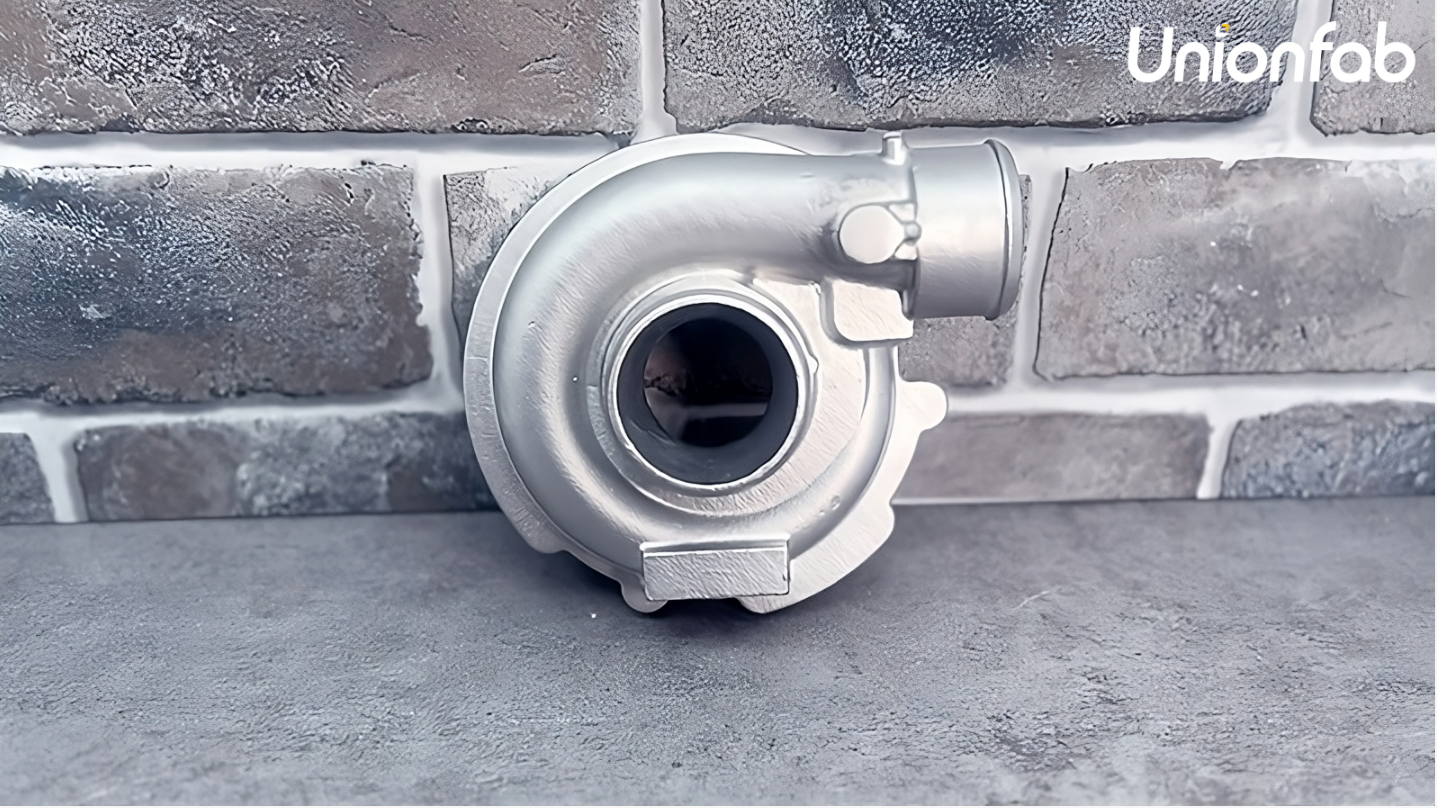

Source: Unionfab
Investment Casting (Lost Wax Casting)
Process
Investment casting uses a wax pattern to create a highly precise mold. The wax is coated with a ceramic material that hardens into a shell.
After the wax is melted out, molten metal is poured into the cavity. This process allows for intricate details and smooth finishes.
Key Steps in Investment Casting
Wax Pattern Creation: A detailed wax model of the part is made, often using injection molding.
Assembly: Multiple wax patterns can be attached to a central sprue to form a "tree."
Ceramic Shell Coating: The wax model is dipped in a ceramic slurry and coated with sand. This process is repeated to build a thick shell.
Dewaxing: The ceramic shell is heated to remove the wax, leaving a cavity for the metal.
Casting: Molten metal is poured into the shell and left to solidify.
Shell Removal: The ceramic shell is broken, revealing the cast part.
Finishing: Parts are trimmed, cleaned, and finished as needed.
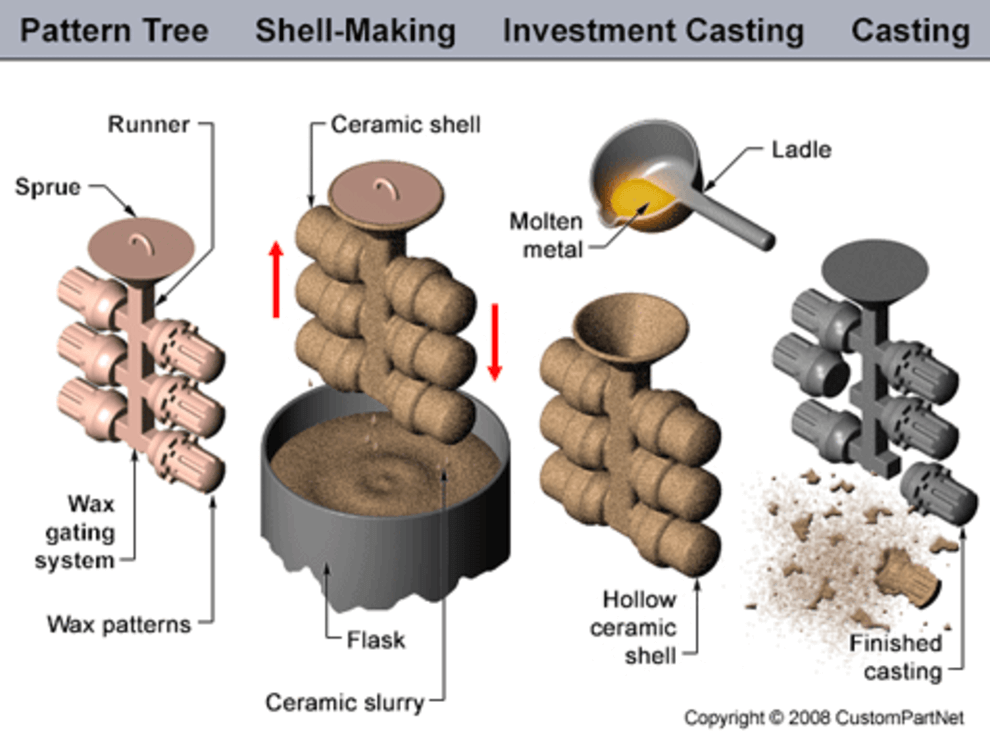
Source: mech4study.com

Common Materials for Investment Casting
Stainless steel
Aluminum alloys
Bronze
Nickel alloys
Advantages of Investment Casting
High precision and smooth surface finish.
Allows for complex designs and thin walls.
Minimal post-processing required.
Challenges
Higher tooling costs compared to sand casting.
Best suited for small to medium-sized parts.
Real-World Applications
Aerospace components like turbine blades.
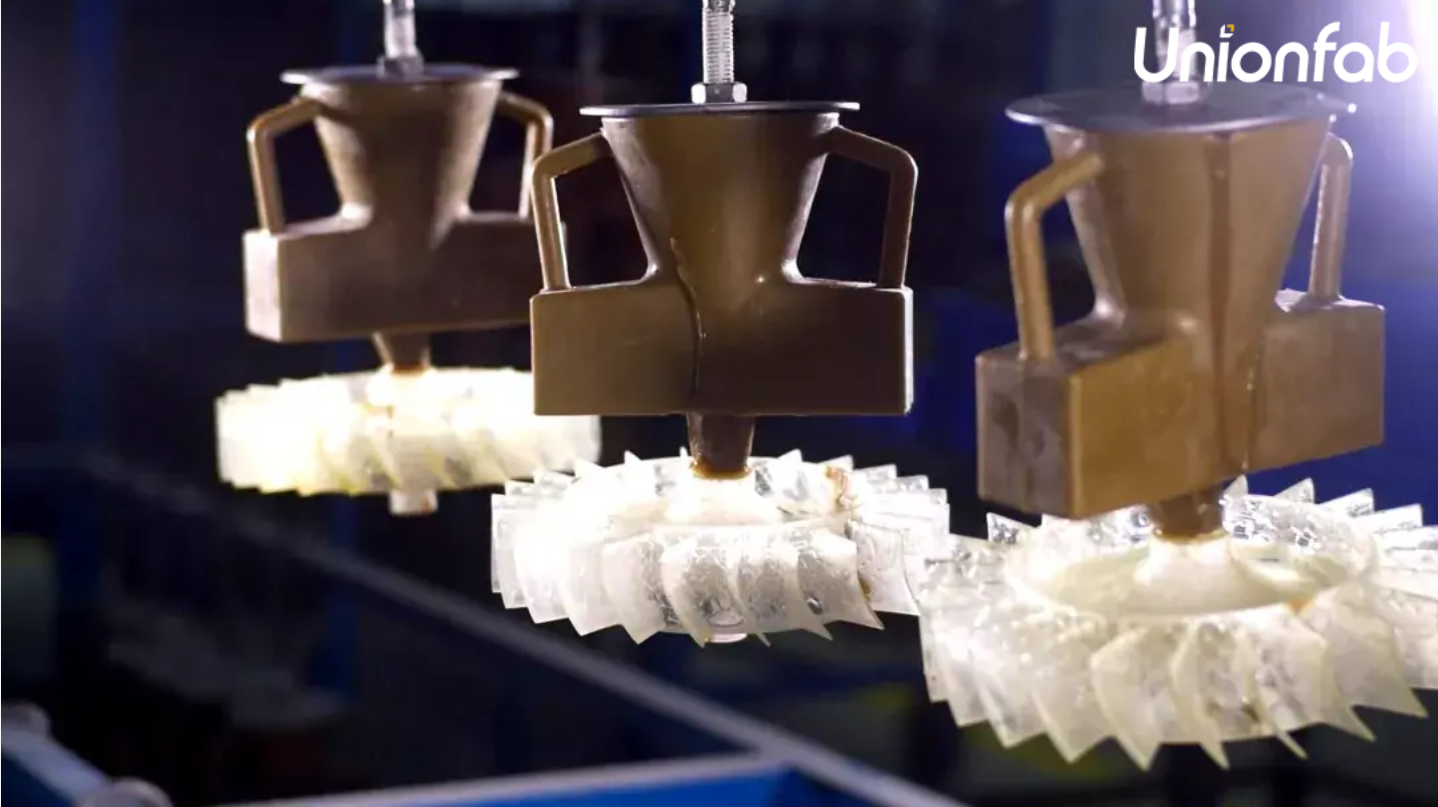

Turbine Blades in Making. 
Turbine Blades by Investment Casting.
Unionfab specialize in small-batch production with high accuracy, providing efficient, cost-effective solutions for intricate components.

Die Casting
In the die casting process, molten metal is injected into a steel mold, known as a die, using high pressure. The mold is held under pressure until the metal cools and solidifies.
Once solidified, the part is ejected from the mold. This process is highly automated, making it ideal for producing large quantities of precise and detailed components.
Common Materials for Die Casting
Aluminum
Zinc
Magnesium
Advantages of Die Casting
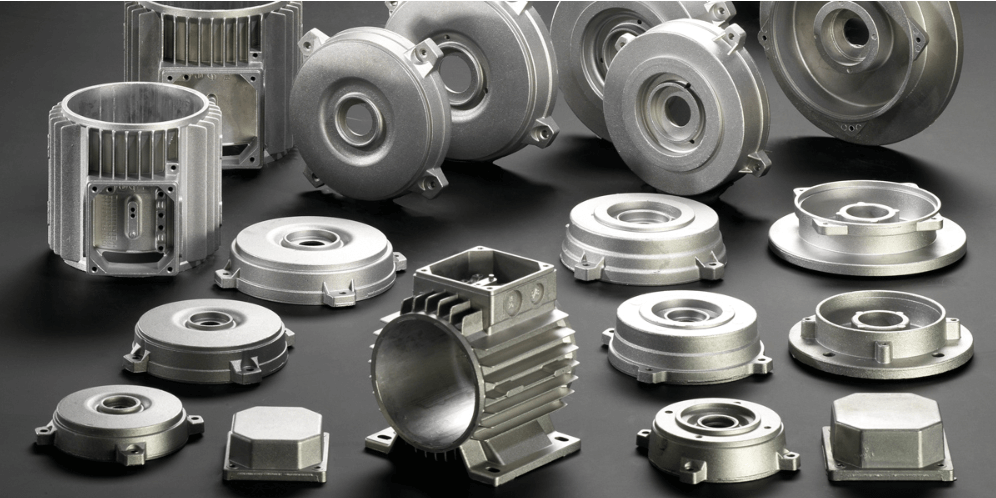
Source: sunrise-metal.com
Provides excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy
Enables high production rates for large volumes
Suitable for complex shapes with fine details
Challenges
High tooling costs make it economical only for large-scale production
Limited to low-melting-point metals⠀
Centrifugal Casting
Centrifugal casting involves pouring molten metal into a rotating mold. The centrifugal force generated by the spinning mold pushes the metal outward, creating a dense and uniform layer against the mold walls.
As the metal cools, it solidifies into a cylindrical or symmetrical shape.
Common Materials for Centrifugal Casting
Steel
Stainless steel
Cast iron
Bronze
Advantages of Centrifugal Casting
Produces dense components with minimal porosity
Well-suited for symmetrical parts requiring high strength
Cost-effective for medium production volumes
Challenges
Restricted to cylindrical or symmetrical shapes
Requires precise control of rotation speed and pouring parameters
Continuous Casting
In continuous casting, molten metal is continuously poured into a water-cooled mold. As the metal enters the mold, it begins to solidify while still being withdrawn from the mold. This creates a continuous length of solid metal, which is later cut into desired shapes and sizes.
For more information on continuous casting, please read this article.
Common Materials for Continuous Casting
Steel, including carbon and stainless steel
Aluminum and its alloys
Copper and brass
Advantages of Continuous Casting
Highly efficient for producing large-scale quantities
Ensures consistent quality and uniform shapes
Reduces material wastage compared to traditional casting methods
Challenges
High initial setup cost for machinery
Primarily limited to basic geometric shapes
Comparison Table: Different Types of Metal Casting
Casting Method | Common Materials | Precision | Surface Finish | Production Volume | Cost (Low Volume) | Cost (High Volume) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sand Casting | Steel, cast iron, aluminum, brass | ★★☆☆☆ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | Engine blocks, pump housings, machinery parts |
Investment Casting | Stainless steel, aluminum, bronze, nickel alloys | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | Aerospace components, medical devices |
Die Casting | Aluminum, zinc, magnesium | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | Automotive parts, electronics, housings |
Centrifugal Casting | Steel, cast iron, alloys | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | Pipes, cylinders, wheels |
Continuous Casting | Steel, aluminum, copper alloys | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ | ★☆☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ | Bars, rods, sheets |
3D Printing for Metal Casting
3D printing has emerged as a powerful tool to enhance traditional metal casting processes. By integrating additive manufacturing with casting techniques, Unionfab achieve greater efficiency, precision, and flexibility for our customers.
Rapid Prototyping of Molds
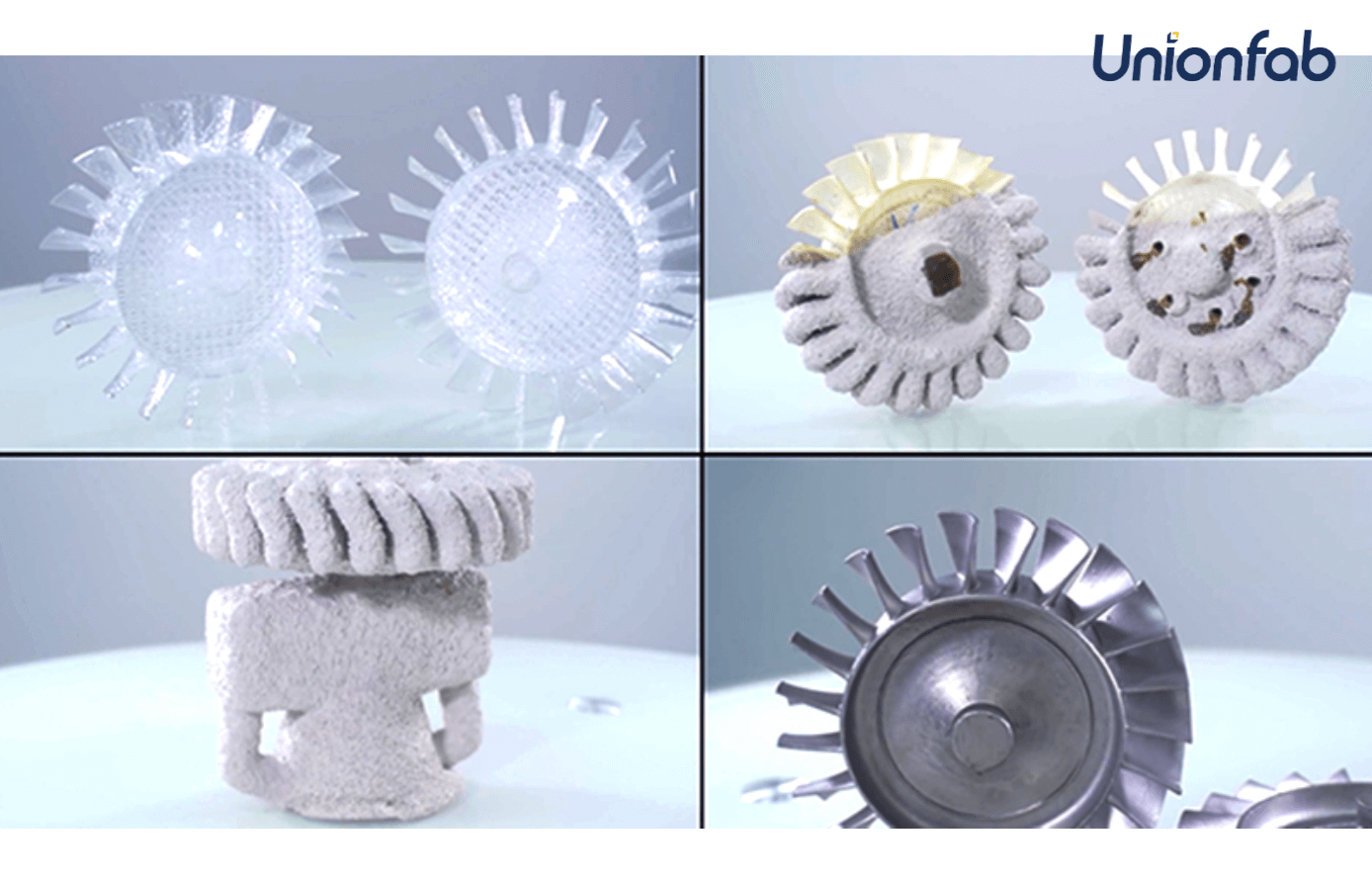
3D printing allows for the quick creation of highly detailed patterns for sand casting or investment casting molds. Patterns can be produced directly from CAD models, significantly reducing lead times and enabling faster iterations.
Complex Geometries Made Easy
Additive manufacturing enables the production of intricate and complex designs that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional tooling. Features like undercuts, internal channels, and thin walls can be incorporated seamlessly.
Cost Savings on Tooling
By eliminating the need for expensive tooling, 3D printing reduces upfront costs, especially for small-batch production.
It also minimizes material waste by producing only the necessary parts or molds.
Customization & Small-Batch Production
For industries requiring unique or customized parts, 3D printing enhances casting by providing on-demand solutions without the need for extensive retooling. This is particularly valuable for aerospace, medical, and artistic applications.
Unionfab’s Capabilities in 3D Printing for Metal Casting
At Unionfab, we leverage Quick Casting, a cutting-edge technology combining Rapid Prototyping (RP) and Investment Casting. By using SLA 3D printing to produce precise prototypes, we enable rapid and efficient casting, reducing production lead times significantly.
Watch the Video by our mother company, Uniontech, to see how Quick Casting bridges the gap between modern and traditional manufacturing, bringing unmatched precision and speed to the casting process.
Real-World Examples
Aerospace: Creating lightweight wax patterns for investment casting of turbine blades, reducing both weight and material waste.
Automotive: Printing intricate molds for sand casting, enabling rapid prototyping of engine components.
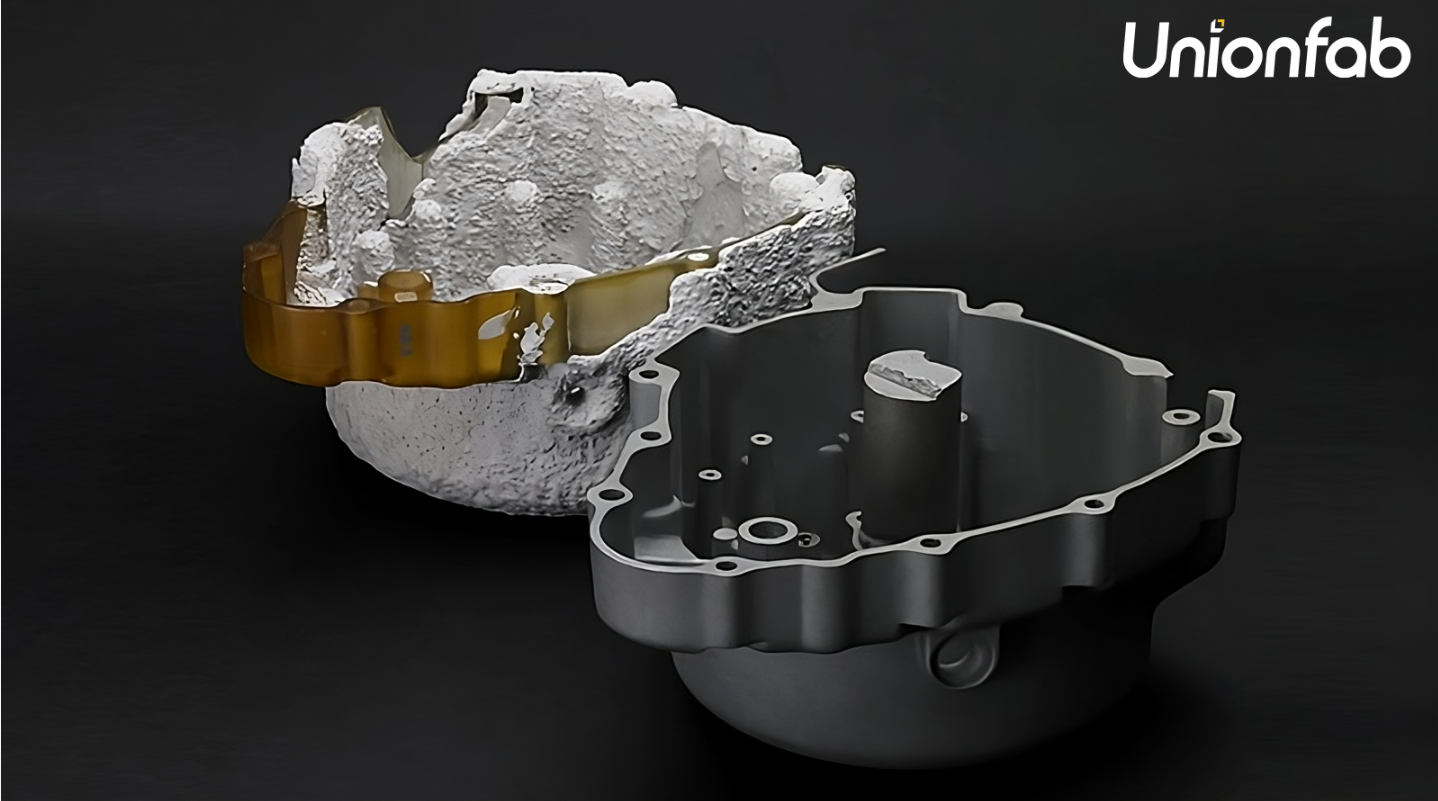

Source: Unionfab
Medical Devices: Producing highly detailed and biocompatible prototypes for implant casting.

Expert Tips for Choosing the Right Metal Casting Type
Selecting the most suitable metal casting method for your project is a critical step in ensuring quality, cost-efficiency, and optimal performance. Here are expert insights to guide you:
1. Evaluate Your Part Complexity
For intricate designs with fine details: Consider investment casting due to its ability to produce high-precision parts with complex geometries.
For simple or bulkier designs: Sand casting is a cost-effective choice and accommodates larger parts.
2. Assess Your Production Volume
Low-volume production: Opt for investment casting or die casting, depending on the material and precision required.
High-volume production: Die casting excels in scalability, especially for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium parts.
3. Material Selection Matters
Different metals behave uniquely in casting processes:
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, ideal for die casting or sand casting in automotive and aerospace.
Steel: Durable and high-strength, works best in investment casting or sand casting for industrial applications.
Zinc: Great for intricate designs and rapid production in die casting due to its low melting point.
4. Surface Finish Requirements
If you need a smooth surface finish with minimal post-processing, investment casting is your best choice.
For parts that require additional machining or painting, sand casting can suffice and reduce upfront costs.
5. Consider Tolerances and Dimensional Accuracy
High precision and tight tolerances: Use investment casting or die casting to minimize post-processing efforts.
Lower precision requirements: Sand casting is more economical but may require additional machining.
6. Budget Constraints
For cost-sensitive projects: Sand casting is the most affordable method for larger parts.
For long-term cost efficiency in large production runs: Die casting provides a lower cost per unit once tooling is set up.
7. Turnaround Time
Fast lead times: Die casting offers rapid production for high volumes.
Prototyping or shorter lead times: Investment casting provides flexibility for low-volume, high-detail parts.
8. Environmental and Sustainability Goals
For recyclability and reduced waste: Choose sand casting or die casting with alloys that are easy to recycle, like aluminum or zinc.
Need Help Choosing?
At Unionfab, our experts are here to guide you through the casting process, ensuring you select the ideal method for your project. Contact us for a free custom quote on metal casting today!

