Understanding Continuous Casting: Process, Benefits, and Challenges

Continuous casting is an important process in metal manufacturing. Discover how it works, its benefits, challenges, and where it is used.
Introduction
What is Continuous Casting?
Continuous casting is a way to make metal products by pouring melted metal into a mold, where it cools and hardens as it moves through a machine. This process is very efficient and can make long, uniform metal shapes like sheets, bars, and rods.
Importance in Metal Manufacturing
Continuous casting is important because it saves time and resources. It makes metal products faster than older methods, like ingot casting, and ensures the final products are of consistent quality. This means manufacturers can make high-quality metal parts more quickly and at a lower cost, which is important for industries like construction, automotive, and aerospace.
What is Continuous Casting?
Definition
Continuous casting is a process where melted metal is poured into a mold and hardens as it moves through a machine. Unlike older methods that make separate pieces of metal called ingots, continuous casting makes long, uniform products like rods or sheets.
Purpose and Basic Principles
The goal of continuous casting is to make metal production faster and cheaper. The process involves feeding melted metal into a mold that cools and solidifies it as it moves. This allows the metal to be made without stopping, which reduces waste and makes production more efficient. The result is high-quality metal that can be used for many different purposes.
History of Continuous Casting
Early Developments
The idea of continuous casting goes back to the mid-1800s when people started experimenting with ways to make metal production more efficient. But it wasn't until the 1950s that continuous casting became a practical method for industry. Reliable cooling and solidifying techniques were key to making it work.
Major Innovations
In the 1960s, better mold designs and control systems made continuous casting more precise. In the 1980s, automated control technology improved efficiency and quality even more. Today, continuous casting uses computer systems to ensure high-quality metal production with fewer defects. These improvements have made continuous casting an important part of metal manufacturing, especially in the steel industry.
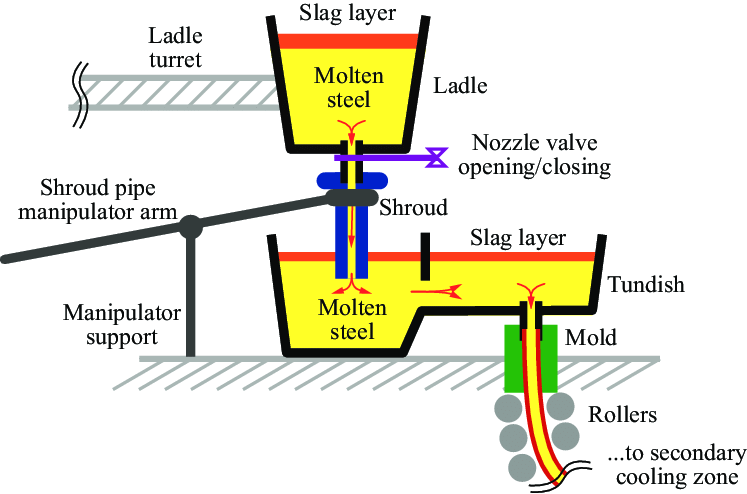
How Does Continuous Casting Work?
Source: researchgate.ne
Step 1: Melting
The process starts by melting raw metal, usually in a special furnace. The melted metal is then cleaned to remove impurities.
Step 2: Casting
The melted metal is poured into a mold that is cooled by water. As the metal enters the mold, it starts to harden at the edges while staying liquid in the center. The mold helps the metal keep its shape as it cools.
Step 3: Solidifying
The partly solid metal moves down through rollers, and it keeps cooling and hardening. The cooling system is very important to make sure the metal solidifies evenly.
Step 4: Cutting
Once the metal has completely hardened, it is cut into the desired lengths using torches or saws. These pieces, called billets, blooms, or slabs, can then be used for other applications.
Materials Used in Continuous Casting
Common Materials
Continuous casting is used for many types of metals, but the most common are:
Material | Description |
|---|---|
Steel | Steel is the most commonly cast metal, used a lot in construction, automotive, and machinery because it is strong and versatile. |
Copper | Copper is often used for electrical products because it conducts electricity well and is easy to shape. |
Aluminum | Aluminum is light and resists rust, making it a popular choice for things like transportation and packaging. |
These metals work well with continuous casting because they can keep good quality and consistency as they harden, which is important for large-scale production.
Advantages of Continuous Casting
Efficiency
Continuous casting is very efficient because it gets rid of extra production steps. The process turns melted metal directly into semi-finished products, which saves both time and energy.
Cost-Effectiveness
By cutting down the number of steps in production, continuous casting lowers costs. It also reduces waste, as the continuous flow of metal means less handling and reheating. This cost-saving feature makes it popular in industries that need large amounts of metal.
Better Metal Quality
Continuous casting produces metal with fewer defects. The controlled cooling makes sure the metal hardens evenly, leading to fewer cracks and impurities. This means a higher quality product for industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Challenges and Limitations
High Setup Costs
One big challenge is the high setup cost. The equipment for continuous casting, like furnaces, molds, and cooling systems, is expensive. This makes it hard for smaller manufacturers to use this technology.
Technical Complexities
Continuous casting needs precise control of temperature, speed, and cooling. If any of these are not right, defects can occur, like cracks or uneven quality. Managing these complexities requires technical knowledge.
Maintenance Requirements
The equipment needs regular maintenance to work well. Any downtime for maintenance can affect production, making it hard to keep operations running smoothly.
Limited Flexibility
Continuous casting is best for making large quantities of standard shapes, like slabs or billets. It doesn't work well for making complex or custom shapes, which makes it less useful for small or specialized jobs.
Applications of Continuous Casting Industries
Continuous casting is used in many industries because it is efficient and cost-effective:
Automotive Industry: Used to make parts like chassis components, engine blocks, and transmission parts.
Construction Industry: Used to make steel beams, rebar, and other structural components.
Machinery and Equipment Manufacturing: Used to make parts like gears and shafts.
Electrical Industry: Copper made through continuous casting is used for wiring and other electrical parts.
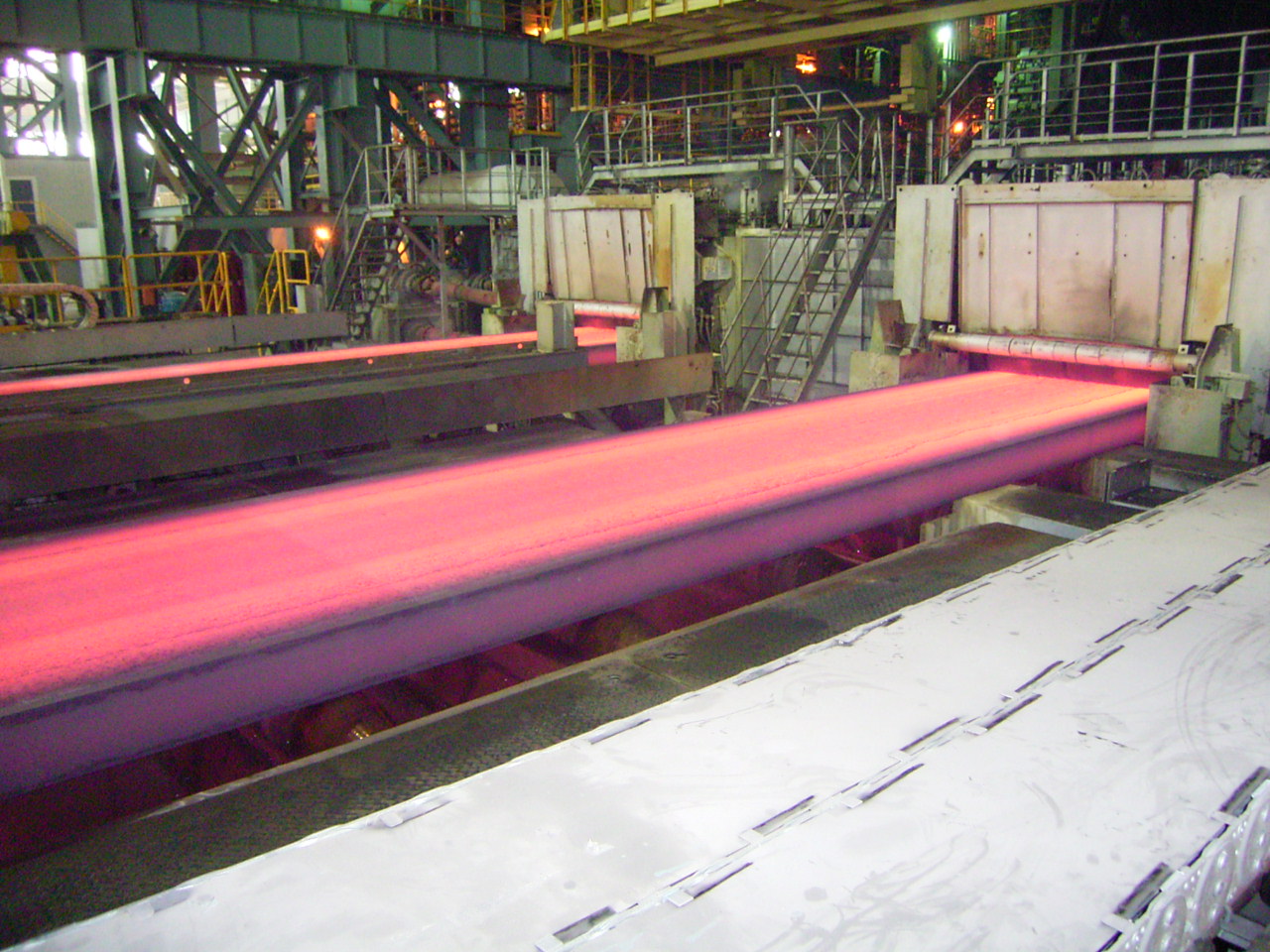
Examples of Products
Products made using continuous casting include:
Steel Slabs: Used to make sheets, plates, and coils.
Source: steelplantech.com
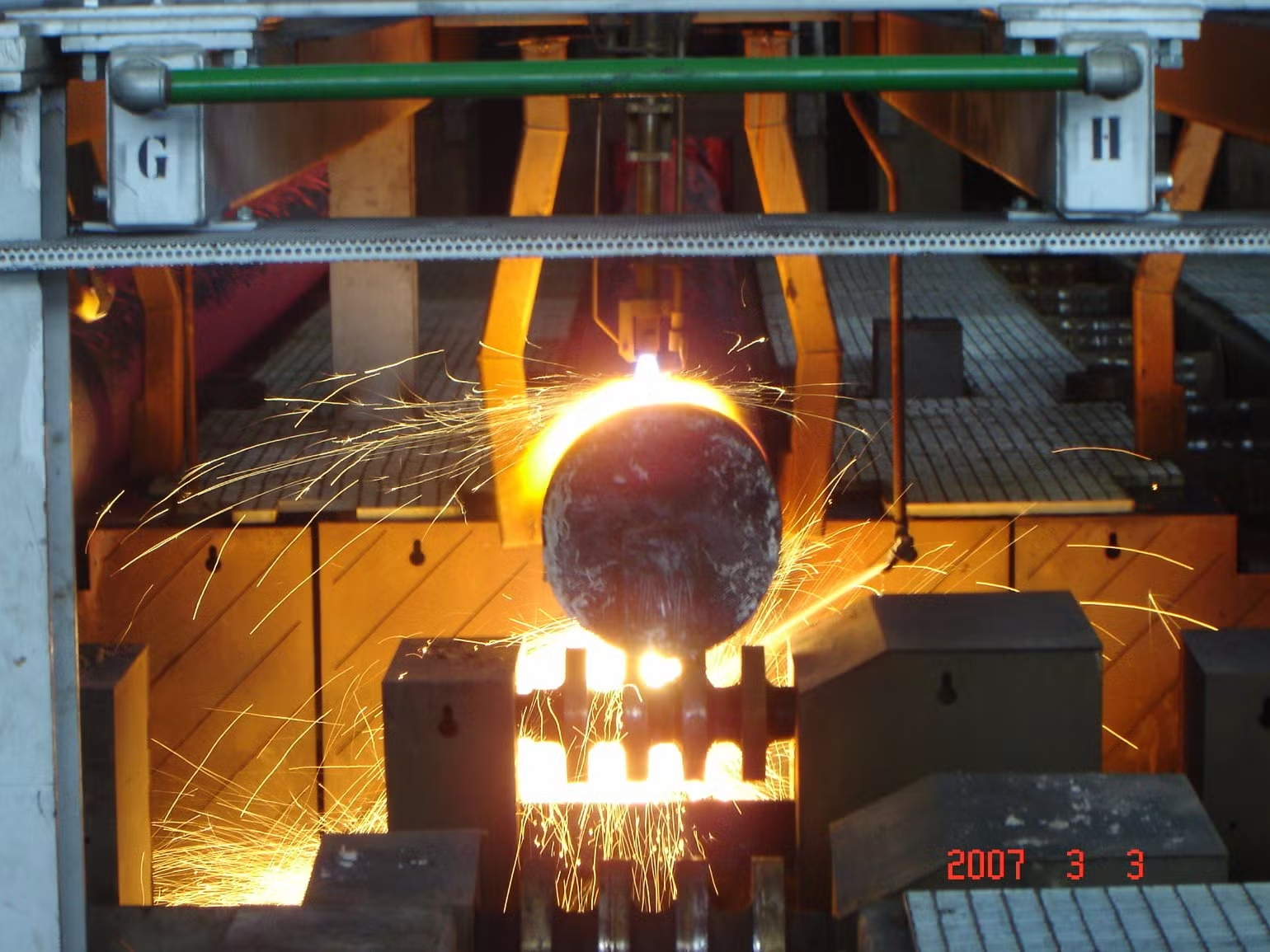
Billets: Smaller pieces of metal that are made into bars, rods, or wire.
Blooms: Larger pieces used to make structural shapes like I-beams or train tracks.
Source:ac-dc-motor-furnace.en.made-in-china.com
Copper Wire Rods: Used in electrical products because of their high quality and conductivity
Continuous Casting vs. Other Casting Techniques
Comparison with Sand Casting
Sand casting uses sand molds to make metal parts. Unlike continuous casting, which makes long, uniform metal products, sand casting is used for complex shapes. Sand casting is more flexible but less efficient and takes more manual labor. The surface finish of sand-cast products is also not as good as continuous casting.
Comparison with Die Casting
Die casting involves forcing melted metal into a mold under high pressure. It is good for making detailed parts, like those in cars or household items. However, die casting is limited by the high cost of molds. Continuous casting, on the other hand, is better for making large amounts of simple metal products and is more energy-efficient.
Unique Features of Continuous Casting
Continuous casting stands out because it can make long, uniform products without stopping. This results in faster production, less waste, and fewer defects. It is especially useful for large-scale production where keeping costs low and quality high is important.
Conclusion
Continuous casting is an efficient way to make metal products by turning melted metal into long, uniform pieces. It is used in industries like automotive, construction, and electrical because it is cost-effective and produces high-quality products. Compared to other casting methods, continuous casting has many advantages, such as reducing waste and making production faster.
Continuous casting is important in manufacturing because it helps make high-quality metal products efficiently. It reduces production costs, increases output, and keeps the quality consistent. With more advancements in technology, continuous casting will continue to be an essential part of making metal products.
Discover Continuous Casting with Unionfab
Ready to improve your metal production? Unionfab offers advanced manufacturing services, including rapid casting solutions made just for you. Work with Unionfab to improve efficiency, quality, and productivity in your projects.
Contact us now to get started!


