Shore Hardness: Assessing for Optimal Material Performance

Learn about shore hardness and master how to assess material hardness for optimal performance.
Introduction
Shore hardness is a critical property that measures the resistance of materials, particularly elastomers and plastics, to indentation.
This measurement is vital for ensuring that materials meet specific performance requirements in various applications.
Understanding Shore hardness allows engineers and manufacturers to select the right materials for their products, ensuring durability, flexibility, and overall functionality.
What is Shore Hardness?
Shore hardness measures how hard materials are, especially polymers and elastomers, by testing their resistance to indentation.
How Does Shore Hardness Work?
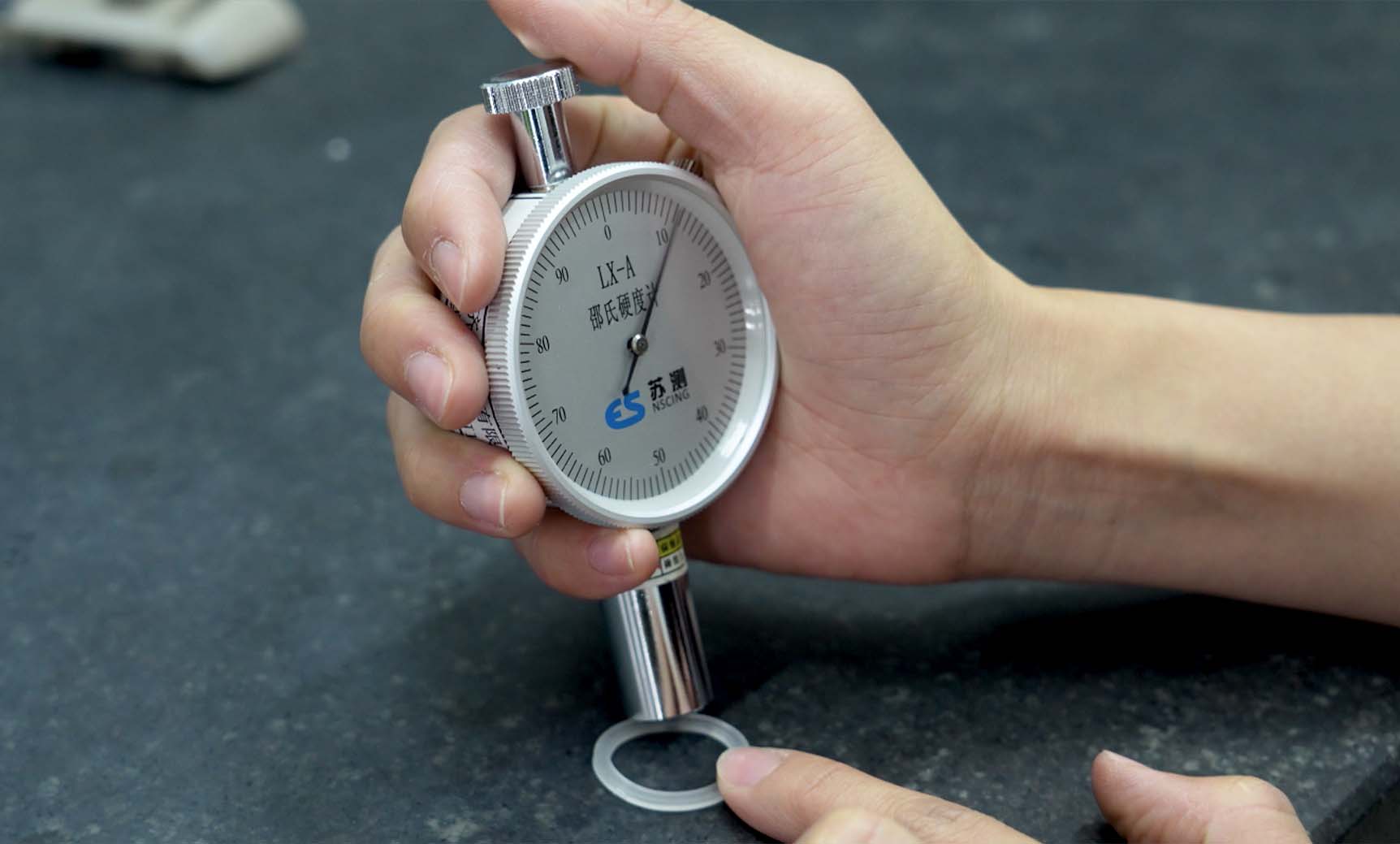
A Shore durometer has a pointed indenter that is pressed into the material with a specific force.
The depth of penetration is measured, and this is directly related to the material's hardness. The deeper the penetration, the softer the material.
What Materials are Measured with Shore Hardness?
Plastics: Both rigid and flexible plastics, including PVC, ABS, and polyurethane.
Rubber: Natural and synthetic rubbers, used in products like tires, gaskets, and hoses.
Foams: Used to measure the firmness of foams, such as those used in cushions and mattresses.
Coatings: To assess the hardness of paint, varnish, and other coatings.
Elastomers: A wide range of elastic materials.
Why is Shore Hardness Important?
Quality control: Ensures that materials meet specific hardness requirements.
Product design: Helps in selecting the right materials for different applications.
Performance prediction: Shore hardness can be correlated with other material properties like wear resistance and tear strength.
Troubleshooting: Can help identify issues with materials, such as excessive softness or hardness.

Source: hlhrapid.com
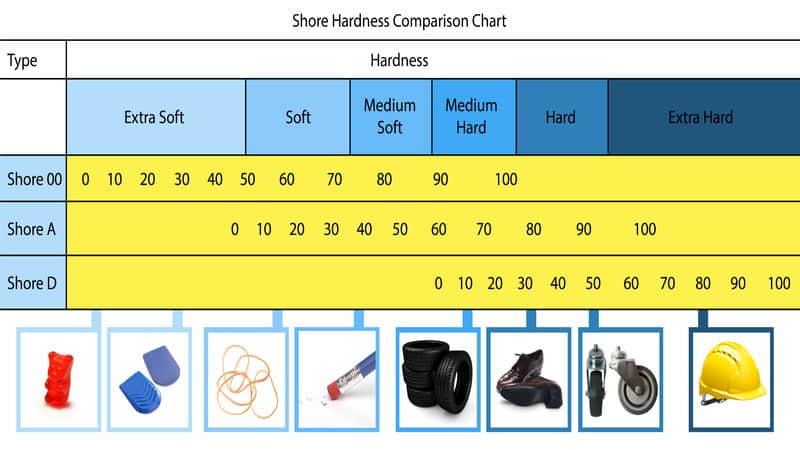
Shore Hardness Scale
The Shore hardness scale primarily consists of two categories: Shore A and Shore D, which are the most widely used.
Shore A Scale
Applications: The Shore A scale is primarily used for softer materials, such as rubber, flexible plastics, and foam. It is essential in industries where material flexibility and cushioning are critical.
Range: The scale ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 90 indicating very hard elastomers. Lower values represent softer materials, providing a clear indication of material softness.
Durometer Type: This scale utilizes a conical indenter that penetrates the softer material. The depth of the indentation is measured and translated into a hardness value.
Shore D Scale
Applications: The Shore D scale is designed for harder materials, including rigid plastics, hard elastomers, and some composites. It is often used in applications where material strength and durability are crucial.
Range: Similar to the Shore A scale, it ranges from 0 to 100 but measures harder materials. Higher values indicate greater hardness.
Durometer Type: This scale employs a sharper indenter, which is more suitable for penetrating harder surfaces and providing accurate readings.
Source: hongjusilicone.com
Benefits and Limitations of Shore Hardness
Benefits
Versatility: Shore hardness testing can be used on many materials, helping in material selection.
Predictive Value: Knowing a material's hardness helps predict how it will perform in real-life situations, like its wear resistance and flexibility.
Quality Control: Regular testing ensures materials meet hardness standards, enhancing product quality and reliability.
Limitations
Surface Preparation: Accurate measurements need clean, smooth surfaces; dirt or roughness can skew results.
Thickness Dependency: Hardness can vary with material thickness, especially in softer types.
Temperature Sensitivity: Shore hardness can change with temperature, so testing conditions should be consistent.
How is Shore Hardness Measured?
Overview of Shore Hardness Testing Methods
Shore A Testing: Uses a durometer for softer materials, giving readings that show how well rubber and flexible plastics resist indentation.
Shore D Testing: Uses a durometer for harder materials, ensuring accurate measurements for rigid plastics and tough elastomers.
Equipment Used in Shore Hardness Testing
Durometer: The main tool for measuring Shore hardness, available in analog and digital versions. Different durometers are used for Shore A and Shore D.
Calibration Standards: Calibration blocks ensure the durometer works correctly.
Step-by-Step Measurement Process
Preparation: Clean the material surface to remove any dirt or contaminants.
Positioning: Hold the durometer perpendicular to the material’s surface.
Applying Pressure: Press the durometer onto the material with steady force for about 15 seconds.
Reading the Measurement: Record the hardness value shown on the durometer. It’s best to take multiple readings in different spots for accuracy.
Applications of Shore Hardness
It's used in many different industries to test how strong and durable materials are. Here are some common uses:
Plastics and Rubber Manufacturing: Shore hardness is crucial for evaluating materials used in products like tires and seals.
Automotive Industry: Important for parts like gaskets, tires, and interior materials where flexibility and durability matter.
Construction Materials: Used to assess insulation, flooring, and sealants, ensuring they meet performance standards.
Medical Devices: Essential for measuring the hardness of materials in implants, catheters, and other equipment that need to be biocompatible.
Alternative Measurement Methods
In addition to Shore hardness testing, other methods for measuring hardness include:
Rockwell Hardness Testing: Measures penetration depth under a heavy load, suitable for harder materials.
Brinell Hardness Testing: Presses a hard ball into the material and measures the indentation, ideal for metals.
Vickers Hardness Testing: Uses a diamond pyramid indenter to measure hardness, applicable to a wide range of materials.
Conclusion
Understanding shore hardness is key to selecting materials that meet performance standards in various industries.
By learning the measurement techniques and recognizing their pros and cons, manufacturers and engineers can ensure their products achieve the best performance, durability, and reliability.
For more information on material hardness, explore our resources at Unionfab.
Whether you are a manufacturer, engineer, or researcher, we can assist you in selecting the right materials for your applications.
Connect us to support your projects and ensure optimal performance and quality in your products.


