TPU 3D Printing [2025]: Tips, Tricks & Best Solutions
Explore everything you need to know about TPU 3D printing, from beginner-friendly filaments to premium options.
Introduction
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is one of the most exciting materials in 3D printing, known for its flexibility, durability, and high-performance qualities. Whether you're designing flexible prototypes, creating custom parts, or looking for a material that can handle wear and tear, TPU is a top choice.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about TPU 3D printing—from TPU filament selection to troubleshooting common issues. By the end of this guide, you’ll have the insights needed to unlock TPU’s full potential.
This guide is perfect for:
3D Printing Enthusiasts looking to take their TPU prints to the next level.
Engineers and Designers integrating TPU into real-world products.
Manufacturers using TPU for prototyping or low-volume production.
R&D Teams experimenting with flexible, durable parts.
What is TPU for 3D Printing?
What is TPU
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a flexible, durable material that combines the best of both worlds: the elasticity of rubber and the toughness of plastics. This thermoplastic elastomer can stretch, compress, and return to its original shape, making it ideal for parts that need to endure repeated stress.
TPU fills a critical gap that other materials struggle with—flexibility combined with durability. From automotive gaskets to wearable tech components, TPU’s unique properties make it indispensable in a wide range of industries.

Why is TPU Ideal for 3D Printing?
1. Unique Balance of Flexibility and Strength
TPU offers where alternative materials fall short: Most rigid plastics (e.g., PLA, ABS or PETG) lack the flexibility needed for soft, stretchable parts, while softer materials (like silicone) are difficult to 3D print.
TPU bridges this gap by offering elasticity and toughness, making it the go-to material for countless applications, from DIY projects to cutting-edge industrial innovations.
2. Perfect for All Skill Levels
One of TPU’s standout features is its ability to work seamlessly with a wide range of 3D printing technologies, from beginner-friendly FDM to industrial-grade SLS and MJF. This compatibility makes it the go-to material for everyone in the 3D printing space.
3. Durability in Harsh Environments
Unlike many flexible plastics that degrade quickly, TPU is highly resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and UV exposure. This makes it indispensable in industries like automotive, medical, and industrial manufacturing, where parts must withstand tough conditions while maintaining flexibility.
Read more: Is TPU Toxic?
Key Properties of TPU
Getting to know TPU's key properties is essential to making the most of this material:
Property | Range/Value | What It Means (for Practical Application) |
|---|---|---|
Shore Hardness (A) | 50–95 | Softer (50–60) = Flexible parts (e.g., seals, wearables); |
Tensile Strength | 30–55 MPa | Moderate (30–40 MPa) = Light-duty; |
Elongation at Break | 300%–700% | Highly elastic (300–500%) for soft grips; |
Abrasion Resistance | 100–250 mm³ | Moderate (100–150 mm³) for general use; |
Compression Set | 10%–25% | Excellent recovery after printing (10–15%) = Good for seals; |
Water Absorption | 0.5%–1.5% | Low (0.5–1.0%) = Outdoor/moisture-exposed parts; |
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) | -40°C to -10°C | Low Tg = Flexibility in cold environments (winter gear, outdoor parts) |
Melt Volume Rate (MVR) | 10–50 cm³/10 min | Low MVR (10–20 cm³) = Fine details; |
Specific Gravity | 1.1–1.2 g/cm³ | Lighter (1.1) = Wearables, shoes; |
Unionfab offer a versatile SLS TPU material, suitable for high-performance applications requiring flexibility, durability, and moisture resistance.
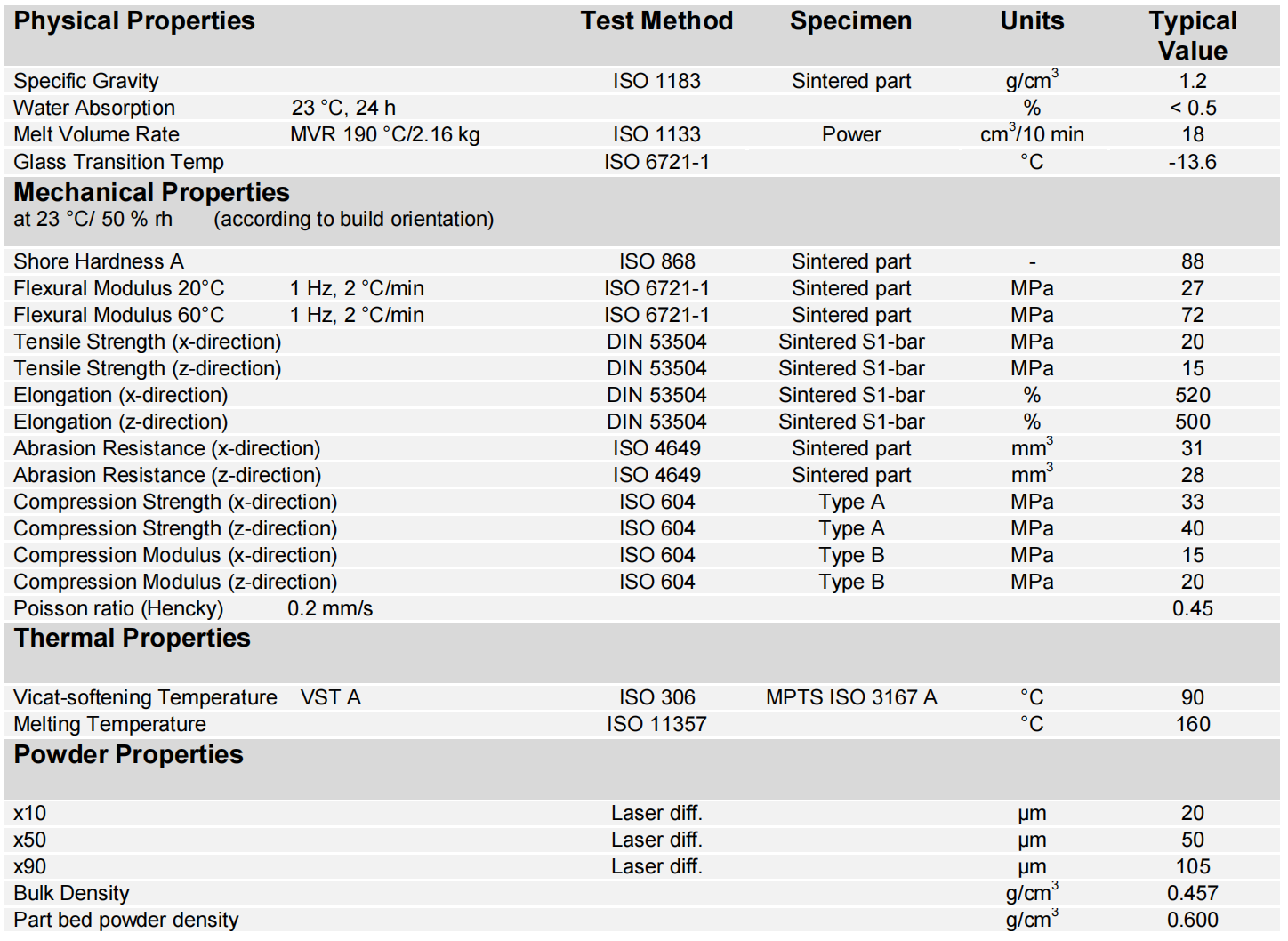
Visit our TPU material page to see all the technical details you need!
Comparing TPU 3D Printing Technology
FDM vs. SLS vs. MJF TPU
When choosing the right 3D printing method for TPU, it's crucial to understand how different technologies impact the final product. Each method—FDM, SLS, and MJF—offers unique benefits and considerations.
In this section, we’ll compare the key differences of FDM, SLS and MJF TPU 3D printing to help you make the best decision for your project.
Parameter | FDM TPU | SLS TPU | MJF TPU |
|---|---|---|---|
Principle | FDM works by melting a filament and extruding it layer-by-layer to form a 3D object. | SLS uses a laser to sinter powdered TPU layer by layer. | MJF uses an inkjet array to deposit a binding agent onto the TPU powder. |
Printing Process |  |  |  |
Printing Result | 
| 
| 
|
Print Temperature (°C) | 220 - 250 | N/A (Laser Sintering) | N/A (HP Powder Printing) |
Bed Temperature (°C) | 40 - 60 | N/A | N/A |
Layer Height (mm) | 0.1 - 0.3 | 0.08 - 0.15 | 0.08 - 0.12 |
Print Speed (mm/s) | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Support Requirement | Requires support | No support required | No support required |
Surface Finish | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
Elasticity Performance | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
Application Scenarios | Home DIY, Soft prototypes | Production-grade parts, Footwear, Automotive parts | High-end medical, Automotive, Footwear |
Below, we use a Spider Chart to compare FDM TPU, SLS TPU, and MJF TPU across important parameters:
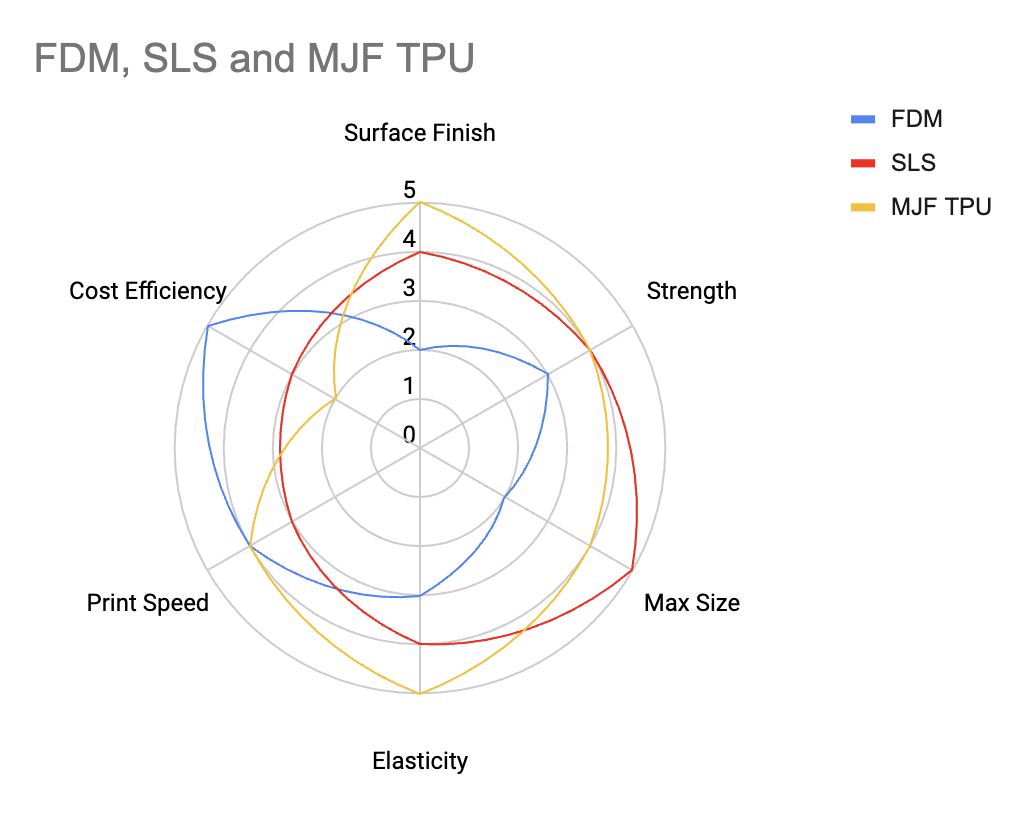
Key Points
FDM TPU: The FDM process is simple and affordable, making it ideal for DIYers, prototyping, and low-cost, low-volume parts. It’s widely accessible and doesn't require advanced equipment.
SLS TPU: SLS prints high-strength, durable parts without the need for support structures, making it excellent for industrial applications where material properties are critical. The process is slower and more expensive, but it delivers high precision and robustness.
MJF TPU: MJF is fast and reliable, producing high-quality parts with consistent mechanical properties, making it ideal for high-end applications. However, It can be expensive and the build size in MJF printers is generally smaller.
Comparing Chinese TPU 3D Printing Providers
China is home to a number of leading providers offering competitive solutions for TPU 3D printing. To help you make an informed decision, we've compared some of the top 3D printing companies in China based on their capabilities and services:
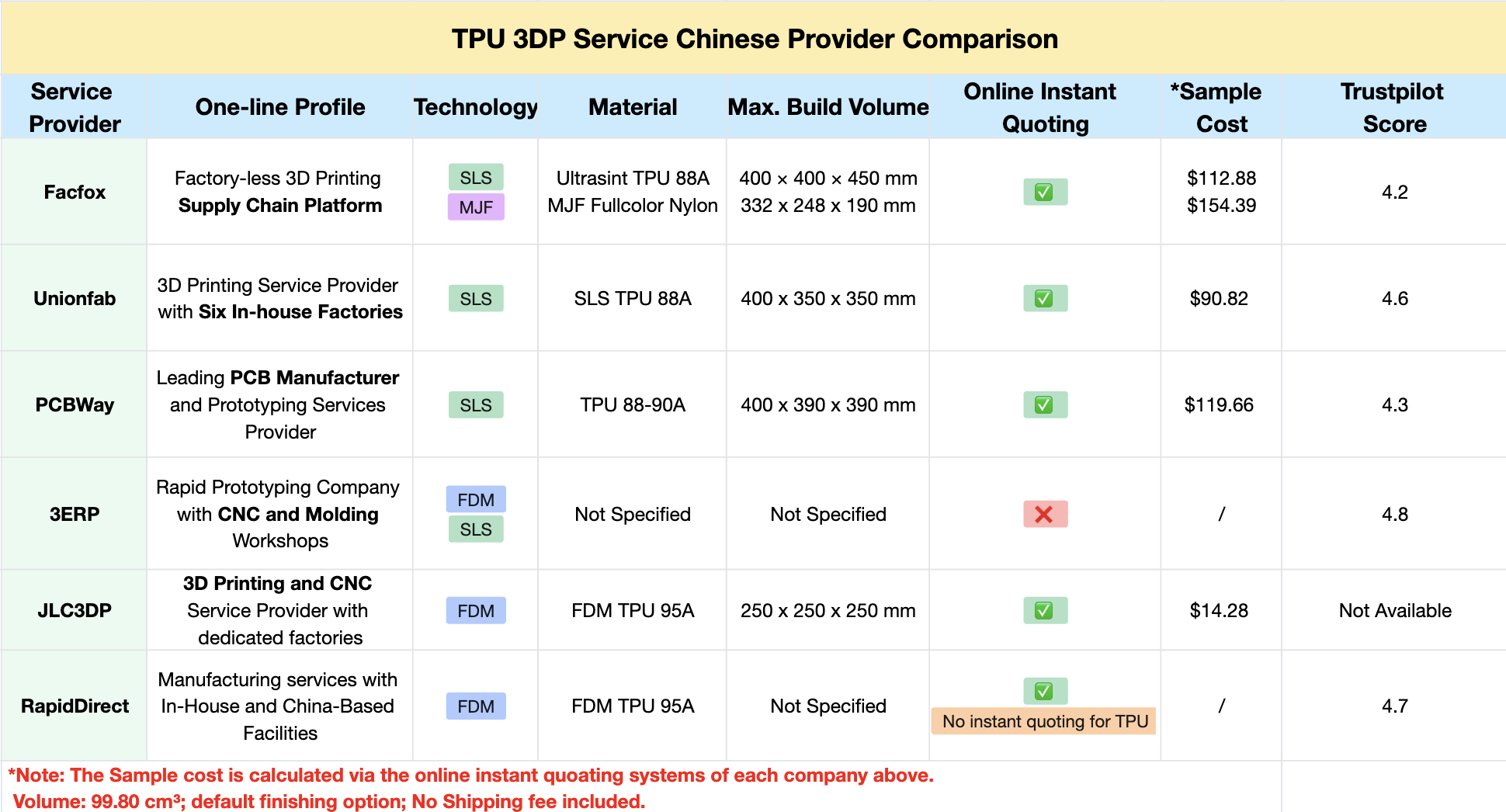
Which Provider to Choose:
For Consistent Quality: Unionfab offers a reliable solution for businesses requiring SLS TPU printing, backed by multiple in-house factories, good customer feedback (view on Trustpilot), and competitive pricing.
For Variety and Flexibility: Facfox is suitable for users who need different technologies (MJF and SLS) and materials, with easy access to various options and instant quoting.
For Budget-Conscious Small Projects: JLC3DP offers affordable FDM TPU printing, ideal for basic prototypes or DIY users with budget constraints.

TPU Filament Selection Guide
Types of TPU Filaments
TPU Type | Shore Hardness | Perfect For | Printing Tips | Available Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Soft TPU 
| Shore 60A-80A | Gaskets, soft seals, wearable devices | Requires direct-drive extruders, slower speeds, and careful temperature settings | - Recreus Filaflex 60A: Max flexibility, best for experienced users |
Medium TPU 
| Shore 80A-95A | Phone cases, protective covers, industrial seals | Easier to print, handle, and feed, even on less advanced printers | - NinjaTek NinjaFlex 85A: Superior flexibility and durability |
High-Performance TPU 
| Customizable | Medical devices, automotive parts, extreme wear resistance | Built for durability, resistance to heat, chemicals, and physical wear | - Ultrafuse TPU 85A by BASF: High wear resistance, tensile strength, oils & greases resistant |
Key Takeaways:
Soft TPU is best for parts requiring maximum flexibility, but it can be tricky to print due to its flexibility.
Medium TPU offers a balance of flexibility and toughness, making it ideal for a wider range of everyday products and easier to handle for most printers. For beginners, starting with medium TPU (85A-95A) is a good choice.
TPU Filament Pricing
Beginner-Level TPU Filaments: $20–$35 per kg
Brand | Product Name | Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
Overture | Affordable, decent flexibility, good printability | $26–$30/kg | |
Duramic 3D | Consistent quality, easy to print | $24–$28/kg | |
SainSmart | Reliable entry-level option with moderate elasticity | $30–$35/kg |
These filaments are affordable, easy to work with, and great for first-time users experimenting with flexible materials.
Key Features:
Ease of Printing: Less prone to warping or clogging, often stiffer (higher Shore hardness, 95A+), making them easier for beginners.
Applications: Basic flexible parts, casual projects, or prototypes without demanding mechanical or environmental requirements.
2. Mid-Tier TPU Filaments: $30–$60 per kg
Brand | Product Name | Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
MatterHackers | MH Build Series TPU Collection | Good balance of strength and flexibility, versatile | $28–$35/kg |
Fillamentum | Flexfill TPU Filament Collection | High abrasion resistance, smooth finish | $40–$60/kg |
Polymaker | Easy to print, combines flexibility and toughness | $30–$40/750g |
Mid-tier filaments strike a balance between affordability and advanced properties, offering better flexibility, toughness, and durability.
Key Features:
Mechanical Properties: Improved flexibility, layer adhesion, and abrasion resistance.
Printability: Slightly more challenging than beginner-level but manageable with experience.
Applications: Functional prototypes, wearable items, or moderate stress components.
3. Premium-Grade TPU Filaments: $40–$100+ per kg
Brand | Product Name | Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|
NinjaTek | Superior flexibility (85A), excellent tear resistance | $50/0.5kg | |
Recreus | Extremely flexible (60A) or durable (95A), great layer adhesion | $45–$60/0.5kg | |
Bambu Lab | Optimized for high-speed printing, industrial-grade quality | $42/kg |
These are high-performance filaments engineered for demanding industrial or professional applications. They excel in properties like flexibility, tear resistance, and precision but come at a higher cost.
Key Features:
Mechanical Properties: Exceptional flexibility (as low as Shore 85A), tear/abrasion resistance, and layer bonding.
Printability: More challenging, often requiring fine-tuned printer settings, a direct-drive extruder, and experience.
Applications: Industrial-grade parts, prosthetics, seals, gaskets, robotics, and other high-performance needs.
While FDM TPU filaments are a popular choice for 3D printing flexible parts, for more demanding applications where precision, consistency, and enhanced performance are critical, MJF and SLS TPU materials stand out.
Why is TPU so Hard to Print?
FDM 3D printing with TPU can be tricky, and if you're a DIY enthusiast or even a pro, you’ve probably run into a few common challenges. But don’t worry—these issues are totally manageable with the right approach.
Here are a few of the main problems you might face when working with TPU:
Warping and Adhesion Issues

TPU, like other flexible materials, is prone to warping and poor adhesion to the print bed. This is especially troublesome for parts requiring fine details or consistency.
Stringing and Blobbing
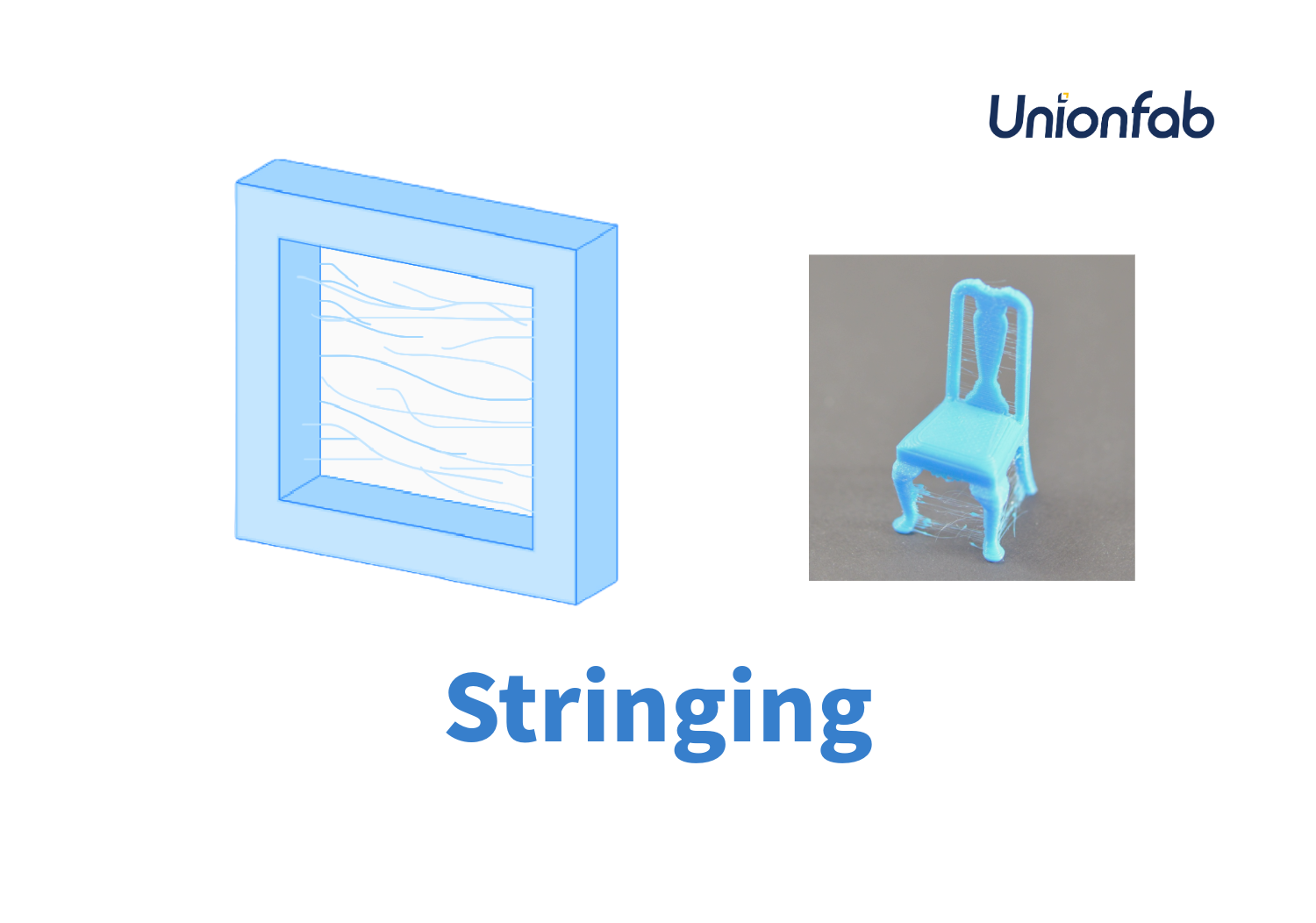
Because TPU is flexible, it tends to string between parts, leaving thin threads of filament that can affect your print’s smoothness, especially on more complex designs.
Clogging and Jamming
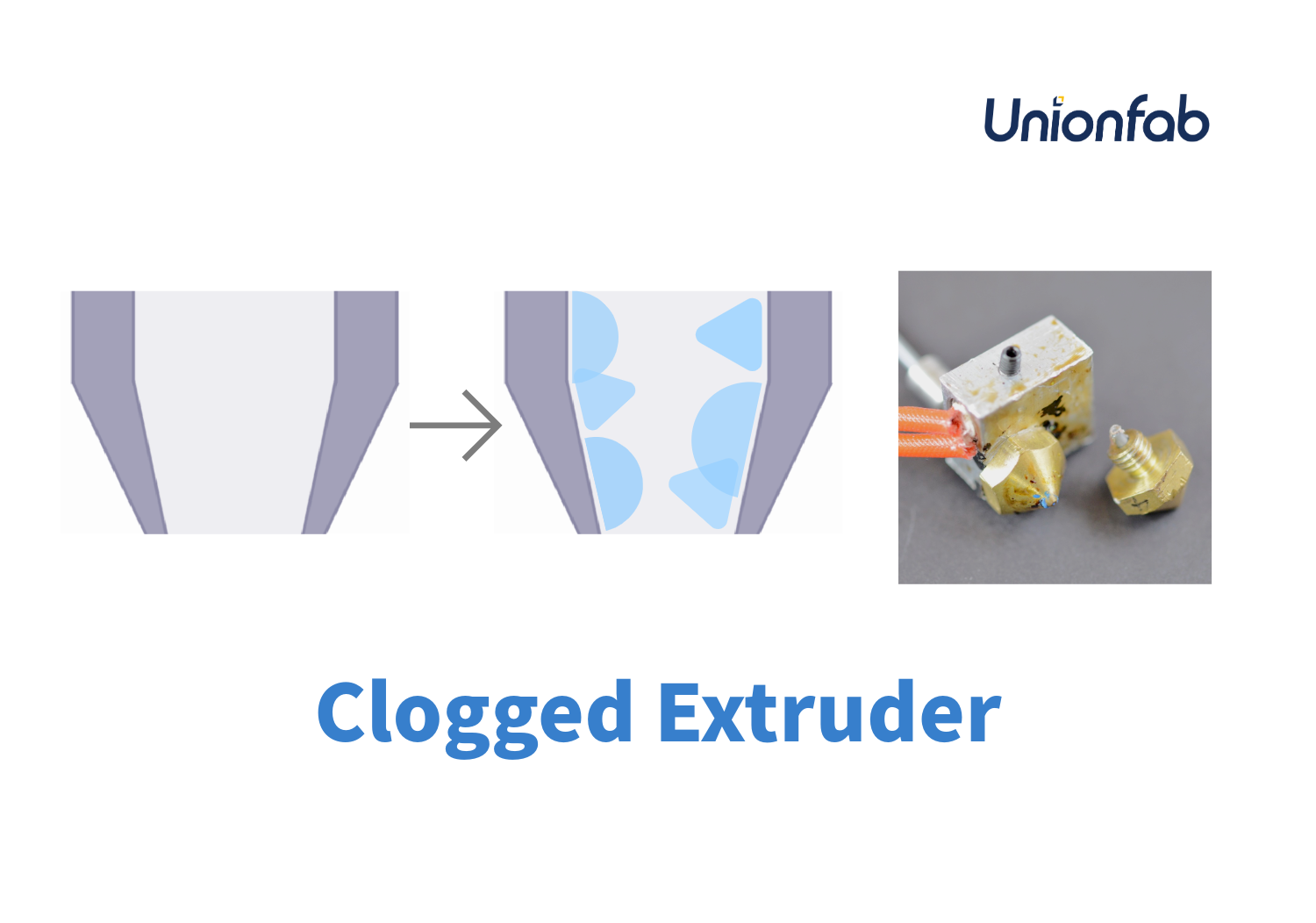
Flexible TPU can sometimes get stuck in the extruder, causing clogs, particularly if your printer isn’t fully equipped for flexible filaments. This can slow things down and waste material.
Now that we’ve gone over the common challenges, let’s take a look at how you can tackle them and start printing with TPU like a pro!
How to Print with TPU Like a Pro
1. Forget Retraction (or Keep It Super Low)
TPU’s flexible nature makes retraction a nightmare. Disable it or minimize it as much as possible to avoid jams — it’ll save you a lot of headaches.
2. Slow Down Your Print Speed
TPU needs a bit more love and patience. Slow down your print speed to around 25mm/s to prevent under-extrusion and avoid those stringy, messy prints.
3. Use a Direct Drive Extruder
If you have a direct drive extruder, use it. It keeps things smooth and avoids the filament from buckling, which can happen with Bowden setups.
4. Dry Your Filament
TPU loves to absorb moisture, and that can make it print poorly. Dry your filament for a few hours at 135°F, or invest in a filament dryer. You’ll get cleaner, more reliable prints.
5. Get Good Bed Adhesion
A PEI sheet works great with TPU, but if you’re having trouble, throw on a thin layer of glue stick for extra adhesion. It’ll keep that first layer in place and prevent any warping.
6. Set the Right Temps
Set your print temperature around 230~250°C and your bed temperature to 50~60°C. This combo works wonders to get your TPU to stick and extrude smoothly.
If you're working on personal or smaller projects, FDM might be your go-to choice. But when it comes to larger, high-precision, or industrial-grade tasks, its limitations can quickly become clear.
For businesses facing higher demands for quality, precision, and production efficiency, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) offers a powerful alternative.
With over 20 years of experience, Unionfab provide high-quality SLS TPU printing solutions, ensuring fast results and exceptional accuracy. Whether you're in automotive, medical, consumer goods, or art design, we understand the specific requirements of your industry.
Contact us today to bring your ideas to life with SLS TPU printing!

Applications of TPU 3D Printing
Consumer Products
TPU has become a go-to material for many consumer products, offering a perfect mix of flexibility and durability. Whether it's for custom footwear or mobile accessories, TPU is changing how we design products that need to withstand wear and tear.
For example, in footwear, TPU is used for insoles and midsoles, providing a comfortable, long-lasting fit.
It’s also the material of choice for protective cases for phones and electronics, offering shock absorption and reliable protection from drops and impacts.

Industrial Uses
In industries where durability and flexibility are key, TPU has found its place.
From custom seals and gaskets to vibration dampeners, TPU parts help keep machines running smoothly. It’s highly resistant to chemicals and abrasion, making it perfect for parts that will see heavy use, like those in industrial machinery.
For example, seals made from TPU ensure tight, reliable performance in demanding environments, protecting sensitive machinery from leaks and damage.
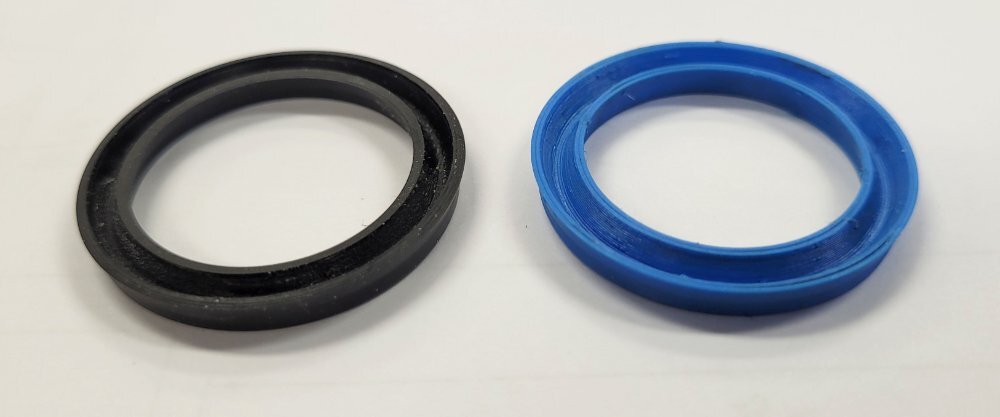

Source: community.ultimaker.com
Medical and Healthcare
In healthcare, TPU is a game-changer, especially for products that require a combination of comfort and flexibility. Orthopedic insoles and supports made from TPU provide personalized comfort while ensuring durability for long-term use.
When it comes to prosthetics and implants, TPU’s flexibility and biocompatibility help create more comfortable, natural-feeling prosthetic sockets and supports, giving patients a better, more functional experience.
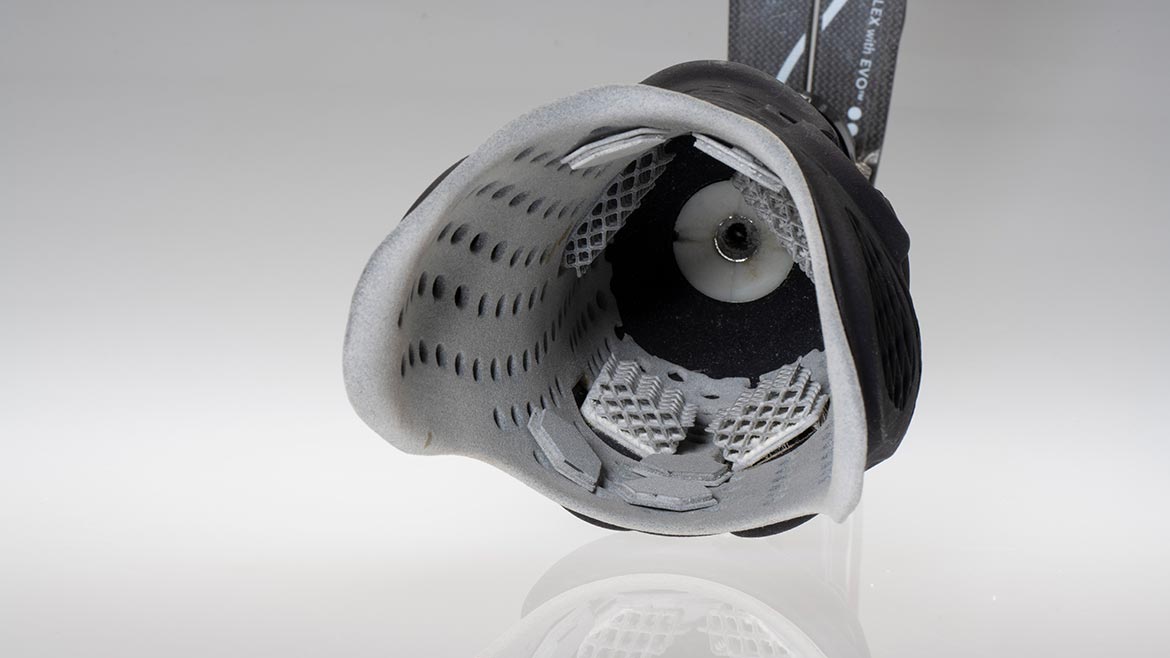

Source: lubrizol.com
Automotive
From custom car parts to hoses and connectors, TPU helps meet the high standards of performance and durability required in vehicles. Its ability to handle stress, wear, and varying temperatures makes it a great choice for automotive applications.
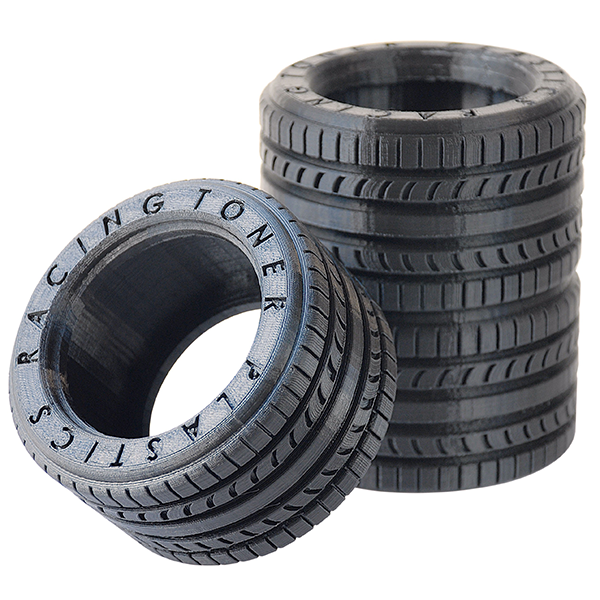

Source: tonerplastics.com
Design and Toys
TPU isn’t just for practical applications—it also sparks creativity in design and the toy industry. Its flexibility and ease of customization allow designers to create unique, dynamic products that stand out.
In the toy industry, TPU is used to make soft, squeezable toys, figures, and parts that are safe for children and easy to play with. Its durability means these toys can withstand rough handling without losing their form, providing lasting fun.

In the world of creative art design, TPU enables artists to craft dynamic, bendable structures that can be molded into intricate, organic shapes.
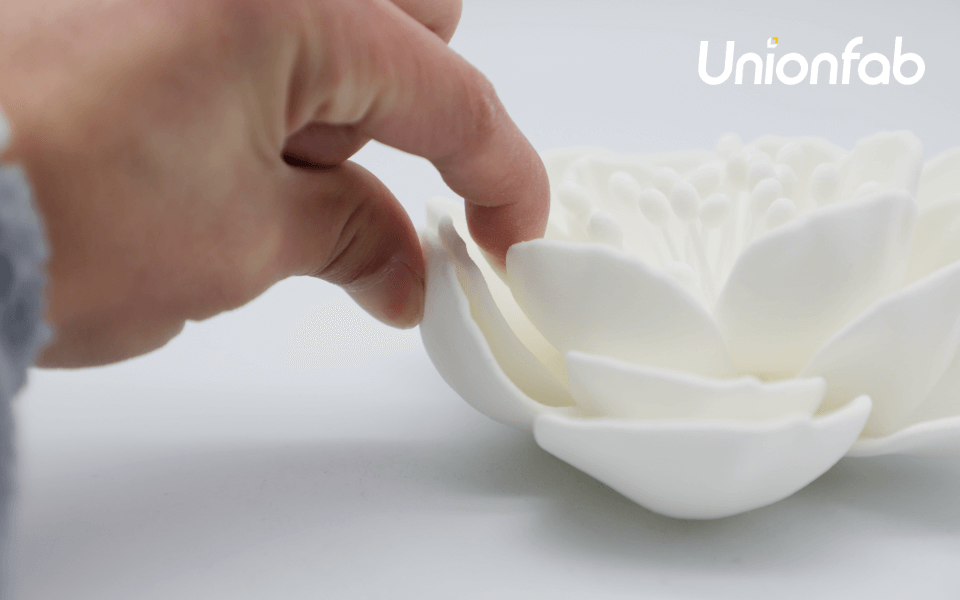

When it comes to product design, TPU offers unparalleled freedom. Designers can create functional prototypes that mimic the final product, ensuring fit and usability before mass production.
Conclusion
TPU 3D printing offers incredible flexibility and durability, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, from consumer products to medical devices and creative design. While FDM is great for personal projects, SLS TPU printing offers the precision and performance required for professional use.
To achieve the best results with TPU, ensure optimal print settings—such as slower print speeds and higher bed temperatures. Also, be sure to keep your TPU filament extremely dry before printing!
Ready to experience the power of SLS TPU printing? Get a free quote or Contact Unionfab today for personalized solutions and unbeatable service!

FAQs about TPU 3D Printing
Is TPU better than PLA?
It really depends on what you're printing! If you're after flexibility, durability, and parts that need to bend or stretch—like phone cases or wearable items—TPU is the way to go. It's tough, resistant to wear, and can handle more stress.
But, if you're a beginner or just need something easy to print for models, prototypes, or decorative items, PLA is a breeze to work with, though it’s not as tough as TPU.
Ultimately, if you need performance and resilience, TPU’s your best bet; if ease and eco-friendliness are priorities, PLA takes the lead.
Here’s a table to help you decide between TPU and PLA:
Property/Feature | ||
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
Strength | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
Durability | ★★★★★ | ★☆☆☆☆ |
Temperature Resistance | ★★★★☆ (-40°C to 120°C) | ★★☆☆☆ (60°C to 70°C) |
Ease of Printing | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Surface Finish | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
Does TPU need a filament dryer?
Absolutely! If you're printing with TPU regularly, investing in a filament dryer or storing your TPU filaments in a sealed, dry place with desiccants can make a noticeable difference in print quality.
TPU is a bit like a sponge when it comes to moisture—it's hygroscopic, meaning it loves to soak up water from the air. If it absorbs too much moisture, you might see issues like bubbling, stringing, or weak layers during printing. That’s where a filament dryer comes in handy. It helps keep your TPU nice and dry, so you can avoid those pesky printing problems and get smooth, reliable results.
Does TPU deform over time?
Yes, TPU can deform over time, especially if it’s constantly under stress or exposed to heat. While it’s super flexible and durable, it’s not invincible.
If you’re using TPU for parts that are frequently bent, stretched, or exposed to extreme temperatures, you might notice it starting to lose its shape or flexibility. But don’t worry, it’s still a lot more resistant to deformation than other flexible materials like PLA.
Just make sure to store it properly and avoid high heat, and your TPU parts will stay in good shape for much longer.

