Resin vs. Filament: Choosing the Best 3D Printing Material
Discover the unique properties, applications, pros, and cons of resin and filament in this ultimate guide.
Introduction
This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of resin and filament 3D printing materials, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
By understanding the differences between these materials, you can make an informed decision about which is best suited for your specific 3D printing project.
Understanding Resin vs Filament
3D Printing Resin
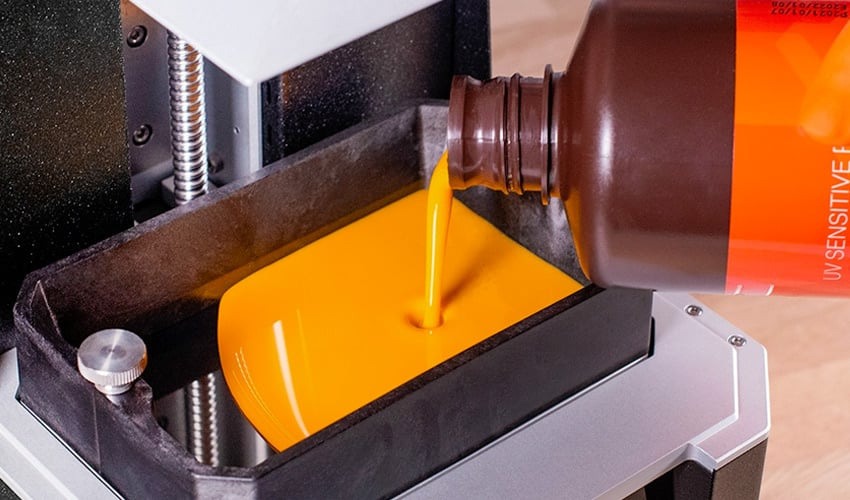

Resin is a liquid polymer material used in 3D printing processes like Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP). In these methods, a laser or projector cures the resin layer by layer, solidifying the 3D model.
Resins are categorized based on their properties and applications:
Standard resins
General-purpose resins for creating detailed models and prototypes.
Examples include:
Clear resins: Ideal for showcasing internal features or creating molds for casting.
Gray resins: Offer a neutral base for painting and post-processing applications.
Flexible resins
Offer elasticity and durability, suitable for flexible parts and prototypes.
Castable resins
Designed for investment casting, allowing for metal replicas of 3D models. Examples include:
Lost wax casting resins: Burn out cleanly without leaving residue, ideal for creating jewelry or detailed metal parts.
Investment casting resins: Specifically formulated for various metals like silver or bronze, ensuring successful casting processes.
Biocompatible resins
Approved for use in medical applications, ensuring safety for dental models or surgical guides. Examples include Denture resins.
Resin 3D printing excels in producing highly detailed, smooth, and accurate parts. It's ideal for creating complex geometries, jewelry, dental models, and miniatures requiring precise dimensions.
3D Printing Filament
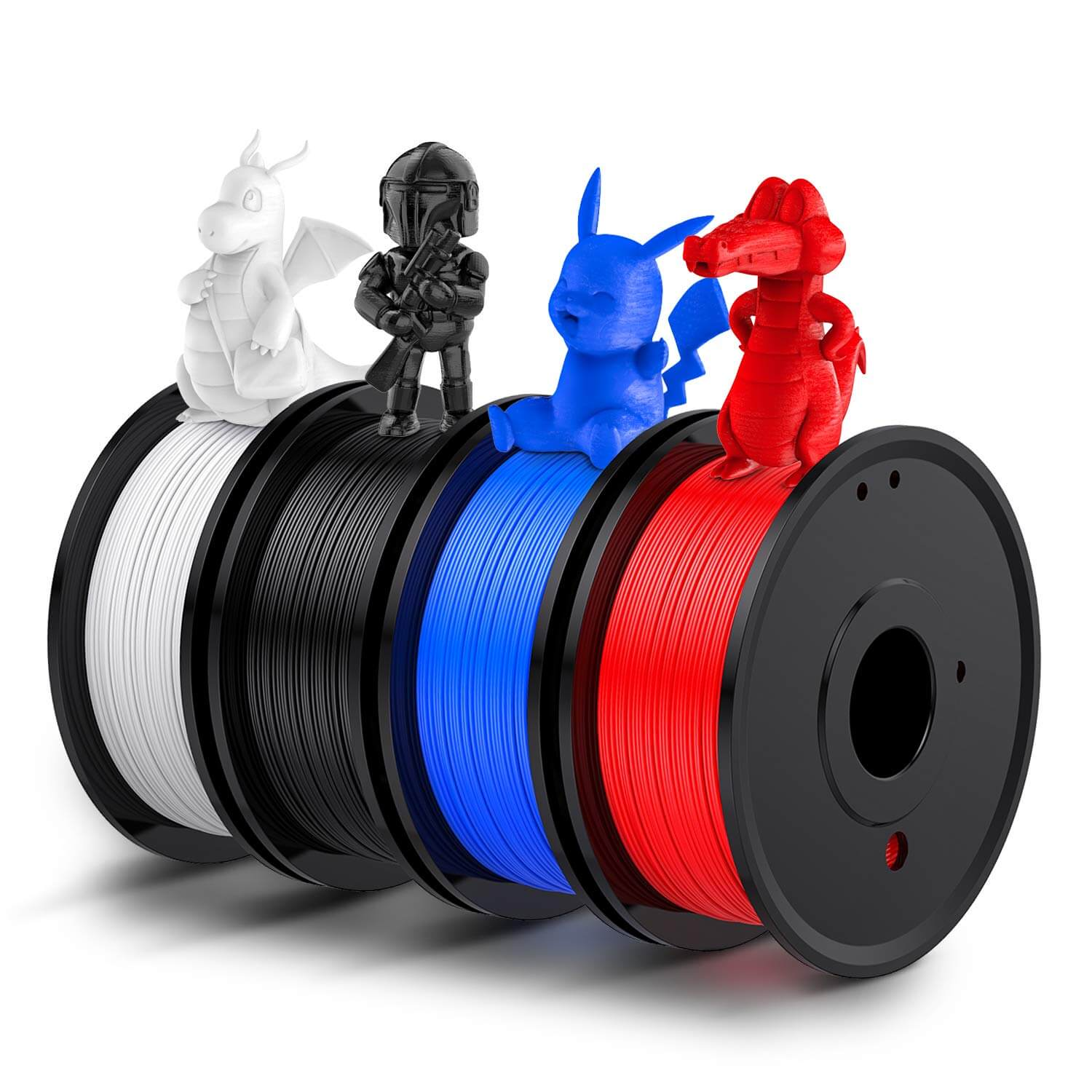

Filament is a thermoplastic material extruded layer by layer in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) 3D printing. A heated nozzle melts the filament, depositing it onto the build platform to create the 3D object.
Common filament types include:
PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable and easy to print, suitable for prototypes and general-purpose objects.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Strong and durable, often used for functional parts and engineering applications. Examples include:
ABS blends: Combine the strength of ABS with other materials like fire retardant additives for specific applications.
High-impact ABS: Offers increased impact resistance for parts that may experience wear and tear.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol: Tough, impact-resistant, and offers good clarity, suitable for various applications.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible and elastic, ideal for creating rubber-like parts and prototypes.
Filament 3D printing is versatile and cost-effective, making it popular for prototyping, functional parts, hobby projects, and educational purposes. It offers a wider range of materials with varying properties and is generally easier to use compared to resin printing.
Key Differences Between Resin and Filament
Feature | Resin | Filament |
|---|---|---|
Material Properties | Stronger, more durable, flexible options | Less strong, less flexible options |
Print Quality | Exceptional detail, smooth surface finish | Moderate detail, may exhibit layer lines |
Printing Process | Curing liquid resin with light | Extruding melted plastic |
Equipment | More expensive, specialized equipment | More affordable, wider range of options |
Cost | Higher initial setup, more expensive material | Lower initial setup, less expensive material |
Environmental Impact | Potential toxicity, disposal concerns | Energy consumption, waste generation |
Safety | Handling hazardous chemicals, proper ventilation required | Heated components, potential fumes |

Resin 3D Printing: Pros and Cons
Advantages of Resin 3D Printing
High-Resolution Prints
Resin printing reigns supreme in producing exceptionally fine details and smooth surface finishes. This is because it cures liquid resin in minute layers, resulting in unmatched precision.
Fine Details & Intricate Designs
Delicate features and intricate designs are resin printing's forte. It excels at capturing even the most minute details, making it ideal for creating jewelry, miniatures, and detailed architectural models.
Smooth Surface Finish
Resin prints boast a near-polish finish, often requiring minimal post-processing. This characteristic is perfect for applications where a flawless appearance is crucial, such as in product prototypes and visual models.
Ideal for Detailed & Intricate Creations
Resin printing's ability to produce high-resolution prints, fine details, and smooth surfaces makes it the go-to choice for intricate designs. This technology thrives in fields like jewelry, dentistry, and medical device manufacturing.
Disadvantages: Considerations Before Committing
Higher Cost
Compared to filament printing, resin printing generally carries a higher upfront cost. This includes the price of specialized equipment and resin consumables.
More Complex Post-Processing
Resin printing often involves a more complex post-processing workflow compared to filament printing. This includes additional steps like washing, curing, and potentially sanding the printed parts.
Exposure to Chemicals
Resin printing involves handling and using liquid resins, which may pose exposure risks to chemicals. Proper ventilation and safety precautions are essential when working with resin printers.
Resin 3D Printing Applications
Jewelry and Figurines
Resin’s ability to capture fine details makes it ideal for creating intricate jewelry pieces, figurines, and collectibles.

Medical Device Prototypes
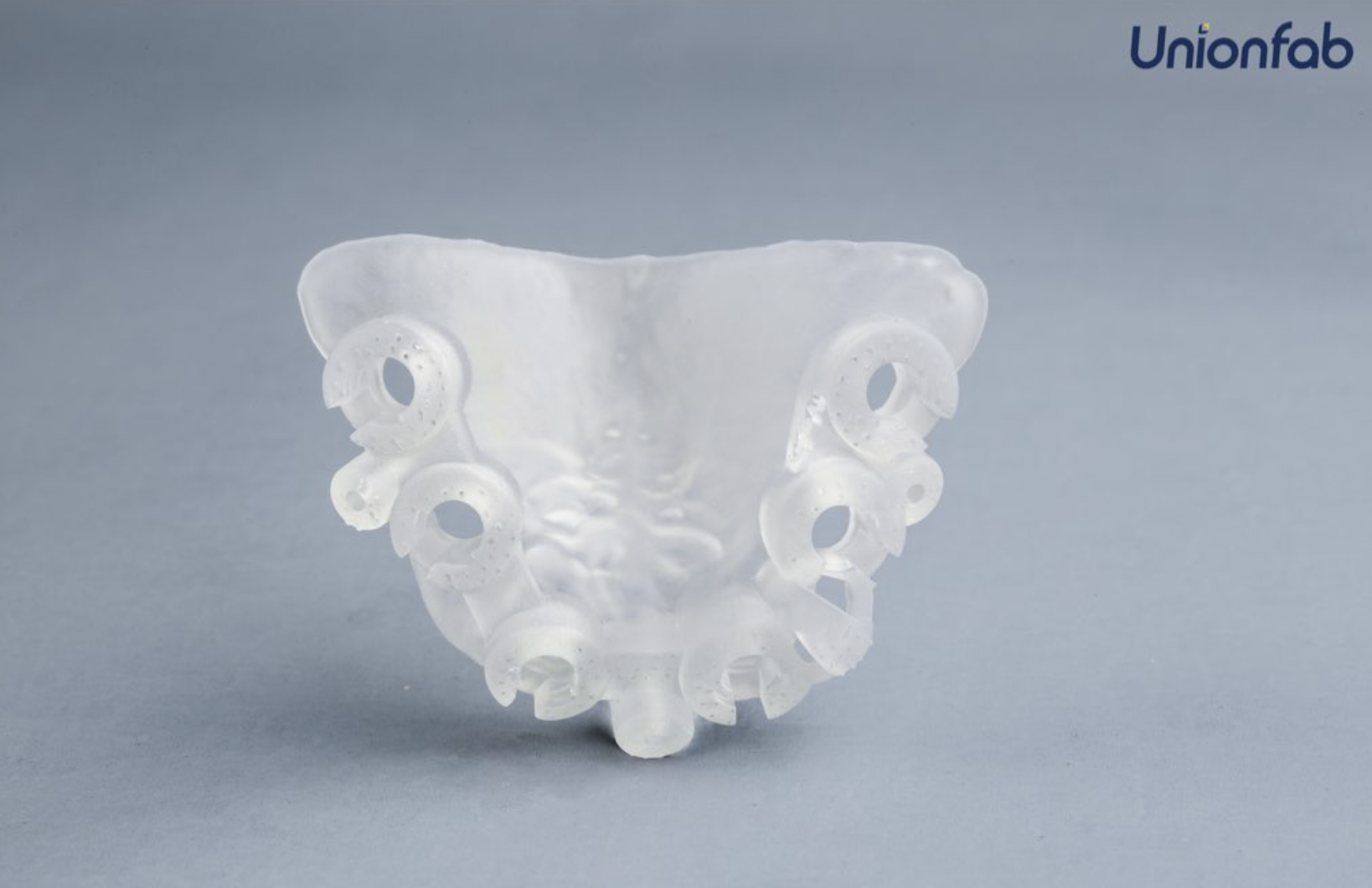
Resin’s ability to produce detailed and biocompatible parts makes it suitable for prototyping medical devices and surgical guides.
Especially, the smooth surface finish and high accuracy of resin prints make them well-suited for dental applications, such as creating dental models and aligners.
Product Prototypes and Visual Models
Resin's high-resolution prints and smooth surface finish make it ideal for creating realistic product prototypes and visual models for design and marketing purposes.
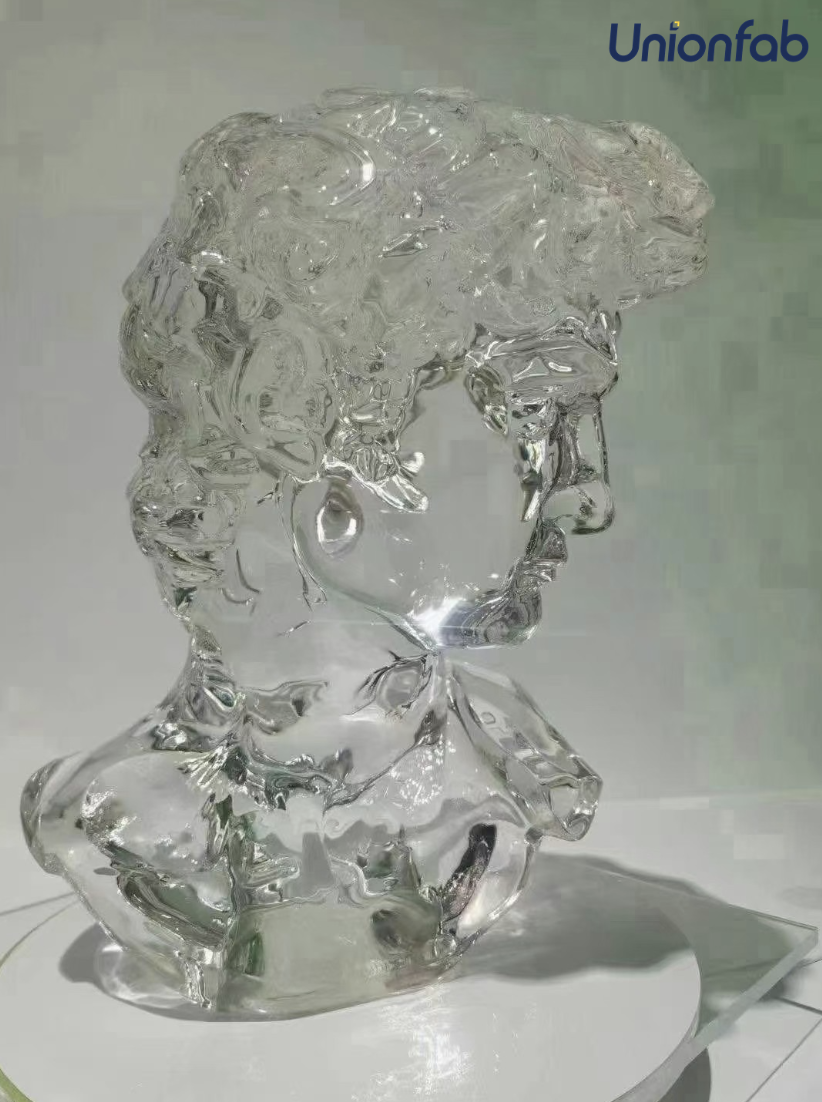

In conclusion, resin 3D printing offers a compelling blend of precision, detail, and surface quality, making it a valuable tool for various applications.
However, it's essential to consider its cost, post-processing requirements, and safety concerns before adopting this technology.
Filament 3D Printing: Pros and Cons
Filament 3D printing has exploded in popularity due to its ease of use, affordability, and versatility. But before diving in, understanding its strengths and limitations is key.
Advantages of Filament 3D Printing
Effortless Printing for Everyone
Compared to resin, filament boasts a streamlined process with minimal setup and maintenance. This makes it ideal for beginners and hobbyists to jump right in and create!
Accessible Creativity
Filament printers are generally more budget-friendly and widely available than resin printers. This makes them an accessible entry point for hobbyists, educators, and even small businesses.
Material Diversity
Filament shines in its material diversity. PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU – the list goes on! This vast selection allows you to create objects with a range of properties, from the strength and heat resistance of ABS to the flexibility of TPU. Plus, a wide spectrum of filament colors fuels your creativity with vibrant and personalized prints.
Functional & Large-Scale Fabrication
Need functional parts or larger objects? Filament has you covered. The durability and strength of filament materials make them ideal for creating objects designed for use. Additionally, filament printers can handle larger volumes without compromising structural integrity, allowing you to tackle ambitious projects on a desktop-sized machine, perfect for the personal hobbyist or maker space!
Disadvantages of Filament 3D Printing
Lower Resolution
Filament printing generally produces prints with less-defined details and visible layer lines on the surface compared to resin printing.
Visible Layer Lines
Due to the deposition process, filament prints often exhibit visible layer lines, which can be noticeable on certain designs. Post-processing techniques can minimize these lines, but they may not be completely eliminated.
Less Detail
When compared to resin, filament printing may struggle to capture extremely fine details and intricate features, especially in smaller objects and complex designs.
Filament 3D Printing Applications
Filament shines in applications that prioritize affordability, versatility, and functional performance. Here are some prime examples:
Prototyping and Functional Parts
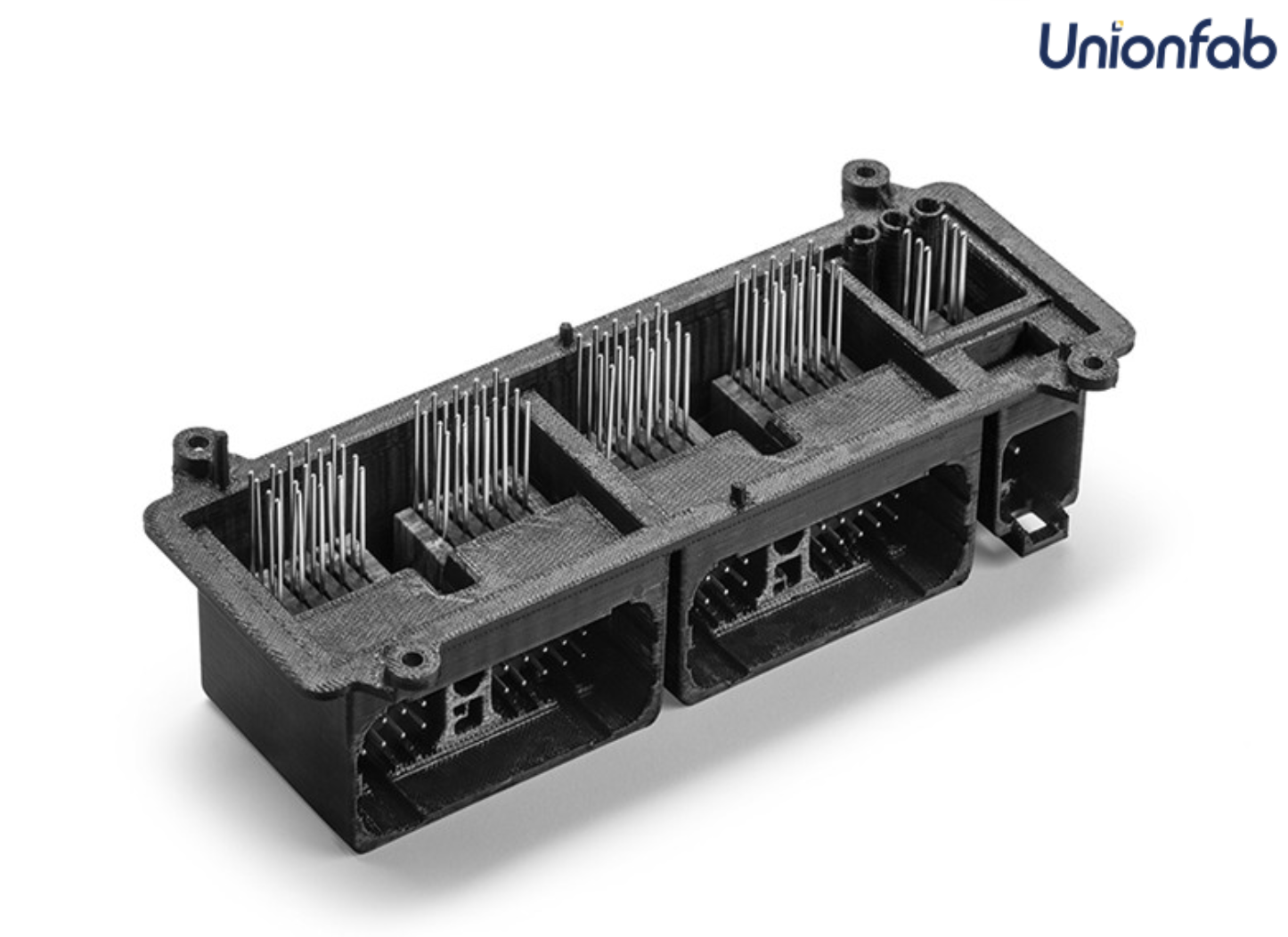
The strength, durability, and affordability of filament materials make it ideal for creating prototypes, functional parts, and tools like mechanical parts, housings, and fixtures.
Educational and Hobbyist Applications
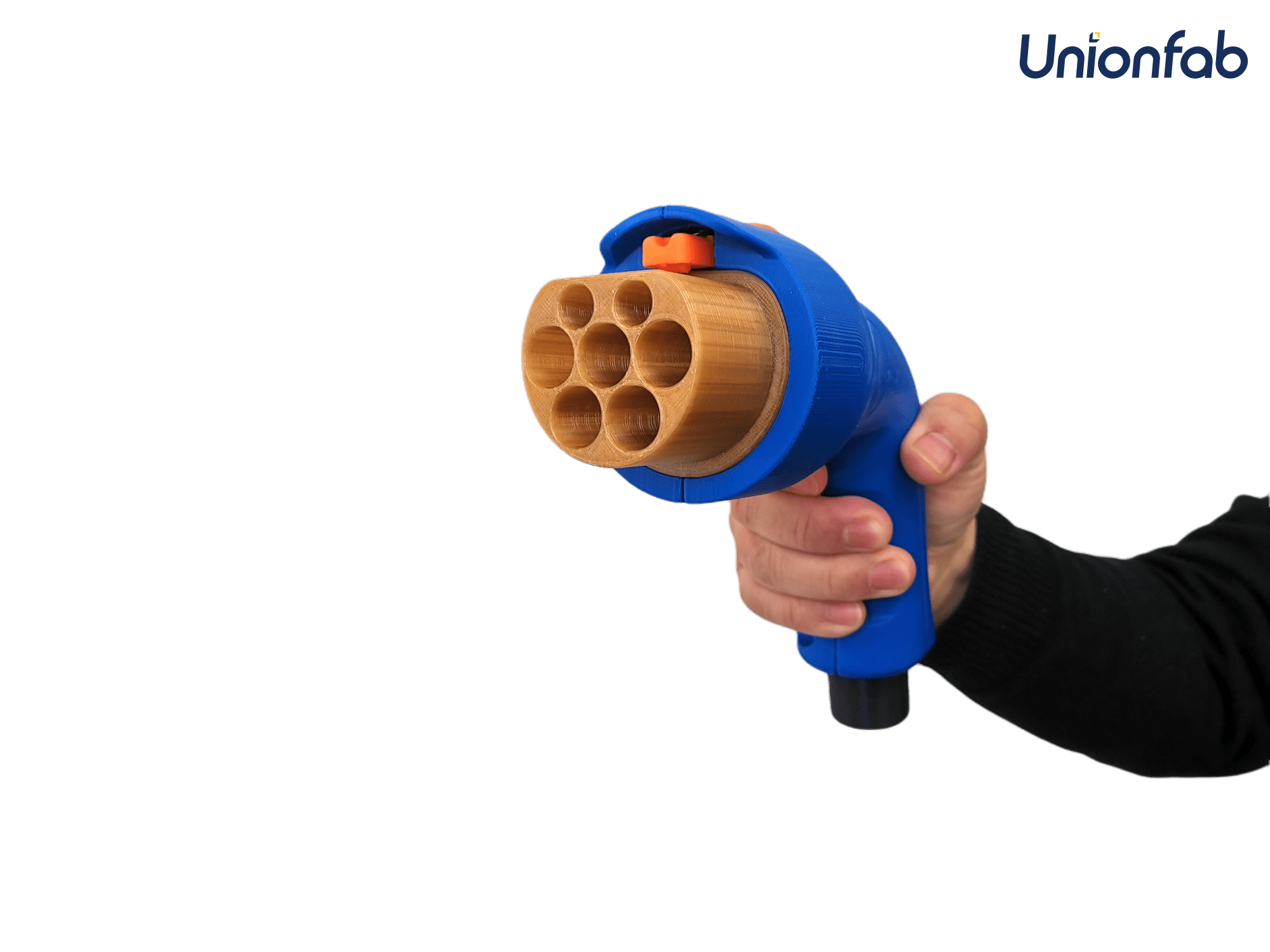

Filament printing's ease of use, accessibility, and wide range of materials make it an excellent choice for educational settings and hobbyist projects.
It allows students and enthusiasts to explore 3D printing and create various objects for learning and enjoyment.
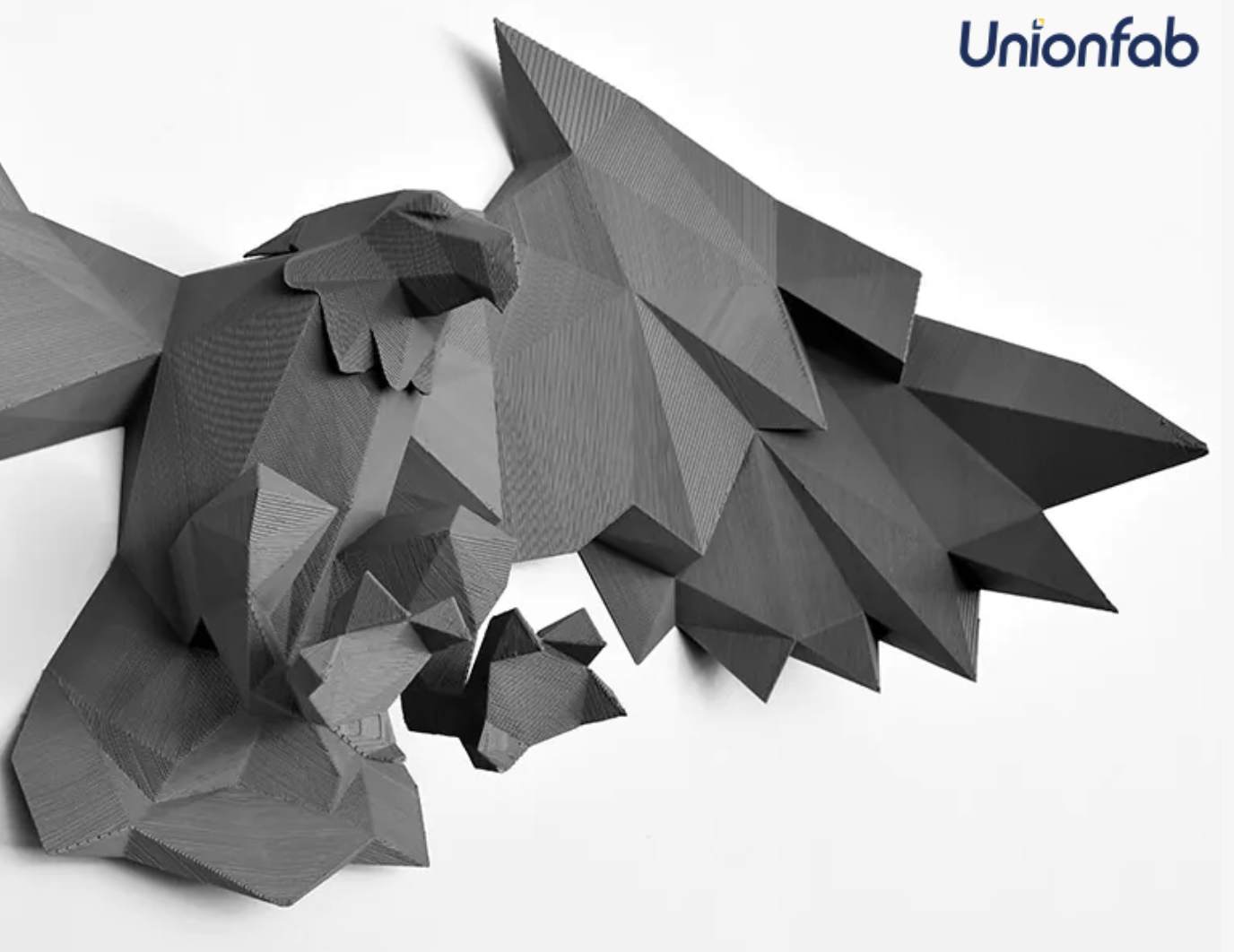
Larger Objects and Decorative Items

Cost-Effective Product Prototypes
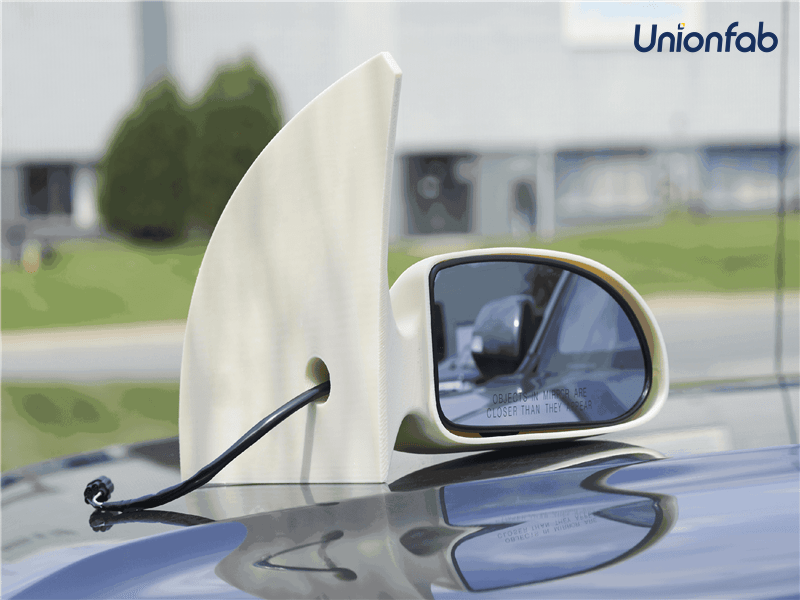

Filament printing can be a cost-effective solution for creating initial product prototypes or concept models.
The affordability of filament materials allows for rapid iteration and design refinement without breaking the bank.
In conclusion, filament 3D printing offers a compelling balance of ease of use, affordability, and versatility, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
However, it’s essential to consider its limitations in terms of resolution and detail when selecting the appropriate technology for your specific needs.
Selecting the Perfect 3D Printing Material
Understanding these factors and your project’s needs will guide you towards the perfect material match.
Key Considerations for Material Selection:
Project Purpose: Functional parts need strength? ABS or PETG are your allies. For aesthetics, consider PLA or resin.
Budget: Material costs vary. Choose based on your financial limitations.
Desired Finish: Smooth and polished? Opt for resin or PETG. Textured or matte? PLA or ABS could work.
Printing Experience: Beginners? Start with user-friendly PLA or PETG. Advanced users can explore ABS or resin.
Printer Compatibility: Ensure your chosen material is compatible with your specific 3D printer.
Beginner's Tips for a Smooth 3D Printing Journey:
Start with PLA: Known for ease of use and minimal warping, PLA is perfect for beginners.
Master the Basics: Focus on proper bed leveling, nozzle temperature, and slicing settings before venturing into complex materials.
Explore and Experiment: As you gain experience, explore PETG, ABS, or TPU to discover their unique properties.
Embrace Online Resources: Utilize tutorials, forums, and communities to learn from experienced users and troubleshoot any issues.
Remember, selecting the ideal 3D printing material is an ongoing learning process. By considering these factors, you'll be well-equipped to make informed decisions and achieve successful 3D printing results!
Conclusion
Your choice depends on your project’s needs. If you need high-precision prints with a smooth surface, resin printing could be the way to go, though it may come with higher costs and a more complex process.
On a budget? Filament printing is affordable with a wide range of materials, making it ideal for functional parts, prototypes, and larger objects. Just note that it might have lower resolution and visible layer lines compared to resin.
Unionfab:The Perfect Material Awaits
Ready to unleash your creativity? At Unionfab, we offer a wide range of top-quality resin and filament materials to bring your vision to life.
Explore our material options or contact our team for expert advice on choosing the perfect material for your project. Let's transform your ideas into reality, together!
FAQs
Q: Which type of 3D printing is better for beginners?
A: Filament printing is generally considered more beginner-friendly due to its lower initial cost, easier setup, and wider range of materials.
Q: Which type of 3D printing is better for creating detailed models?
A: Resin printing excels in producing highly detailed models with smooth surface finishes.
Q: Which type of 3D printing is more environmentally friendly?
A: Both resin and filament printing have environmental impacts, and the specific concerns vary depending on the materials and processes used.
Q: Which type of 3D printing is safer?
A: Both resin and filament printing require safety precautions. Resin printing involves handling hazardous chemicals and proper ventilation, while filament printing involves heated components and potential fumes.
Remember: The choice between resin and filament depends on your specific needs, budget, and available equipment. Carefully consider the factors mentioned above to make an informed decision.

