Flexible 3D Printing: Materials, Techniques, and Applications
From prosthetics to fashion, flexible 3D printing transforms industries. Discover how it can revolutionize your next project.
Introduction
Flexible 3D printing, also known as soft 3D printing or elastomeric 3D printing, utilizes a range of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and other flexible materials to create objects that can bend, stretch, and deform without breaking.
This capability has revolutionized various industries, from healthcare and product design to prototyping and special effects.
Understanding Flexible 3D Printing
Building upon the introduction, let's delve deeper into the world of flexible 3D printing:
Definition of Flexible 3D Printing
Flexible 3D printing is a specific additive manufacturing process that utilizes materials with inherent bendability, elasticity, and the ability to deform without breaking.
These materials, primarily thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and other flexible filaments, are deposited layer-by-layer to create three-dimensional objects.
Unlike traditional rigid 3D printing, flexible prints offer a unique combination of functionality, comfort, and design freedom.
Key Benefits of flexible 3D printing
The advantages of flexible 3D printing extend far beyond aesthetics, offering significant benefits across various industries:
Enhanced Functionality: Flexible materials can be tailored to mimic real-world movements and deformations. This opens doors for applications like.
Comfort and Wearability: The soft and pliable nature of these materials makes them ideal for applications that require comfort and close contact with the body.
Impact Resistance: The ability of these materials to absorb shock and impact makes them suitable for applications requiring protection.
Design Freedom: The ability of flexible materials to bend and stretch allows for more intricate and creative designs.

Techniques and Materials for Flexible 3D Printing
Flexible 3D printing brings together innovative techniques and adaptable materials to produce durable, customizable, and functional prints.
This section will delve into various 3D printing technologies and their compatible flexible materials, providing a clear picture of how these elements work in harmony to achieve impressive results.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM, the most widely used 3D printing technology, is also well-suited for flexible printing.
It utilizes a filament spool that feeds the material through a heated nozzle, depositing it layer-by-layer to create the desired object.
Materials
Flexible Filaments:
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): A class of elastomeric plastics known for their rubber-like properties, offering both flexibility and elasticity.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): A versatile TPU material renowned for its exceptional durability, abrasion resistance, and high elasticity, making it ideal for demanding applications.
Soft PLA: A modified PLA filament with enhanced flexibility, offering a balance between the rigidity of traditional PLA and the suppleness of TPE filaments.
Properties
FDM offers several advantages for flexible printing:
Durability: Flexible filaments can withstand considerable wear and tear.
Elasticity: Prints can bend and stretch without breaking, ideal for functional parts.
Ease of Use: FDM is a relatively user-friendly technology, making it accessible to a wider range of users.
Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP)
SLA and DLP utilize lasers to cure liquid resin into solid layers, building the 3D object with exceptional detail.
These technologies are well-suited for applications requiring high precision and smooth surface finishes.
Materials
Flexible Resins: Unlike filament for FDM, SLA and DLP employ specialized resins formulated for flexibility and resilience. These resins come in varying Shore A durometer hardness ratings to meet specific application needs. Example include:
Rubber-like Resin: a flexible 3D printing material for DLP printers, mimicking the elasticity and durability of rubber, ideal for prototyping flexible parts like shoe soles.
Properties
SLA and DLP offer distinct advantages for flexible printing:
Precision: These technologies produce highly detailed and accurate prints.
Resilience: Flexible resins offer good tear and impact resistance.
Smooth Surface Finish: SLA and DLP prints are known for their smooth surface finishes, ideal for aesthetic applications.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
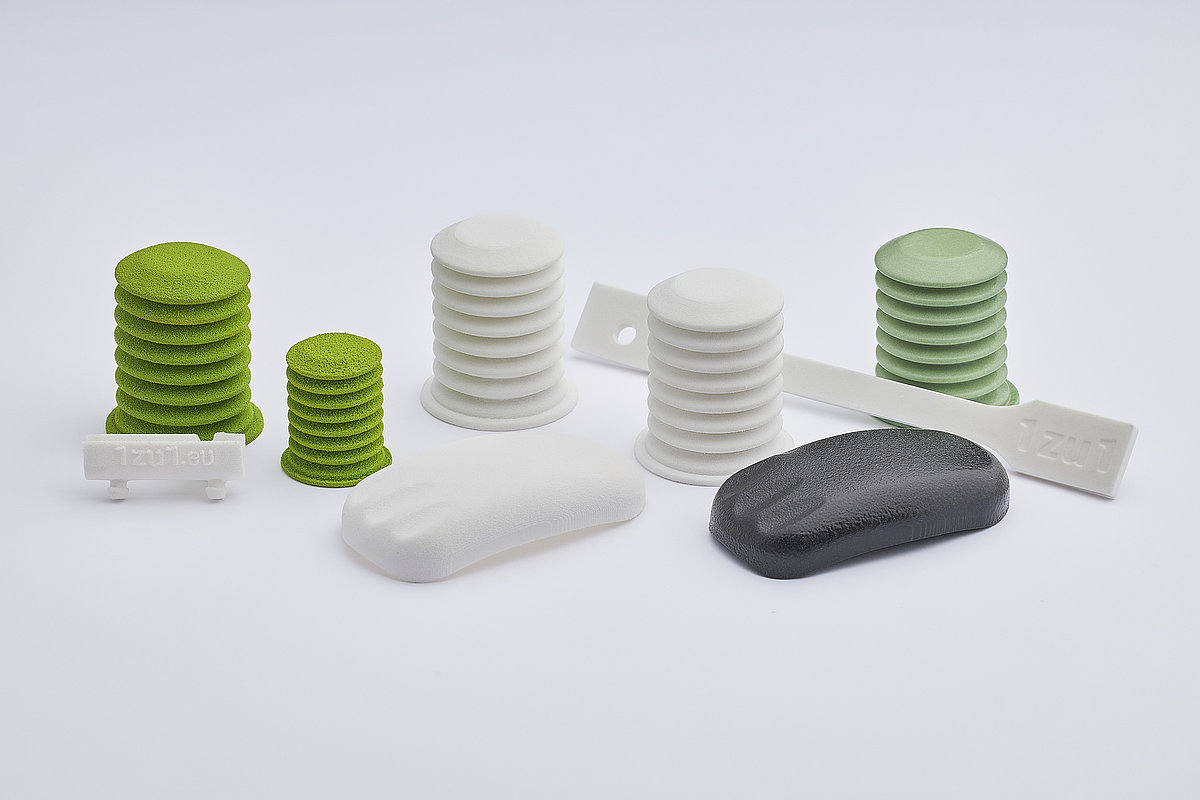

SLS employs a laser to selectively sinter powdered materials, creating robust and functional parts. This technology is particularly suited for applications requiring high strength and durability.
Materials
SLS TPU: a strong, elastic material for 3D printing that's ideal for serial production of durable, flexible parts like footwear components and prosthetics.
Properties
SLS offers unique advantages for flexible printing:
High Durability: SLS prints are known for their exceptional strength and durability.
Flexibility: Flexible powders enable the creation of parts with a degree of bendability.
Suitability for Functional Parts: SLS is ideal for printing functional parts requiring both flexibility and strength.
Multi-material 3D Printing
A growing trend in 3D printing is the ability to utilize multiple materials within a single print. This opens up exciting possibilities for flexible printing.
Materials
Combinations: Multi-material printers can combine rigid and flexible materials, such as PLA for rigid structures and TPU filaments like those mentioned earlier for flexible elements.
Properties
Multi-material printing offers unmatched versatility:
Versatility: This technique allows for the creation of complex objects with both rigid and flexible features within a single print.
Complex Objects: Multi-material printing opens doors for innovative designs with integrated flexible components.
Applications of Flexible 3D Printing
Let's explore some of the groundbreaking applications across diverse fields:
Consumer Products
Shoe Soles

Flexible filaments can be used to print customized shoe soles that provide optimal comfort, support, and traction for individual needs.
Phone Cases
Phone Cases Flexible prints can create durable and personalized phone cases that protect devices while expressing individual style.
Sports Braces and Supports
Flexible materials can be used to print custom-fit braces and supports for enhanced comfort and performance during activities.
Medical and Healthcare
Prosthetics
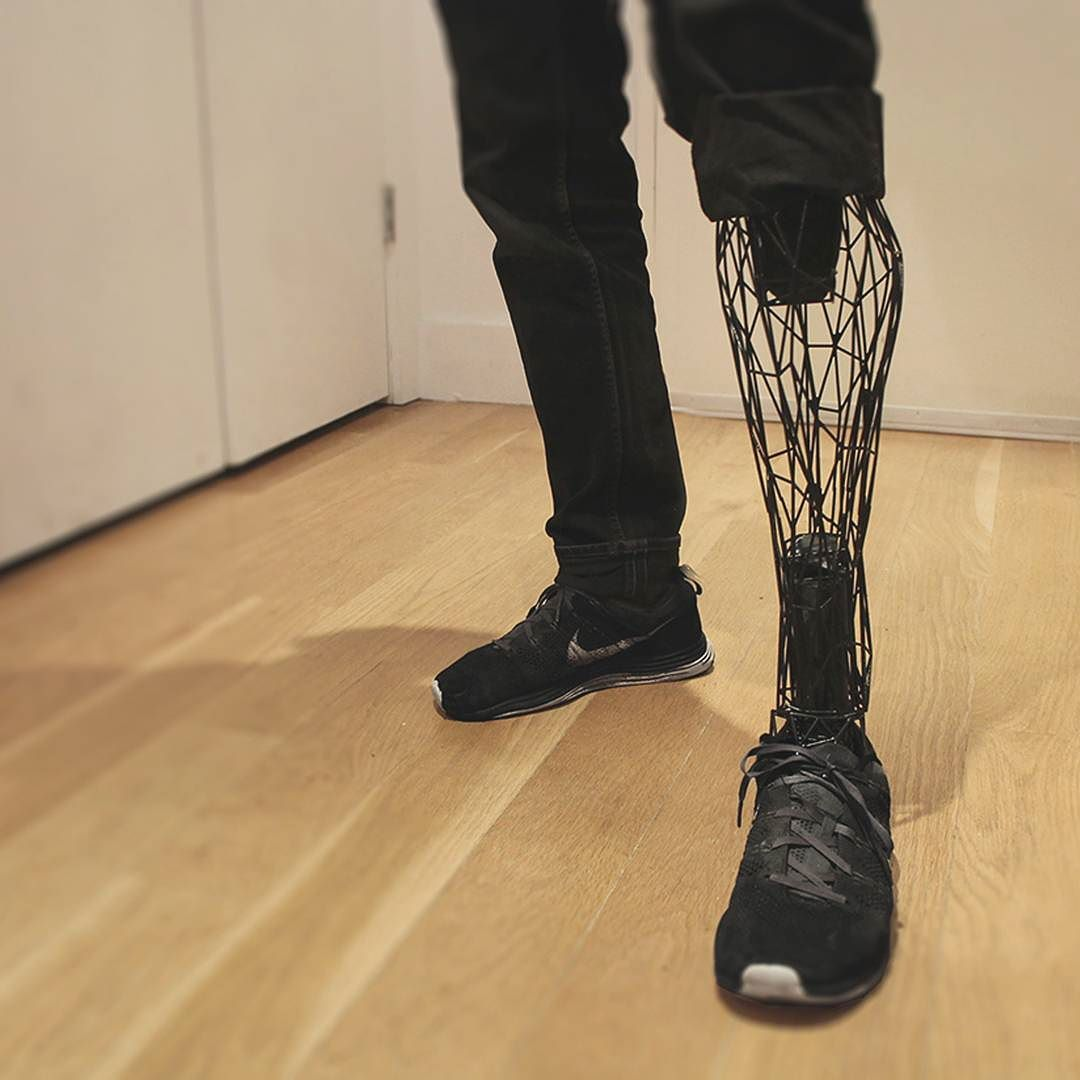
Flexible filaments can be used to create customized prosthetic limbs that mimic natural movements and provide a more natural feel for wearers.
Orthotics
Flexible prints can be used to create custom orthotics that provide support and comfort for individuals with foot and ankle conditions.
Surgical Guides
Flexible materials can be used to print patient-specific surgical guides, enhancing precision and reducing surgical time.
Automotive and Aerospace
Engine Seals
Flexible seals can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, ensuring optimal engine performance.
Aerospace Gaskets
Flexible gaskets can be used in aircraft and spacecraft to maintain pressure integrity and prevent leaks.
Art and Creativity
Articulated Figures
Flexible joints and hinges can be printed to create articulated figures that can bend, twist, and perform various movements.
Interactive Art Installations
Flexible prints can be used to create interactive art installations that respond to touch, light, or sound.
Why Choose Flexible 3D Printing?
Flexible 3D printing offers a compelling alternative to traditional manufacturing methods for a wide range of applications.
Here's a closer look at the key advantages that make it a standout choice:
Advantages Over Traditional Manufacturing
Design Freedom: Traditional manufacturing processes can be limited in their ability to create complex geometries with bends and curves. Flexible 3D printing eliminates these limitations, allowing for the creation of intricate and innovative designs with ease.
Reduced Lead Times and Prototyping: Traditional methods often require the creation of expensive molds and tooling, leading to longer lead times. Flexible 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling quick design iterations and faster product development cycles.
Minimal Material Waste: Traditional manufacturing often generates significant material waste during the cutting and shaping process. Flexible 3D printing utilizes an additive approach, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability.
Cost-Effectiveness
Lower Tooling Costs: Compared to traditional methods that require expensive molds and tooling, flexible 3D printing often requires minimal upfront investment. This makes it cost-effective for small batch production and customized projects.
Reduced Inventory Costs: With on-demand printing capabilities, flexible 3D printing allows for just-in-time production, minimizing the need for large inventories and associated storage costs.
Customization and Rapid Prototyping
Personalized Products: The ability to create custom-fit products is a major advantage. This is particularly valuable in fields like healthcare ( prosthetics and orthotics) and consumer wearables (customized phone cases and shoe soles).
Rapid Prototyping: Flexible 3D printing allows for the creation of functional prototypes quickly and efficiently. This facilitates design iterations, testing, and product development at a faster pace.
Durability and Versatility
Enhanced Functionality: Flexible materials can withstand wear and tear, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and functionality, such as seals, gaskets, and protective gear.
Versatility Across Industries: The diverse range of flexible materials caters to various applications across industries like automotive, consumer goods, healthcare, and art. This versatility opens doors for innovative product design and development.
Flexible 3D Printing: Case Studies
Here are case studies showcase the transformative power of flexible 3D printing across diverse applications
Case: LifeNabled and Flexible 3D-Printed Prosthetic Sockets
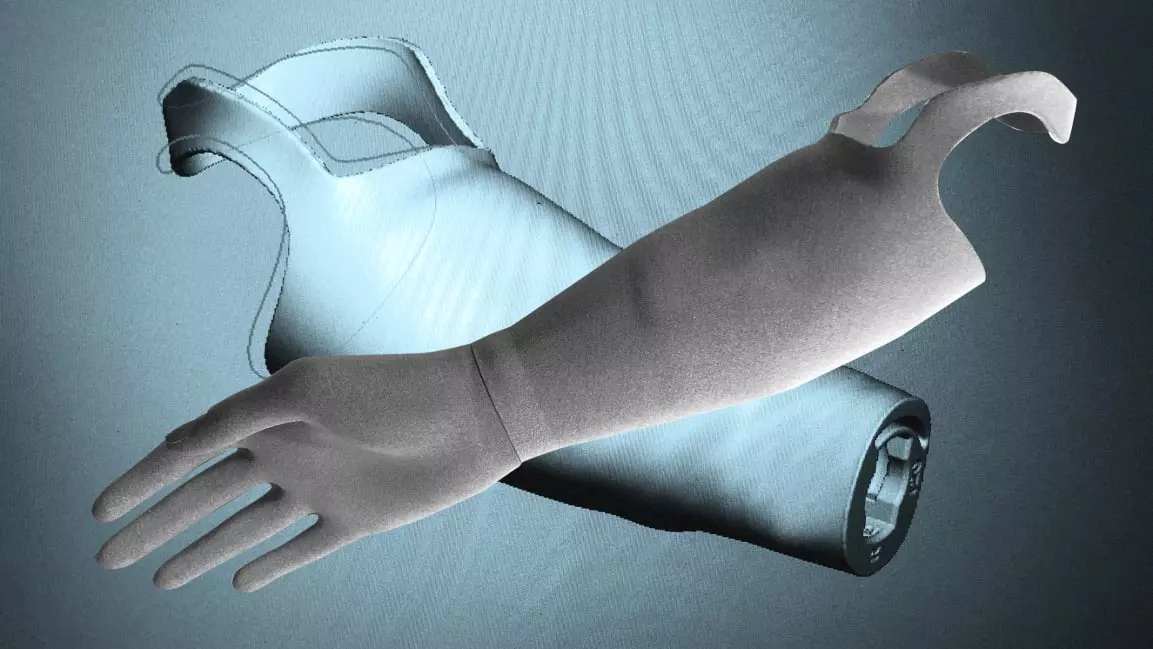
LifeNabled is a non-profit organization that provides prosthetic care to amputees in developing countries. LifeNabled partnered with nTopology, a 3D printing design software company, to develop custom 3D-printed prosthetic sockets with flexible inner liners. These sockets offer several advantages:
Enhanced flexibility: Flexible inner liners conform to the residual limb, improving comfort and reducing the risk of sores.
Faster production: 3D printing allows for rapid creation of sockets, reducing wait times for patients.
Improved fit: Sockets can be scanned and custom-designed for each patient, leading to a more comfortable and secure fit.
Reduced cost: 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional methods, especially for complex designs. LifeNabled can now serve more patients with improved prosthetics, allowing them to regain mobility and independence.
Future of Flexible 3D Printing: Innovation and Challenges
Let's explore some emerging trends and innovations that will shape this exciting field, alongside potential challenges and solutions:
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Material Innovations
Enhanced TPUs: Improved formulations of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) offer superior elasticity, durability, and abrasion resistance, ideal for flexible parts requiring both flexibility and toughness.
Example: Elastollan by BASF
Conductive Filaments: New conductive filaments combine flexibility with electrical conductivity, paving the way for innovative wearable electronics and soft robotics.
Example:Filaflex by Recreus
Sustainable Options: Biodegradable and eco-friendly filaments are catering to environmentally conscious consumers and industries, offering a balance between flexibility and sustainability.
Example:EcoFlex by Filamentar
Technical Advancements
Multi-Material Printing: Multi-material printers enable the creation of complex objects with integrated flexibility in specific areas, combining rigid and flexible materials in a single print.
High-Resolution Printing: Advancements in printing technology have resulted in higher resolution capabilities, enabling production of intricate and detailed flexible prints for applications like custom wearables and medical devices.
Faster Print Speeds: New developments in print head technology and optimized printing processes have significantly reduced print times for flexible materials, boosting productivity and making it more viable for commercial applications.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Material Consistency: Maintaining consistent material properties across a printed object can be challenging with flexible materials. Advancements in material science and printing techniques will be crucial to ensure uniformity and predictable performance.
Post-Processing: Flexible materials often require additional post-processing steps, such as support removal and surface finishing. Automation and streamlined post-processing techniques will be necessary for broader adoption.
Design Complexity: Designing for flexible 3D printing requires specialized knowledge and software tools. Educational resources and user-friendly design platforms will be essential to empower a wider range of designers to leverage this technology.
Environmental Impact: While offering benefits in terms of material waste reduction, the environmental impact of 3D printing needs to be addressed. Sustainable practices and recyclable materials will be crucial for a responsible future of flexible 3D printing.
By overcoming these challenges and further developing the technology, flexible 3D printing has the potential to transform numerous industries.
Conclusion
Flexible 3D printing offers a unique combination of durability, customization, and versatility, opening doors for innovative applications across various fields.
Whether you're a designer, engineer, entrepreneur, or simply someone with a creative vision, consider the possibilities that flexible 3D printing can unlock for your next project.
Explore the Possibilities with Unionfab
Unionfab is at the forefront of flexible 3D printing technology. Let us help you bring your innovative ideas to life with the power of our SLS, FDM, SLA and DLP technology.
Don't hesitate to contact us and unlock a world of flexible possibilities!

