5052 Aluminum vs 6061: A Comprehensive Comparison

This article compares the mechanical properties, applications, and overall performance of 5052 aluminum vs 6061 aluminum.
Introduction
Aluminum alloys are widely used in various industries due to their excellent properties such as lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high strength-to-weight ratio. Among these alloys, 5052 and 6061 are two of the most commonly used.
Understanding their differences in terms of chemical composition, physical and mechanical properties, as well as their suitability for different applications, can help in making informed decisions for specific projects.
5052 Aluminum vs 6061: Chemical and Physical Properties
Property | 5052 Aluminum | 6061 Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
Chemical Composition | ||
Primary Alloying Element | Magnesium (Mg) 2.2-2.8% | Magnesium (Mg) 0.8-1.2%, Silicon (Si) 0.4-0.8% |
Other Elements | Chromium (Cr) 0.15-0.35%, traces of Si, Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn | Chromium (Cr) 0.04-0.35%, Fe, Cu 0.15-0.4%, Mn, Zn, Ti |
Impact on Mechanical Properties | ||
Strength | Higher due to Mg | Excellent |
Corrosion Resistance | Enhanced | Good |
Machinability | Moderate | Excellent |
Physical Properties | ||
Density | 2.68 g/cm³ | 2.70 g/cm³ |
Thermal Conductivity | 138 W/m-K | 151-167 W/m-K |
Electrical Conductivity | Lower | Better |
Corrosion Resistance | ||
General | Excellent, especially marine | Good, less in seawater |
Chemical Composition
Elements in 5052 Aluminum
The primary alloying element in 5052 aluminum is Magnesium (Mg) (2.2-2.8%), significantly enhancing strength and corrosion resistance. Chromium (Cr) (0.15-0.35%) adds more corrosion resistance and controls grain structure.
Trace elements include Silicon (Si), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), and Zinc (Zn), each with maximum limits of 0.25%, 0.4%, 0.1%, 0.1%, and 0.1%, respectively.
Elements in 6061 Aluminum
In 6061 aluminum, the primary alloying elements are Magnesium (Mg) (0.8-1.2%) and Silicon (Si) (0.4-0.8%), forming magnesium silicide for enhanced mechanical properties and machinability.
Other elements like Chromium (Cr), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Zinc (Zn), and Titanium (Ti) aid in corrosion resistance, strength, and grain refinement.
Impact on Mechanical Properties
5052 Aluminum: The higher magnesium content in 5052 aluminum alloy enhances its overall strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for environments where these properties are critical.
6061 Aluminum: The combination of magnesium and silicon in 6061 aluminum results in excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and good machinability. The presence of other elements like copper and chromium further optimizes its performance for a wide range of structural applications.
Physical Properties
Density
5052 Aluminum: With a density of approximately 2.68 g/cm³, it's slightly lighter than 6061, making it a consideration for weight-sensitive applications where every gram counts.
6061 Aluminum: Marginally denser at approximately 2.70 g/cm³, which may not be significant in most cases, but could matter in precision engineering where minute differences matter.
Thermal Conductivity
5052 Aluminum: Exhibits a thermal conductivity of 138 W/m-K, suitable for applications needing efficient heat dissipation.
6061 Aluminum: Shows superior thermal conductivity, ranging from 151-167 W/m-K, making it advantageous for heat exchangers and environments where dissipating heat is crucial.
Electrical Conductivity
5052 Aluminum: Its higher magnesium content results in lower electrical conductivity, making it less suitable for electrical applications compared to 6061.
6061 Aluminum: Boasts better electrical conductivity compared to 5052, making it more appropriate for electrical components and applications prioritizing conductivity.
Corrosion Resistance
5052 Aluminum: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and saltwater environments, making it perfect for marine applications and areas with high humidity or exposure to seawater.
6061 Aluminum: Offers good corrosion resistance but is less effective than 5052 in seawater. It's still suitable for a range of environments but might require protective coatings in extremely corrosive conditions.
5052 Aluminum vs 6061: Mechanical Properties
Property | 5052 Aluminum | 6061 Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
Tensile Strength | 210-260 MPa | 290-310 MPa |
Yield Strength | ~130 MPa | ~240 MPa |
Hardness (Brinell) | ~61 HB | ~95 HB |
Fatigue Strength | Moderate | Higher |
Tensile Strength Comparison
5052 Aluminum: Tensile strength is approximately 210-260 MPa, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate strength.
6061 Aluminum: Tensile strength is approximately 290-310 MPa, offering higher strength for more demanding applications.
Yield Strength Comparison
5052 Aluminum: Yield strength is around 130 MPa, indicating moderate resistance to deformation under load.
6061 Aluminum: Yield strength is around 240 MPa, providing better resistance to permanent deformation under stress.
Hardness Comparison
5052 Aluminum: Brinell hardness is about 61 HB, making it easier to work with but less resistant to wear.
6061 Aluminum: Brinell hardness is about 95 HB, indicating higher wear resistance and durability.
Fatigue Strength Comparison
5052 Aluminum: Has moderate fatigue strength, making it suitable for applications with moderate cyclic loads.
6061 Aluminum: Exhibits higher fatigue strength, better for applications that endure higher cyclic loads and require more durability.
5052 Aluminum vs 6061: Forming and Working
Formability and Workability
Machinability
5052 Aluminum: Fair machinability, making it more difficult to machine compared to 6061. The higher magnesium content can cause more tool wear and requires careful control of machining parameters to avoid poor surface finishes and rapid tool degradation.
6061 Aluminum: Excellent machinability, largely due to its balanced composition of magnesium and silicon. This alloy machines well and allows for higher machining speeds and better surface finishes, making it a preferred choice for precision components and complex parts.
Weldability
5052 Aluminum: Offers excellent weldability, which makes it ideal for projects requiring extensive welding. It can be welded using various techniques, including TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, without significant risk of cracking or weakening the material.
6061 Aluminum: Good weldability, but it requires more careful control during welding to avoid issues such as cracking. Pre-weld and post-weld heat treatments are often recommended to reduce the risk of weld defects and to restore the mechanical properties of the heat-affected zone.
Forming and Bending Characteristics
5052 Aluminum: Exhibits very good formability and bendability, making it suitable for complex shapes and intricate designs. Its high ductility allows it to be formed into tight radii without cracking, which is beneficial for applications that require extensive forming operations.
6061 Aluminum: Has fair formability and is not as easily formed as 5052. It is better suited for simpler shapes and less demanding forming processes. While it can still be bent and formed, it requires larger bend radii and more careful handling to avoid cracking.
Heat Treatment and Hardening
Heat Treatability of 6061
6061 Aluminum can be heat-treated to enhance its mechanical properties, increasing its strength and hardness.
The T6 temper is the most common heat treatment for 6061, involving solution heat treatment and artificial aging.
This versatility allows 6061 to be used in a wide range of applications requiring varying levels of strength and durability.
Non-Heat Treatability of 5052
5052 Aluminum cannot be heat-treated, but it can be work-hardened to improve its strength.
This is achieved through processes such as rolling or cold working, which increase its hardness and strength by inducing plastic deformation.
While it does not achieve the same strength levels as heat-treated alloys like 6061, work-hardening makes 5052 suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and high ductility.
5052 vs 6061 Aluminum: Applications
Applications of 5052 Aluminum
Marine Industry
5052 aluminum is highly valued in the marine industry for its outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater environments.
This makes it ideal for boat hulls, ship superstructures, and other marine components that are constantly exposed to harsh, corrosive conditions.
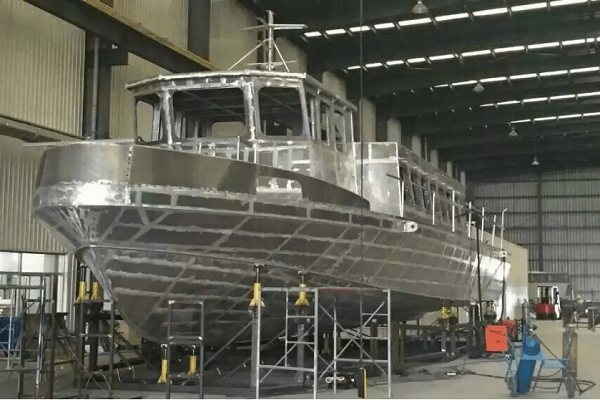

Source: hcaluminum.com
Automotive Components
In the automotive industry, 5052 aluminum is commonly used for fuel tanks, panels, and other components where its excellent formability and corrosion resistance are critical.
Its ability to be easily shaped into complex forms without cracking makes it suitable for various body panels and structural parts.
Source: formonictech.com
Consumer Goods
5052 aluminum is widely used in the production of consumer goods such as electronics, kitchenware, and home appliances. Its combination of strength, lightweight, and good corrosion resistance makes it ideal for these applications.
For example, it is often found in laptops, kitchen utensils, and various household items.
Aerospace Applications
While not typically used in critical structural components, 5052 aluminum is used in aerospace applications for non-critical parts where corrosion resistance and weight savings are beneficial. This includes components such as ducts, brackets, and non-load-bearing panels.
Applications of 6061 Aluminum
Structural Components
6061 aluminum is extensively used in structural applications due to its excellent strength and versatility. It is found in construction projects, including bridges, buildings, and pipelines, where it provides strong, durable support structures.
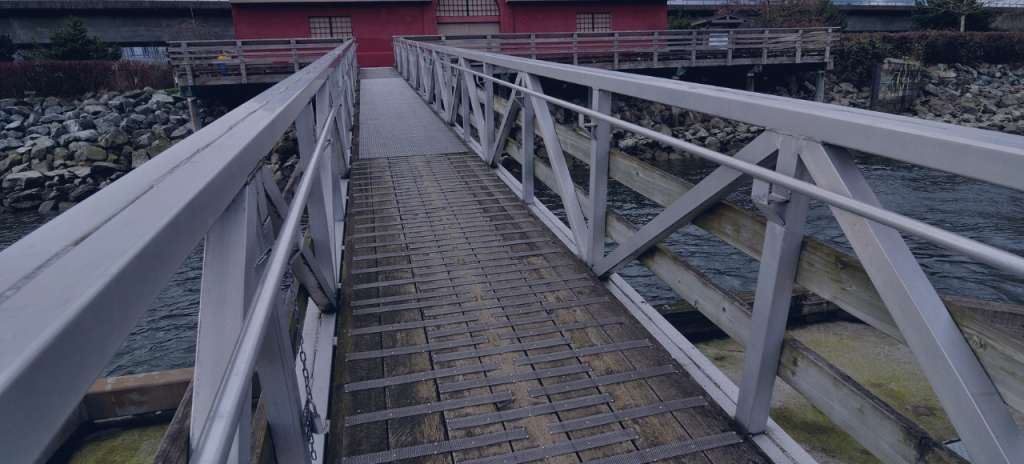

Source: formonictech.com
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sectors, 6061 aluminum is used for a variety of structural parts and components. Its strength, combined with its ability to be heat-treated for enhanced properties, makes it suitable for aircraft frames, landing gear, and military vehicles.
Automotive Industry
6061 aluminum is applied in automotive parts that require a combination of good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. This includes suspension components, engine parts, and chassis. Its ability to be machined into precise parts also makes it ideal for custom automotive applications.

Source:formonictech.com
Recreational Equipment
Due to its strength and lightweight properties, 6061 aluminum is popular in the manufacturing of recreational equipment such as bicycles, boats, and sporting goods. It provides the necessary durability and performance while keeping the equipment lightweight and easy to handle.
5052 vs 6061 Aluminum: Factors to Consider When Choosing
Project Requirements
Strength
5052 Aluminum: Offers moderate strength, suitable for applications where extreme strength is not the primary requirement but good formability and corrosion resistance are crucial.
6061 Aluminum: Provides higher strength, making it ideal for structural applications and components that need to withstand significant loads or stress.
Corrosion Resistance
5052 Aluminum: Excels in corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater and marine environments. It is the preferred choice for applications exposed to harsh or corrosive conditions.
6061 Aluminum: While it has good corrosion resistance, it is not as robust as 5052 in highly corrosive environments like seawater. However, it is sufficient for most general-purpose applications.
Formability
5052 Aluminum: Highly formable, making it suitable for complex shapes and intricate designs. It can be easily bent, stamped, and shaped without cracking.
6061 Aluminum: Has fair formability, more suitable for simpler shapes. It can be formed and bent, but requires larger bend radii and more care to avoid cracking.
Budget Constraints
5052 Aluminum: Generally more affordable than 6061, making it a cost-effective choice for projects with tight budget constraints or where the superior properties of 6061 are not necessary.
6061 Aluminum: Typically more expensive due to its higher strength and versatility. The cost difference can be justified by its enhanced mechanical properties and suitability for a broader range of applications.
Environmental Conditions
5052 Aluminum: Ideal for environments with high humidity, saltwater exposure, or other corrosive conditions. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures long-lasting performance in these settings.
6061 Aluminum: Suitable for a wide range of environments but may require protective coatings or treatments in highly corrosive conditions. It performs well in most general environments and is often used in structural applications.
Required Mechanical Properties
Tensile Strength
5052 Aluminum: Offers moderate tensile strength, adequate for many applications but not suitable for high-stress structural uses.
6061 Aluminum: Provides higher tensile strength, making it suitable for applications where higher load-bearing capacity is required.
Yield Strength
5052 Aluminum: Lower yield strength compared to 6061, which may limit its use in applications where deformation resistance is critical.
6061 Aluminum: Higher yield strength, suitable for components that must maintain their shape and integrity under stress.
Hardness
5052 Aluminum: Has lower hardness, which makes it easier to work with but less suitable for wear-resistant applications.
6061 Aluminum: Higher hardness, providing better wear resistance and durability for applications that involve friction or impact.
By carefully assessing these factors, you can select the aluminum alloy that best meets the specific needs of your project, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both 5052 and 6061 aluminum alloys offer distinct advantages depending on the application. 5052 is preferable for projects requiring excellent corrosion resistance and formability, while 6061 is ideal for applications demanding higher strength and better machinability.
Understanding these differences ensures the selection of the right alloy for your specific needs, leading to optimal performance and longevity of the final product.
Achieve Perfect Products with Unionfab
Selecting the right aluminum alloy is crucial for your project's success. Unionfab leverages advanced aluminum materials to bring your designs to life.
At Unionfab, we provide a wide range of essential services, including CNC machining and finishing to ensure your products meet higher standards.
Contact us today to learn more about our offerings and how we can help you achieve perfect results.


