Exploring Electron Beam Melting: Process and Applications

Discover the revolutionary Electron Beam Melting (EBM) technology in additive manufacturing, exploring its process, benefits, applications, and future potential.
Introduction
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has transformed the manufacturing landscape by enabling the creation of complex geometries and custom parts with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Among the various additive manufacturing techniques, Electron Beam Melting (EBM) stands out for its unique capabilities and applications in high-performance industries.
What is Electron Beam Melting
Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is an advanced additive manufacturing technique that uses a high-energy electron beam to selectively melt and fuse metallic powders layer by layer, building up a three-dimensional object from a digital model.
This process takes place in a high-vacuum environment, ensuring the purity and integrity of the finished part.
Comparison of Additive Manufacturing Technologies: EBM vs. SLM vs. SLS
Feature | EBM | SLM | SLS |
|---|---|---|---|
Energy Source | Electron beam | Laser | Laser |
Environment | High vacuum | Inert gas | Controlled atmosphere |
Heat Management | Preheating reduces stress | Higher residual stresses | Minimal preheating |
Material Suitability | High-temp metals | Various metals | Plastics, ceramics, metals |
Build Speed | Faster | Slower | Medium |
Material State | Full melting | Full melting | Sintering |
Surface Finish | Rougher | Smoother | Smoother |
Mechanical Properties | Superior | High | Lower |
Part Size | Smaller | Variable | Larger |
Applications | Aerospace, medical | General metal parts | Prototyping, functional parts |
Technical Insights
Electron Beam Generation
Electron Beam Generation involves several key steps: an electron gun with a tungsten filament emits electrons through thermionic emission when heated, an electric field accelerates these electrons towards the anode, electromagnetic lenses focus the electron beam to a fine point, and magnetic coils deflect the beam to target specific areas of the powder bed.
Interaction with Material
Interaction with the material involves the powder absorbing the kinetic energy of electrons, causing localized heating and melting; the high energy density of the beam leads to rapid melting and solidification of the powder, forming a solid part layer by layer, while effective heat distribution and rapid cooling rates impact the microstructure and mechanical properties of the finished part.
The Electron Beam Melting Process
Source: 3dprintingindustry.com
Detailed explanation of the EBM process
Step 1. Preparation of the build platform
Preparing the build platform involves ensuring it is clean and free of contaminants, followed by evenly spreading a thin layer of metal powder across the surface.
Step 2. Layer-by-layer powder melting
In layer-by-layer powder melting, each new layer of powder is spread after the previous layer is melted, and the electron beam selectively melts the powder according to the digital model, ensuring precise construction layer by layer.
Step 3. Electron beam generation and control
Electron Beam Generation and Control involve the electron gun generating a focused beam of electrons, while electromagnetic lenses and deflection coils precisely control the beam's position and focus to ensure accurate melting.
Step 4. In-process monitoring and quality control
In-Process Monitoring and Quality Control involve real-time monitoring of the melting process using sensors and cameras, while systems track build parameters and adjust the process to ensure high-quality output.
Key components and machinery used in EBM
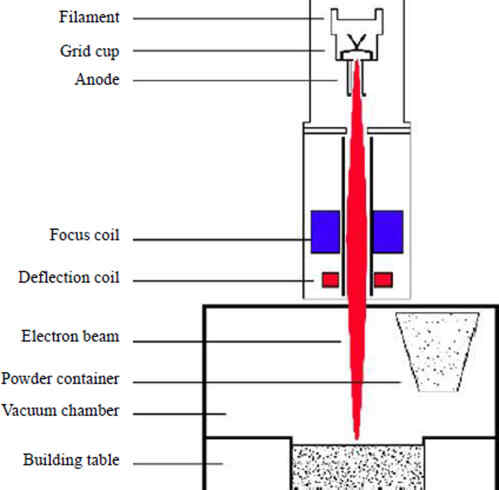
Source: sciencedirect.com
Electron Gun: Generates the electron beam.
Electromagnetic Lenses: Focus the beam.
Deflection Coils: Control the beam's direction.
Vacuum Chamber: Maintains a high-vacuum environment.
Powder Dispenser: Spreads the metal powder layers.
Build Platform: Supports the part being built.
Monitoring Systems: Track and control the build process in real-time.
Advantages of Electron Beam Melting
High Precision and Accuracy: EBM offers exceptional precision and accuracy, allowing for the creation of parts with intricate details and tight tolerances.
Ability to Create Complex Geometries: The layer-by-layer approach enables the production of complex geometries, including internal structures and undercuts, that are challenging to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Material Efficiency and Minimal Waste: EBM is highly material-efficient, using only the necessary amount of powder for each part and reducing waste compared to subtractive manufacturing processes.
Superior Mechanical Properties of EBM-Produced Parts: Parts produced with EBM exhibit superior mechanical properties, including high strength and durability, due to the fine microstructure and strong metallurgical bonds formed during the process.
Challenges and Limitations
High Initial Investment Cost: EBM systems require significant upfront investment due to complex technology and high operational costs.
Technical Challenges: Residual stresses and limited part size are common technical issues in EBM. Achieving smooth surface finishes often requires additional post-processing.
Material Constraints and Availability: EBM primarily works with high-melting-point metals, limiting material options compared to other technologies. Availability and cost of suitable metal powders can be prohibitive for some applications.
Comparison with Other Technologies: Compared to Selective Laser Melting (SLM), EBM offers superior mechanical properties but may have slower build times and higher costs. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses a broader range of materials but typically produces parts with lower mechanical strength and precision.
Applications of Electron Beam Melting
Aerospace industry
In the aerospace industry, Electron Beam Melting (EBM) enables the production of high-strength, lightweight turbine blades with intricate cooling channels, enhancing performance and efficiency.
EBM also benefits aerospace structural components by creating complex geometries and providing high mechanical strength, thereby improving aircraft performance and durability.
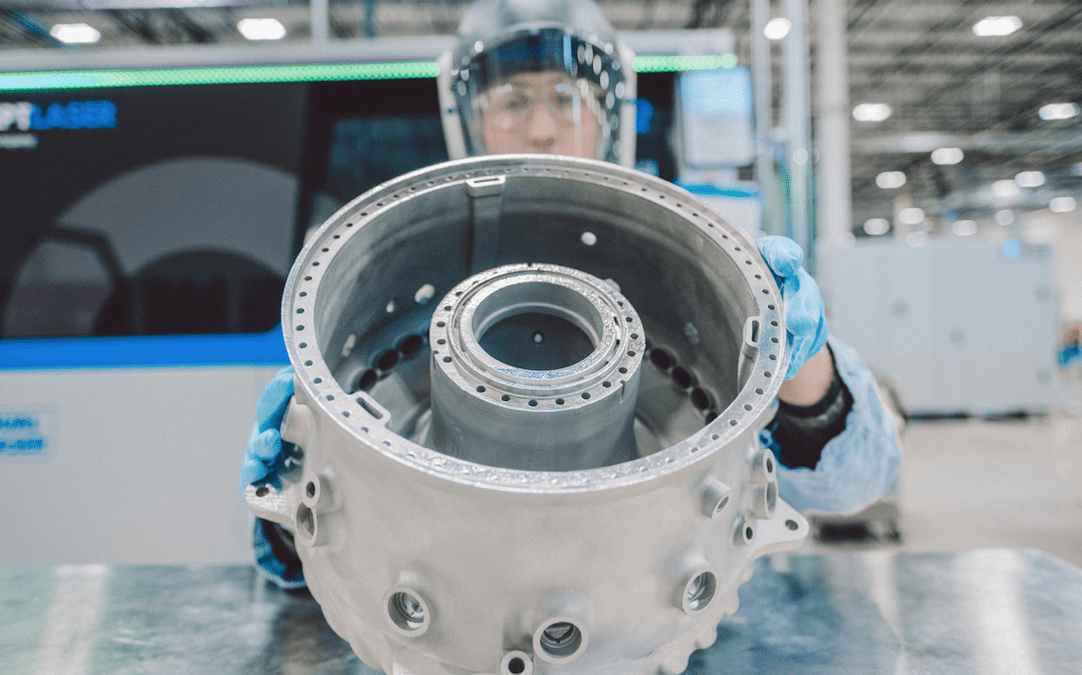

Source: geaerospace.com
Medical field
In the medical field, Electron Beam Melting (EBM) produces custom orthopedic implants with tailored designs for patient-specific applications, ensuring better fit and integration.
EBM's precise manufacturing capabilities also enable the production of durable and biocompatible dental prosthetics, improving patient comfort and longevity in dental applications.
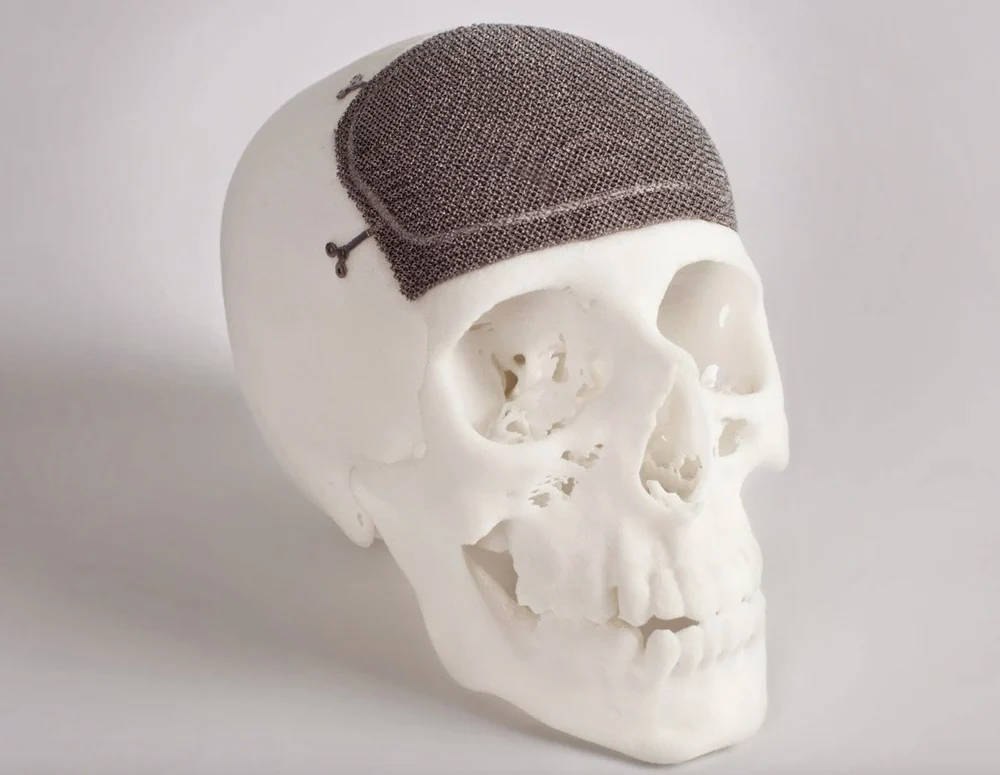

Source: Custom Cranio-Maxillofacial implant
Automotive industry
In the automotive industry, Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is utilized to manufacture lightweight components such as engine parts and structural elements, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
EBM also supports automotive manufacturers in prototyping and producing custom parts, accelerating design iterations and reducing time to market.

Source: Additive Manufacturing Media via Youtube
Research and development
In research and development, Electron Beam Melting (EBM) enables rapid prototyping of complex designs, facilitating quick iteration and validation across various industries.
Additionally, research institutions and industries utilize EBM to create custom parts with unique geometries and material properties, supporting innovation and specialized applications.
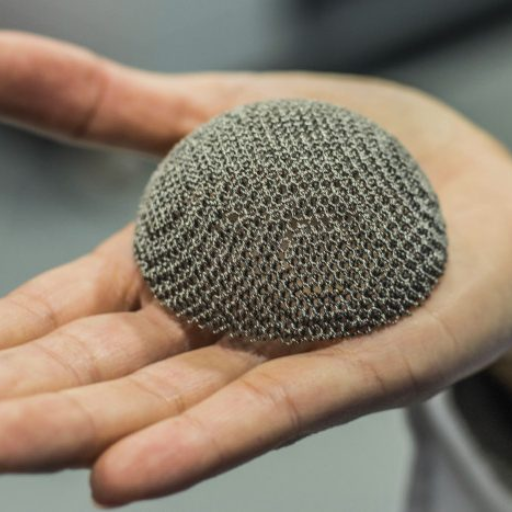

Source: blog.goldsupplier.com
Future Trends and Developments
Innovations in EBM Technology
Continuous innovations aim to enhance precision, speed, and quality. Advancements in electron beam systems promise faster scans and improved control over build parameters, aiming to minimize residual stresses and optimize part production.
Emerging Materials for EBM
Future developments will expand EBM's material compatibility beyond traditional metals like titanium and nickel alloys. Research focuses on new alloys and composites with superior mechanical properties and biocompatibility, opening new possibilities in aerospace, medical, and other specialized industries.
Potential Industry Impact
EBM could revolutionize industries by enabling the production of lightweight, complex parts with high strength. In aerospace, this means improved fuel efficiency and performance.
Medical applications benefit from personalized implants, while automotive industries benefit from rapid prototyping and custom part production, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Predictions for EBM in Manufacturing
With ongoing advancements in materials and processes, EBM's adoption is expected to grow. It may expand from prototyping to mainstream production, offering on-demand manufacturing, reduced lead times, and minimized material waste.
EBM is poised to play a crucial role in additive manufacturing, enhancing production efficiency and meeting diverse manufacturing needs.
Conclusion
Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is advancing additive manufacturing with its ability to create precise, high-strength parts efficiently.
Despite initial challenges, ongoing innovations in EBM technology and materials are expanding its applications in aerospace, medical, automotive, and research sectors.
EBM's potential to streamline production, minimize waste, and foster innovation positions it as a key player in the future of manufacturing.
Advancing Manufacturing: Unionfab's EBM Capabilities
Unionfab offers precise and efficient additive manufacturing solutions. Specializing in automotive, medical, and industrial applications, Unionfab integrates 3D printing with advanced CNC Machining for superior production outcomes.
Contact us today to discover how Unionfab can enhance your manufacturing efficiency with state-of-the-art EBM technology!

