Vapor Polishing: Achieve a Seamless Surface Finish

This article explores what vapor polishing is, how it works and the benefits it can offer for your 3D prints.
Introduction
Vapor polishing, akin to polypropylene's versatility, is a key technique for refining 3D printed objects.
This article explores its mechanics, including molecular dynamics and precise temperature control, and highlights its transformative potential across industries.
Science of Vapor Polishing
Molecular Dynamics of Polymers
- Polymers Structure: Polymers like PLA are composed of long chains of repeating molecules, arranged in a particular structure.
- Solvent Interaction: When exposed to a solvent vapor, the molecules in the polymer chains can temporarily break down due to the interaction with the solvent.
- Flow and Reform: This breakdown allows the material to flow and reform when the solvent evaporates, resulting in a smoother surface by filling in imperfections and irregularities.
Solvent Action Principles
- Affinity: The choice of solvent is crucial as it needs to have a strong affinity for the polymer being treated, ensuring effective dissolution of the surface layer.
- Surface Layer Dissolution: The solvent acts selectively on the surface layer of the printed part, dissolving it without compromising the structural integrity of the underlying material.
Temperature and Pressure Dynamics
- Temperature Control: Higher temperatures within the vapor polishing chamber accelerate the action of the solvent, facilitating the dissolution and reformation of the polymer chains.
- Pressure Uniformity: Maintaining consistent pressure across the chamber ensures uniform treatment of the entire surface of the part, preventing uneven results or incomplete polishing.
Mechanics of Vapor Polishing
Essential Equipment
- Sealed chamber: A typical setup includes a sealed chamber to contain the vaporized solvent.
- Reservoir of solvent: A supply of the chosen solvent, such as dichloromethane or tetrahydrofuran (THF), is necessary.
- Heating elements: These are used to elevate the temperature within the chamber to facilitate solvent action.
- Controls: Systems for regulating temperature and pressure ensure precise treatment conditions.
Setup Procedures
Step 1. Cleaning
The printed part must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any debris or contaminants.
Step 2. Suspension
The part is then suspended within the chamber, ensuring adequate exposure to the solvent vapor.
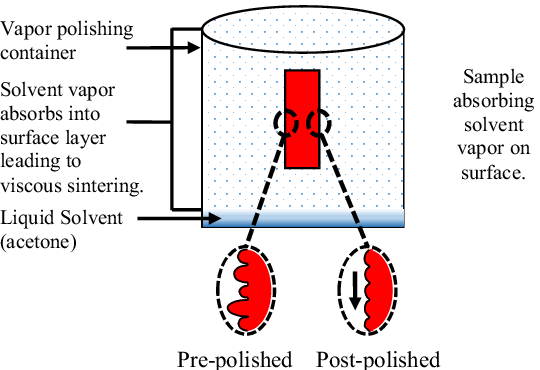
Source: researchgate.net
Step 3. Temperature and pressure adjustment
Parameters are set according to the specific requirements of the material and desired finish.
Temperature Control
Maintaining precise temperature control is crucial to the success of vapor polishing.
For PLA, temperatures typically range between 50°C to 70°C to achieve optimal results.
Solvent Selection
Different polymers require different solvents for effective vapor polishing.
For PLA, commonly used solvents include dichloromethane and tetrahydrofuran (THF), each with its own advantages and safety considerations.
Safety Considerations
Vapor polishing should be conducted in a well-ventilated environment, preferably with proper personal protective equipment (PPE).
Solvents used in the process can be hazardous and should be handled with care to avoid exposure.
Vapor Polishing PLA
Properties and Characteristics of Vapor Polishing PLA
- Biodegradability and Ease of Use: PLA is a preferred filament in 3D printing due to its environmentally friendly nature and user-friendly properties.
- Glossy, Smooth Finish: Vapor polishing PLA results in a surface with a glossy and smooth texture, significantly enhancing its aesthetic appeal.
- Suitability for Appearance-Critical Applications: The enhanced finish makes vapor-polished PLA suitable for applications where appearance matters, such as consumer products or prototypes.
Challenges and Solutions in Vapor Polishing PLA
- Inconsistent Results and Surface Irregularities: Vapor polishing PLA can sometimes lead to inconsistent results or surface irregularities, impacting the overall finish.
- Optimization of Parameters: By adjusting process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and exposure time, thi process can be optimized to overcome challenges and achieve consistent, desired outcomes.
Comparison with Vapor Polishing ABS
- Less Aggressive Solvents and Lower Temperatures: PLA typically requires less aggressive solvents and lower temperatures compared to ABS for effective process.
- Smoother Finishes with Less Warping: Vapor polished PLA tends to yield smoother finishes with minimal risk of warping or distortion, making it a preferred choice for certain applications where surface quality is critical.
Benefits of Vapor Polishing
Smooth Finish and Surface Quality
- Uniform, Glossy Surface: Vapor polishing produces a uniform, glossy surface finish on 3D printed parts, enhancing their visual appeal.
- Hide Layer Lines and Imperfections: The process effectively hides layer lines and imperfections present in the printed part, resulting in a smoother, more professional-looking end product.
Strength and Durability Enhancement
- Fusing Polymer Chains: Vapor polishing can strengthen the surface of printed parts by fusing the polymer chains together.
- Increased Durability and Mechanical Strength: This fusion process increases the overall durability and mechanical strength of the object, making it more resistant to wear and tear.
Time and Cost Efficiency
- Faster Process: Compared to traditional post-processing methods like sanding or coating, vapor polishing offers a faster solution for achieving a smooth finish.
- Reduced Manual Labor: It reduces the need for manual labor-intensive processes, saving time and labor costs.
- Minimal Secondary Treatments: There is less reliance on expensive secondary treatments, leading to overall cost savings in the production process.
Applications of Vapor Polishing
Medical Instruments
- Hygiene and Functionality: In the production of medical instruments and devices, smooth surfaces are essential for maintaining hygiene and ensuring proper functionality.
- Common Use: The method is commonly employed in the medical industry to achieve the required smoothness and cleanliness standards for these instruments.
- Enhanced Performance: The smooth finish improves the usability and cleanliness of medical instruments, contributing to better patient outcomes.
Microfluidic Devices
- Surface Quality Improvement: This techinique is utilized to improve the surface quality of 3D printed microfluidic components.
- Performance Enhancement: By refining the surface finish, vapor polishing enhances the performance and reliability of microfluidic devices.
- Critical for Fluid Flow: Smooth surfaces are crucial in microfluidic devices to ensure the efficient flow of fluids through tiny channels and chambers, minimizing friction and improving accuracy.
Optical Components
- Stringent Requirements: Optical components have stringent requirements for surface smoothness to minimize light scattering and ensure clarity.
- Refined Surfaces: This method is employed to refine the surfaces of 3D printed optical components, ensuring they meet these strict requirements.
- High-Quality Output: The process results in high-quality optical components suitable for applications where precision and clarity are paramount, such as in lenses, prisms, and mirrors.
Conclusion
Vapor polishing is a versatile and effective post-processing technique for enhancing the surface quality of 3D printed parts, particularly those made from PLA.
By understanding the science and mechanics behind this finishing method, manufacturers can achieve smooth, polished finishes that meet the demands of various industries and applications.
Achieve Perfect Finishing at Unionfab
At Unionfab, we specialize in offering a range of advanced
finishing solutions, including vapor polishing services, to ensure high-quality surface finishes for your projects.
Additionally, we provide diverse CNC Machining solutions for our clients. Feel free to Contact Us for further details.


