HDPE vs. Polypropylene: A Comprehensive Comparison
By examining hdpe and polypropylene's properties, advantages, and common uses, readers will gain a clear understanding of these materials.
Introduction
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Polypropylene (PP) are both common plastics, but with key differences.
HDPE is denser, making it stronger and more rigid for things like pipes and jugs. It's also generally more flexible at lower temperatures.
Polypropylene, lighter and more moldable, is ideal for packaging, textiles, and parts that need to withstand higher heat.
HDPE vs. Polypropylene (PP): Chemical Composition and Structure
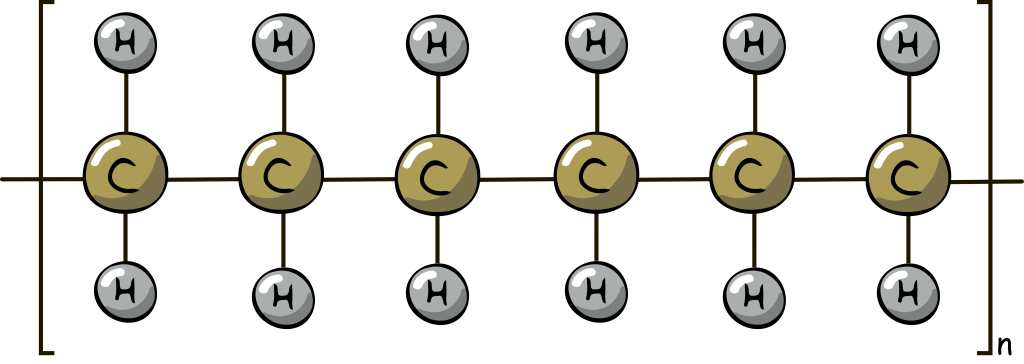
HDPE's Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure
Source: entecpolymers.com
Chemical Composition: (C2H4)n
Molecular Structure: Linear, non-branched hydrocarbon chain
Explanation
(C2H4)n represents a repeating unit of two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms.
The 'n' signifies a long chain of these repeating units, giving HDPE its high density.
The linear, non-branched structure allows for tight packing of molecules, leading to strength and rigidity.
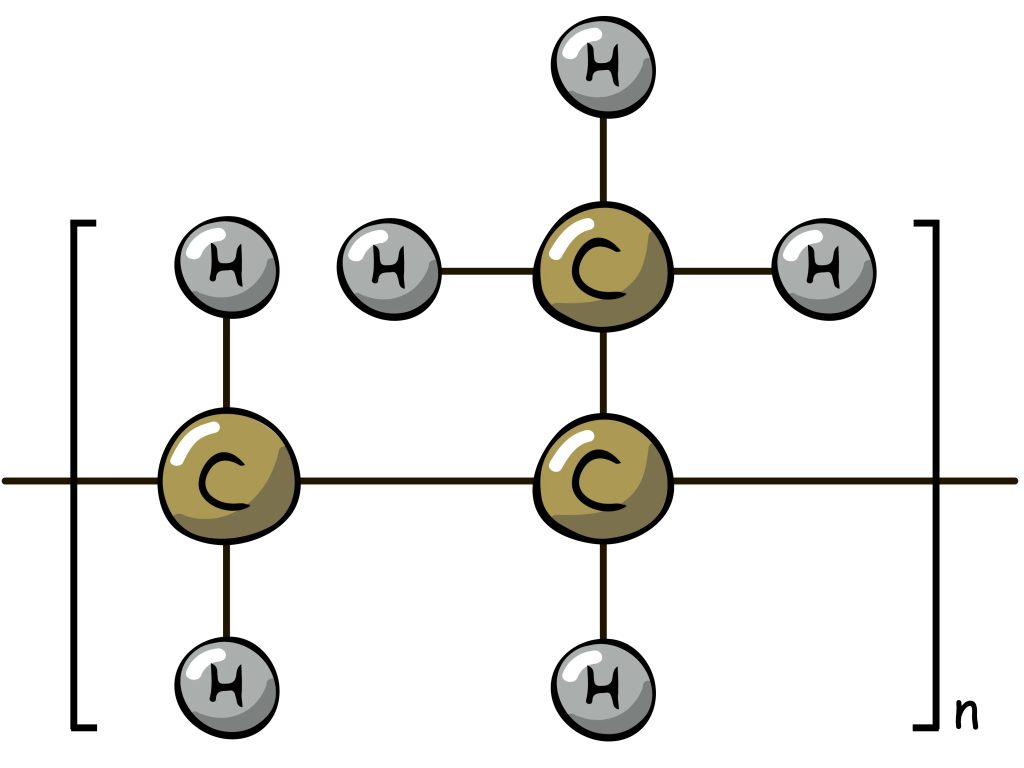
Polypropylene's Chemical Composition and Molecular Structure
Source: ik.imagekit.io
Chemical Composition: (C3H6)n
Molecular Structure: Semi-crystalline, slightly branched hydrocarbon chain
Explanation
(C3H6)n represents a repeating unit of three carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
Similar to HDPE, 'n' signifies a long chain of these repeating units.
The presence of methyl groups (CH3) creates slight branching in the chain.
This branching reduces packing density compared to HDPE, but enhances flexibility and heat resistance.
HDPE vs. Polypropylene (PP): Physical and Mechanical Properties
Property | HDPE | PP |
|---|---|---|
Density (g/cm³) | 0.92 - 0.96 | 0.85 - 0.90 |
Weight | Heavier for same volume | Lighter for same volume |
Tensile Strength | Good | Good (lower than HDPE) |
Durability | High | Moderate |
Flexibility | More flexible (esp. at low temp) | Stiffer, more rigid |
Rigidity | Lower | Higher |
Temperature Resistance (°C) | Lower melting point (130-137) | Higher melting point (160) |
Heat Resistance | Good at moderate temperatures | Better for hot liquids/sterilization |
Impact Resistance | Good (esp. at low temp) | Lower (can be improved with modification) |
HDPE vs. Polypropylene (PP): Manufacturing and Processing
Polymerization Process
Both HDPE and PP are manufactured through a process called polymerization, but with slight variations.
Similarities
Both HDPE and PP are produced via Ziegler-Natta catalysis, a type of coordination polymerization.
This process uses a catalyst to link together ethylene (C2H4) monomers for HDPE and propylene (C3H6) monomers for PP, forming long chains.
Differences
The specific catalyst used and reaction conditions can be tailored to influence the properties of the final product.
For example, variations in the polymerization process can affect the degree of branching in PP, impacting its flexibility and heat resistance.
CNC Machining
HDPE
Offers good machinability due to its flexibility and lower melting point. However, it can generate more chips and require careful tool selection to avoid overheating and melting.
Polypropylene (PP)
Generally more challenging to machine due to its rigidity and higher melting point. Special techniques like cryogenic machining (using very low temperatures) can improve machinability of PP.
3D Printing
HDPE
Can be challenging to print due to warping and curling tendencies. Filament with additives can improve printability.
Polypropylene (PP)
Generally considered easier to print than HDPE with less warping. However, it requires proper temperature settings to avoid stringing and ensure good layer adhesion.
Injection Molding
Both HDPE and PP are well-suited for injection molding due to their good melt flow properties.
HDPE requires slightly lower processing temperatures compared to PP due to its lower melting point. Additionally, mold design needs to account for the potential shrinkage of HDPE during cooling.
HDPE vs. Polypropylene (PP): Common Applications
Industrial Uses
HDPE
Pipes and Tubes: HDPE's strength and flexibility make it a popular choice for pressure pipes for water, gas, and sewage. It's also used for drainage pipes, irrigation systems, and conduit for electrical wiring.

Source: shandongsiffo.en.made-in-china.com
Chemical Tanks and Containers: HDPE's excellent chemical resistance makes it suitable for storing and transporting various chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents.

Source: aliexpress.com
Geomembranes: Large sheets of HDPE are used as geomembranes for lining landfills, ponds, and canals due to their impermeability and durability.

Source: earthshields.com
Polypropylene (PP)
Fibers and Textiles: Polypropylene is a major component of synthetic fibers used in carpets, clothing (like fleece), and ropes due to its lightweight nature and good strength.

Source: palmetto-industries.com
Films and Sheets: PP films are used for food packaging, wrapping materials, and industrial applications like strapping and bundling. Its clarity and printability make it versatile for packaging.

Source: sdzlplastic.com
Automotive Parts: PP's lightweight and moldable properties make it ideal for various automotive parts like bumpers, interior trim panels, and battery cases.

Source: made-in-china.com
Consumer Product Applications
HDPE
Bottles and Jugs: HDPE's strength and clarity make it a preferred material for milk jugs, detergent bottles, and other containers requiring good chemical resistance.

Source: aaronpackaging.com
Food Storage Containers: HDPE's flexibility allows for containers with lids that snap shut, making them ideal for reusable food storage containers.

Source: indiamart.com
Toys: Some toys, particularly outdoor playthings, can be made from HDPE due to its durability and impact resistance.

Source: Fceat.com
Polypropylene
Storage Containers: PP's rigidity and chemical resistance make it suitable for reusable food containers and storage bins.
Cutlery and Utensils: Lightweight and disposable PP utensils are commonly used for picnics and takeout meals.

Source: mdsassociates.com
Stationery and Office Supplies: PP is used for binders, folders, and other office supplies due to its durability and flexibility.

Source: temu.com
HDPE vs. Polypropylene (PP): Considerations When Using
Selection Criteria Based on Application
Strength and Durability
If the application demands high load-bearing capacity or impact resistance, HDPE's strength might be preferable. For applications requiring flexibility and some give, PP can be suitable.
Temperature Resistance
Consider the operating temperatures involved. HDPE might be better for moderate temperatures, while PP excels in high-heat environments.
Weight Considerations
If weight is a critical factor, PP's lighter weight might be advantageous.
Transparency or Clarity
HDPE offers better clarity for applications requiring visibility, while PP is typically translucent.
UV Resistance
If the product will be exposed to sunlight for extended periods, HDPE's inherent UV resistance is better. PP often requires UV additives for outdoor use.
Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Constraints
Material Cost
HDPE and PP generally have comparable costs, but slight variations can exist depending on market conditions and specific grades.
Processing Costs
HDPE might require slightly lower processing temperatures for techniques like injection molding, potentially leading to some cost savings. However, the complexity of the application and production volume also play a role.
Long-Term Considerations
Factor in the expected product lifespan and potential replacement costs. HDPE's excellent durability can be a cost advantage in applications requiring long-term performance.
Material Performance Requirements
Flexibility
If flexibility is a key requirement, HDPE's ability to bend without breaking might be crucial. PP, with its rigidity, might not be suitable in such cases.
Transparency
HDPE offers good clarity, making it a preferred choice for applications where visibility is important, like food containers.
Impact Resistance
HDPE exhibits good impact resistance, especially at lower temperatures.
Long-Term Performance and Maintenance
Environmental Factors
HDPE's inherent UV resistance makes it a good choice for outdoor applications without needing additional protection. PP often requires UV additives for extended outdoor use.
Chemical Exposure
HDPE is a good choice for storing many common household cleaning products like bleach, detergents, and some disinfectants due to its inherent chemical resistance.
PP might not be suitable for some harsh chemicals like concentrated bleach or strong acids. It's best to check the MSDS of the specific chemical for compatibility with PP.
Conclusion
HDPE and PP, while sharing some similarities, offer distinct advantages for various applications. When making your choice, consider factors like required strength, temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, weight limitations, and budget constraints.
HDPE excels with its strength, flexibility, and inherent UV resistance, making it ideal for pipes, bottles, and outdoor applications.
PP shines with its lightweight nature, rigidity, and good heat resistance, finding use in packaging, textiles, and parts requiring dimensional stability.
Achieve Perfet Products with Unionfab
Beyond various materials like HDPE and PETG, Unionfab offers a range of manufacturing services, including 3D Printing, CNC machining, [vacuum casting](Vacuum Casting/Silicone Molding/Urethane Casting Services | Unionfab), and more.
By partnering with Unionfab, you gain access to expertise, diverse capabilities, and commitment to quality. From concept to completion, we can help you achieve "perfect products" that meet your specific needs.


