3D Printed Prosthetics: Innovations in Rehabilitation

Check out this article on how 3D printing prosthetics are made and what are the most common used 3d printed prosthetics in life.
Introduction
Prosthetics have long been crucial to individuals with limb loss. However, traditional prosthetics can be expensive, time-consuming to create, and often lack a perfect fit.
3D printing is transforming the creation of prosthetics, offering exciting innovations that are making rehabilitation more effective, accessible, and personalized than ever before.
What Are 3D Printed Prosthetics
Explanation of 3D Printed Prosthetics
3D printed prosthetics are artificial limbs created using a special 3D printing technology called additive manufacturing.
Unlike traditional prosthetics that are carved or molded from rigid materials, 3D printed ones are built layer by layer based on a digital design. This allows for a much more precise and customized approach to creating prosthetics.
Definition and Components of Prosthetics
Prosthetics Defined
Prosthetics are artificial limbs designed to replace a missing limb due to amputation, birth defect, or injury.
They can range from simple devices for basic functionality to complex, technologically advanced limbs that can restore a high degree of movement and control.
Components of a Prosthetic
A typical prosthetic limb consists of three main parts:
- Socket: This component interfaces with the residual limb (the remaining part of the limb) and provides a secure and comfortable fit.
- Pylon: The pylon is a rigid structure that connects the socket to the artificial limb itself. It can be made of various materials like metal or carbon fiber.
- Terminal Device: This is the artificial hand, foot, or other body part that replaces the missing limb.
Common 3D Printed Prosthetics Limbs
The revolution of 3D printing in prosthetics extends to all three major limb replacements: hands, arms, and legs.
3D Printed Prosthetics Hand
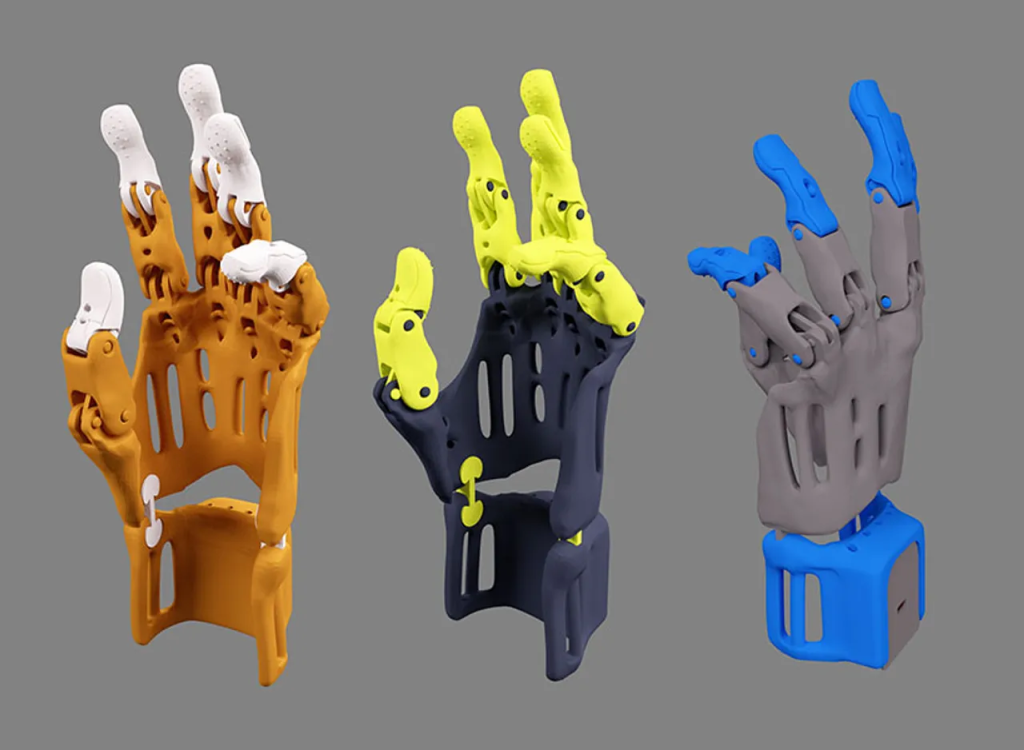

Source: printables.com
Functionality
These hands range from basic designs for gripping and grasping objects to more advanced models with multiple, individually controlled fingers. Some even integrate sensors that detect muscle contractions for intuitive control.
Customization
3D printing allows for customization of finger length, flexibility, and even the inclusion of cosmetic features like fingernails.
Applications
These hands can be used for daily activities like eating, dressing, and writing. Advanced models can even handle more complex tasks like using tools or playing sports.
3D Printed Prosthetics Arm
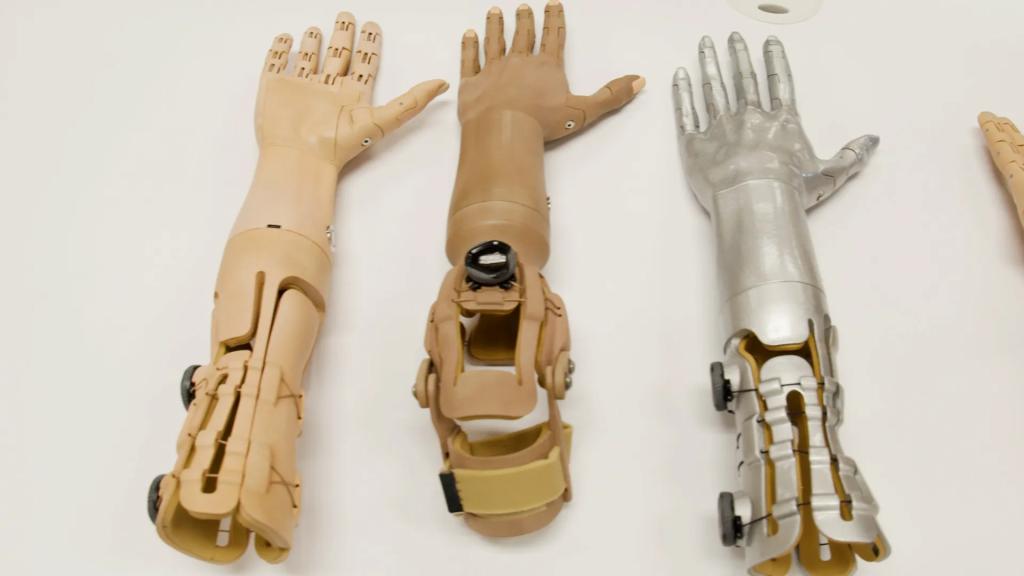

Source: thehill.com
Design
Arms can be printed with different levels of complexity, from simple above-elbow designs to full prosthetic arms with elbows and wrists.
Integration
3D printing allows for seamless integration of sockets and prosthetic components, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit.
Functionality
Basic arms may focus on providing support and stability, while advanced models can incorporate motors and gears for elbow and wrist movement, significantly improving functionality.
3D Printed Prosthetics Leg
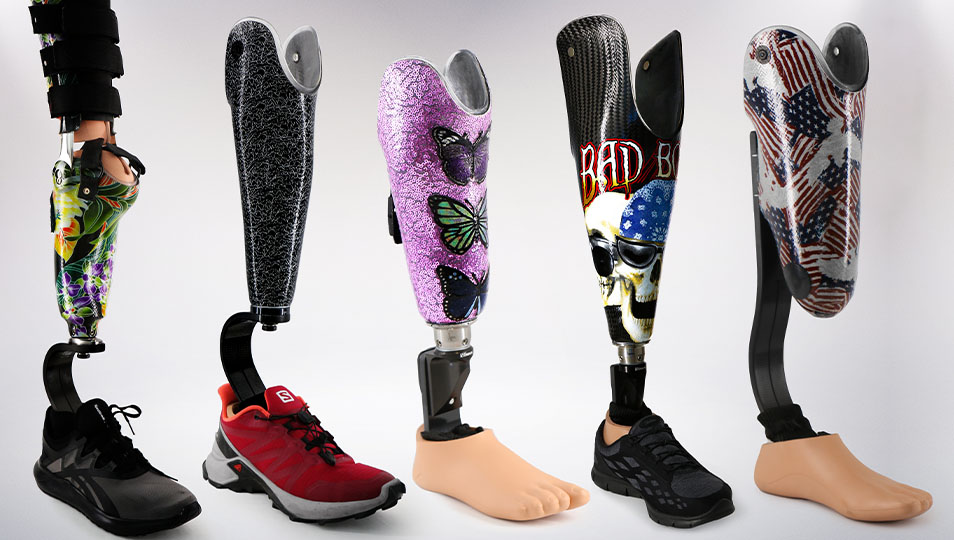
Source: nassit.org
Customization
3D printing allows for tailoring the leg to the specific needs of the patient, accommodating different levels of amputation and weight distribution.
Weight and Comfort
3D printed materials can be lightweight and strong, making the leg comfortable for extended wear.
Functionality
These legs can range from basic designs for walking to more advanced models with features like adjustable ankle joints and variable stiffness for different terrains.
How to Make 3D Printed Prosthetics
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) Modeling
The first step involves creating a digital blueprint of the prosthetic. This is done using CAD software, where a 3D model is meticulously designed based on:
- Patient Scans: 3D scans of the residual limb are taken to ensure a perfect fit and comfortable socket design.
- Functionality Needs: The design is tailored to the specific needs of the patient, considering the desired level of functionality and range of motion.
- Customization: The model can be customized for aesthetics, incorporating color variations or even integrating cosmetic features.
Material Selection
The choice of material for 3D printing a prosthetic is crucial. Here are some common options:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A durable and affordable plastic, often used for basic prosthetic components.
- Nylon: Offers greater flexibility and strength compared to ABS, suitable for some prosthetic parts.
- PEEK (Polyetheretherketone): A high-performance material known for its strength, lightweight nature, and biocompatibility, ideal for advanced prosthetics.
Printing Techniques for Prosthetic Production
Several 3D printing techniques can be used, each with its own advantages:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): The most common method, using a heated filament to build the prosthetic layer by layer.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Creates strong and lightweight parts by sintering powdered materials with a laser.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Offers high-resolution printing for intricate prosthetic components, using a liquid resin cured by a laser.
Post-Processing
Once printed, the prosthetic components may require additional finishing touches such as:
- Support Removal: Removing any temporary support structures used during printing.
- Smoothing and Finishing: Sanding or polishing the printed parts for a smooth and comfortable fit.
- Coloring and Customization: Applying paint or other finishing touches for a personalized look.
Assembly of Prosthetic Components
Depending on the complexity of the design, the printed parts may need to be assembled with additional components. This could include:
- Liners: Soft inner layers for comfort and improved fit.
- Straps and Harnesses: Securing the prosthetic to the residual limb.
- Joints and Mechanisms: For advanced prosthetics with moving parts.
Advantages of 3D Printed Prosthetics
Customization and Personalization
Traditional prosthetics are often manufactured in standard sizes and configurations. 3D printing breaks this mold by enabling prosthetics to be precisely tailored to each individual's needs.
Through 3D scans and CAD software, prosthetics can be designed to perfectly match the wearer's residual limb, ensuring a comfortable and secure fit.
This level of customization extends beyond just fit. 3D printing allows for the incorporation of cosmetic features like skin tones or even fingernails, boosting confidence and self-image.
Cost-Effectiveness
3D printing offers a more streamlined approach. The digital design can be easily replicated, reducing production costs.
Additionally, 3D printing allows for less material waste due to precise design and on-demand printing capabilities. This translates to potentially lower costs for patients and prosthetics facilities.
Improved Functionality
Lighter materials can be used for complex internal structures, resulting in prosthetics that are strong yet comfortable to wear.
Advanced features like variable stiffness in prosthetic legs or multi-grip positions in hands can be incorporated during the design phase.
This improves the range of motion, dexterity, and overall functionality of the prosthetic limb.
Comfort
A well-fitting prosthetic is crucial for comfort. 3D printing's customization capabilities ensure a perfect fit, reducing pressure points and friction.
Lighter materials further enhance comfort, especially for long-term wear.
Additionally, 3D printing allows for integration of comfort features like padding or specially designed liners directly into the prosthetic during the printing process.
Accessibility and Scalability in Healthcare
3D printing technology has the potential to make prosthetics more accessible, particularly in remote areas.
With advancements in portable 3D printers and open-source designs, prosthetics can be potentially manufactured on-site at healthcare facilities.
This can significantly reduce waiting times and costs associated with traditional prosthetic manufacturing.
Conclusion
3D printing is revolutionizing prosthetics. From the intricate customization that empowers individuals to the potential for wider accessibility, 3D printed limbs are not only improving functionality but also transforming the lives of those who rely on them.
Unionfab Provides a Variety of 3D Printing Services
At Unionfab, we understand the need for flawless results. With a wide range of material options and expert 3D printing services, our team is dedicated to helping you unlock the full potential of 3D printing in various areas.


