3D Print Layer Shift: Definition and Solution
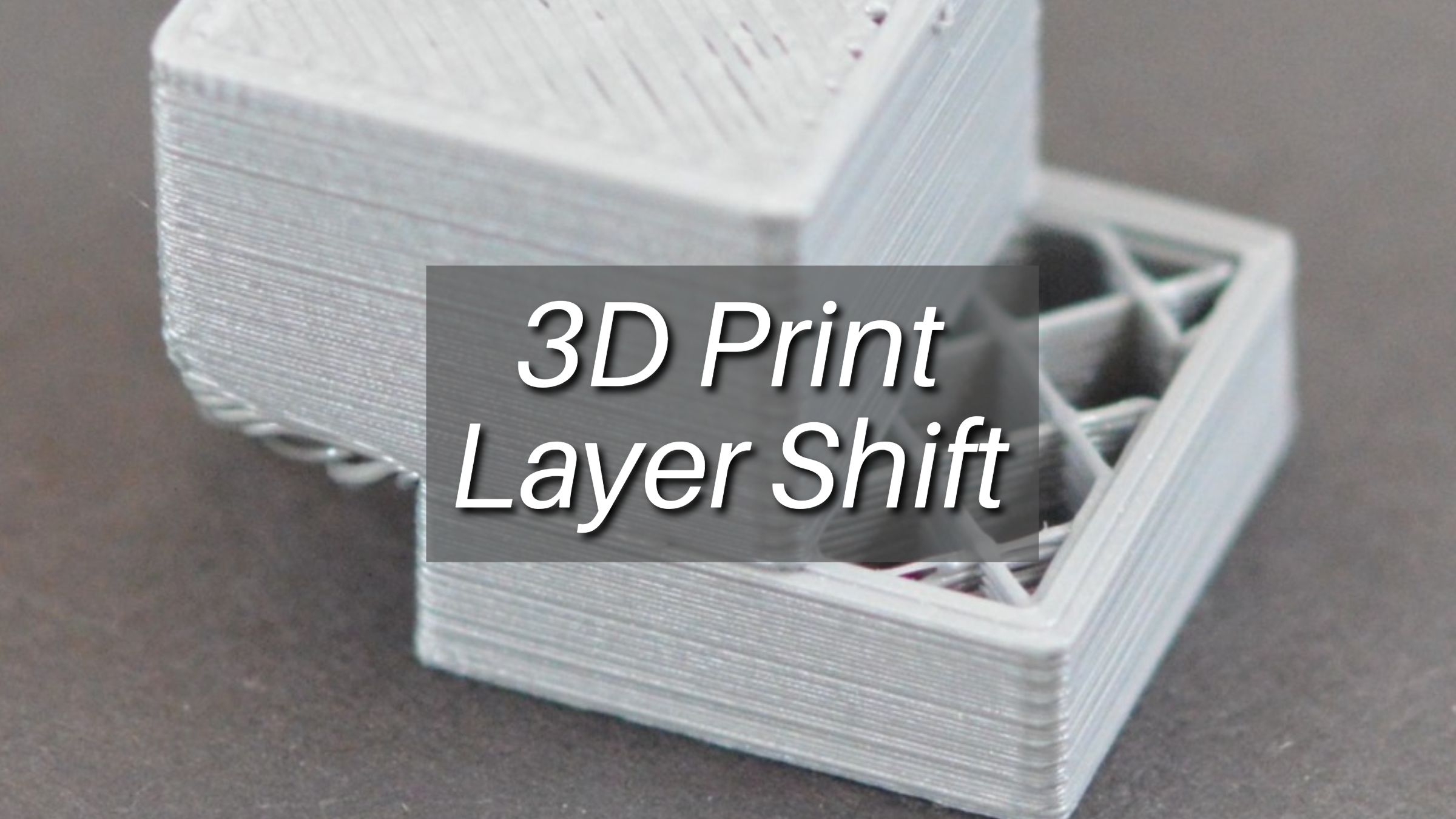
This article provides an overview of 3D print layer shift, including its causes, effects, troubleshooting methods, and prevention strategies.
Introduction
3D print layer shift refers to a situation where the layers of a 3D printed object are not properly aligned, causing the print to shift position horizontally or vertically during the printing process.
This misalignment can occur due to various reasons such as mechanical issues with the printer, software glitches, or external factors like vibrations or interference during printing. Layer shift can result in a skewed or distorted print, compromising its accuracy, structural integrity, and overall quality. Troubleshooting and fixing the underlying causes of layer shift are essential to ensure successful and precise 3D printing.
Source: matterhackers.com
Causes of 3D Print Layer Shift
Mechanical Causes
- Belt and Pulley Issues
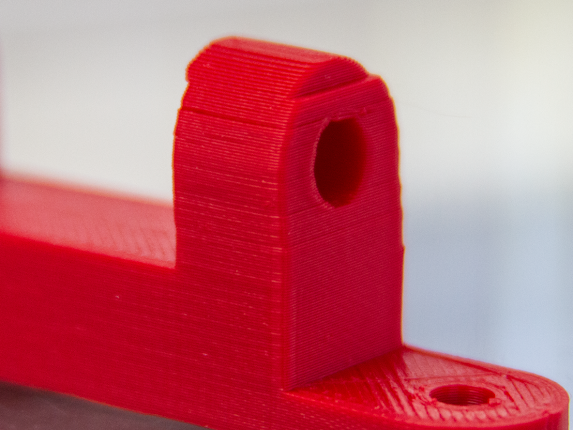
One of the primary mechanical causes of layer shift is related to the belts and pulleys of the 3D printer. If thebelts are not tight enough, there is insufficient tension to transfer movement accurately to the printheads, resulting inlayer shifts.
Similarly, pulleys that are not securely fastened can slip, especially the pulley on the stepper motor, leadingto misalignment. Regular maintenance, such as checking the tightness of belts and the security of pulleys, isessential to prevent these issues.\
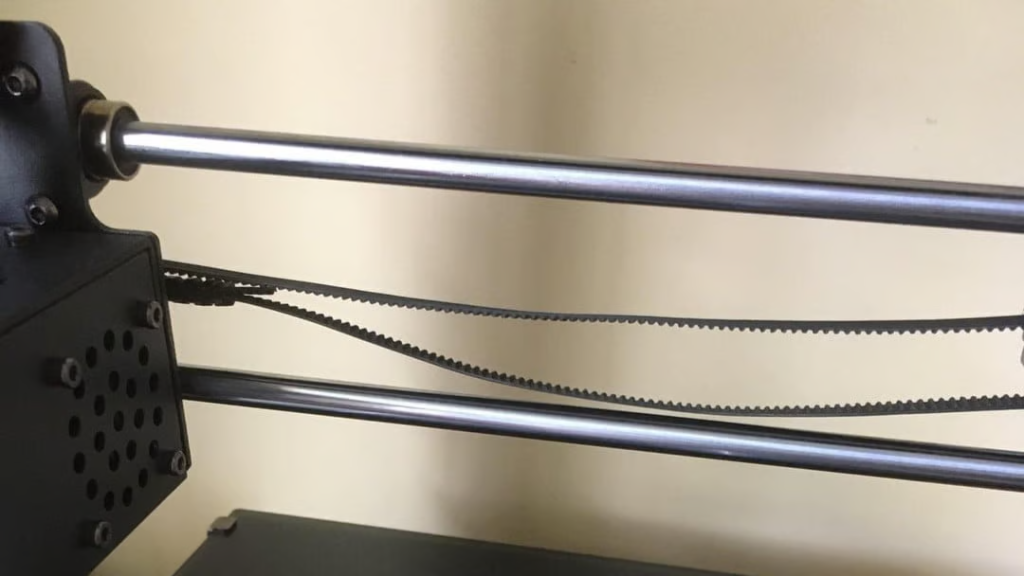

Source: Ohboibigbirdiscoming via Reddit
- Printer Stability
The stability of the 3D printer itself is another significant factor. Vibrations or bumps can cause the printer frame,which is generally sturdy and heavy to prevent shifting, to move unexpectedly. This instability can momentarily set theprint head off course, causing layers to shift. Ensuring the printer is on a stable surface and not subject to externalmovements is a key preventive measure.
- Print Head and Axis Movement
Abnormal movement of the X-axis and/or Y-axis, leading to misalignment of the extruder head mid-printing, is acommonly cited mechanical cause. Issues such as improper belt tension, loose axis pulleys, or the printer beingimproperly leveled and calibrated can contribute to these abnormal movements.
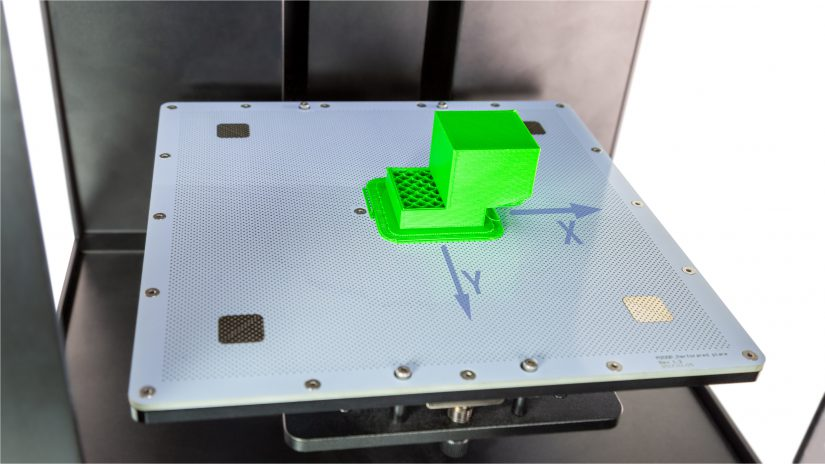
Source: zortrax.com
Electrical Causes
- Overheating Components
Overheating of stepper motor drivers and other electronic components can cause the motors to skip steps, leading tolayer shifts. This is often due to overworked or poorly cooled electronics. Ensuring adequate cooling andmonitoring the printer for signs of overheating are critical steps in addressing this issue.
- Motor and Electrical System Failures
While less common, failures within the motors or the electrical system (including cables, connectors, and driver chips)can also lead to layer shifting. These components may have high failure rates, and issues here can result inerratic movements and misaligned layers. Before replacing motors, it is advisable to thoroughly check these othercomponents.
Software Causes
- Incorrect Print Settings
Problems in the G-code or the slicing settings can cause defects in layer alignment. Issues with slicer software,incorrect settings, or corrupted files can lead to improper instructions for the printer, resulting in layer shifts.Adjusting the print settings and re-slicing the model can often resolve these issues.
- Calibration and Maintenance
Regular maintenance and proper calibration of the 3D printer are crucial in preventing layer shifts. This includesroutine checks of the belts, pulleys, print head, and motors, as well as ensuring the print bed is level and the printer iscalibrated correctly. Additionally, adjusting advanced settings like print speed and acceleration can help mitigatethe risk of layer shifting.
Diagnosing 3D Print Layer Shift
Diagnosing layer shift in 3D printing involves identifying the underlying causes that lead to the misalignment of layersduring the printing process.
This condition is characterized by the layers of the printed object shifting away from theirintended positions, which can significantly affect the quality and integrity of the final product. Recognizing the axis inwhich the layers have shifted is crucial for troubleshooting and resolving the issue effectively.
Finding Causes
Layer shifting can occur due to several factors, each associated with different components of the 3D printer or the printing process itself. Finding causes is the first thing to do when diagose 3D print layer shift.
- Hardware Issues
Hardware issues such as loose belts, obstructed components, vibrations, and unsteady platforms are among the primarycauses of layer shifting. Loose or damaged belts can lead to inaccurate movements of the print head or the printbed, resulting in layers that do not align properly. Similarly, obstructions in the path of moving components, excessivevibrations, or instability in the printing platform can interfere with the precise positioning required for each layer.
- Filament Quality
The quality of the filament used in 3D printing also plays a critical role in preventing layer shifts. Poor quality ordamaged filament that has absorbed moisture, contains knots or tangles, or is inconsistent in diameter can contributeto layer shifting. Such filament issues can cause irregularities in the extrusion process, leading to misaligned layers.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Check belt tension: Loose belts on the X and Y axes can cause the print head to slip during movement. Tighten the belts according to your printer's instructions.
- Inspect pulleys and wheels: Make sure pulleys are secure on the motor shafts and that wheels roll smoothly without any wobble.
- Reduce printing speed: Slowing down the print head allows for more precise movements, reducing the chance of layer shifting.
- Adjust slicer settings: Some slicer programs have settings to adjust acceleration and jerk, which can affect print head movement. Experiment with these settings to find a smoother travel pattern.
- Stabilize the printer: Place your printer on a sturdy, level surface to minimize vibrations that can cause misalignment. You can also try using vibration dampeners.
- Ensure proper bed adhesion: The first layer needs to adhere well to the print bed to provide a stable base for subsequent layers.
Preventing 3D Print Layer Shift
Layer shifting in 3D printing is a common issue where the layers of the printed object misalign during the printingprocess. This problem can significantly affect the quality and structural integrity of the final print.
Preventing layer shiftinvolves addressing both hardware and software aspects of the 3D printer to ensure smooth and accurate printing.
Hardware Fixes
A thorough inspection and maintenance of the printer's hardware components are crucial for preventing layer shift.
- Belts and Pulleys
Ensure that the belts are adequately tight. Loose belts can lead to insufficient tension, causing the motors to fail inaccurately moving the printheads, which results in layer shifts. It is also advised to mark the pulleys and shafts; if alayer shift occurs, check these marks to identify any slippage.
- Printer Stability
Verify that the printer is stable and not subject to any vibrations or bumps during the printing process. Even minordisturbances can misalign the print head temporarily and lead to layer shifting.
- Stepper Motors and Drivers
Stepper motors should be in good working condition as they are critical for precise movements. In cases of layershifting, assessing whether the problem is mechanical or electrical can prevent unnecessary replacements. High-qualitystepper motors rarely fail unless external factors like power driver issues or connection problems arise.
Software Fixes
Adjusting settings in your printer’s firmware and slicer software can also help prevent layer shifting.
- Slicer Settings Adjustment
Adjusting slicer settings is another effective strategy for correcting layer shift. This includes dialing back the printspeed and fine-tuning jerk and acceleration settings in the slicer software. These settings directly impact the qualityof the print and making slight adjustments can lead to significant improvements.
- Layer Height and Print Resolution
Considering the layer height and overall print resolution in the slicer settings can also make a difference. Thinnerlayers tend to produce more detailed prints but may require adjustments to speed and temperature settings to preventlayer shifting.
Correcting Layer Shift
Correcting layer shift involves a combination of troubleshooting and fine-tuning the printer settings to mitigate andprevent the problem from reoccurring.
Identifying the Cause
The first step in correcting layer shift is also to identify the axis (X-axis or Y-axis) where the shift has occurred. This determination is crucial as it directs the troubleshooting efforts towards the specific axis that is causing the problem.
Hardware Checks and Adjustments
- Tightening and Calibration
Loose components are a common cause of layer shifting. Check for loose bolts and screws, slack belts, and improperlyconnected wires. Tightening these components can often resolve the issue.
Additionally, calibrating the printer toensure all parts are properly aligned and operating smoothly is essential. This includes verifying that the print headassembly and bed move freely without obstructions.
- Motor and Speed Adjustments
If the layer shift persists, examining the axis motors is the next step. Adjusting the printing speed can also have asignificant impact. Reducing the printing speed by 50% is a recommended starting point to see if it helps mitigate thelayer shifting[18]. Keeping the printing speed below 60mm/s and reducing the travel speed to prevent the printheadfrom making contact with the print can prevent layer shifts.
- Preventive Measures
To prevent layer shifts from occurring, it's advisable to print in well-ventilated spaces or within an enclosure. This helpsin minimizing the impact of environmental factors that could contribute to layer shifting. Regular maintenance andcalibration of the printer are also essential in preventing layer shifts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article has provided an in-depth exploration of 3D print layer shift, elucidating its causes, effects, troubleshooting methods, and prevention strategies.
By understanding the mechanical, electrical, and software factors contributing to layer shift, individuals can effectively diagnose and address issues to ensure the accuracy and quality of their 3D prints.
Through diligent maintenance, calibration, and adjustment of hardware and software settings, layer shift can be minimized, allowing for smoother and more precise printing outcomes.
Unleash Your Creativity with Unionfab
At Unionfab, we're passionate about helping you bring your 3D designs to life. We offer a wide range of advanced printing techniques, like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Selective laser melting (SLM) and Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) and comprehensive finishing options to ensure your projects look their best.
Our team of experts is here to support you at every step, so you can focus on what matters most - unleashing your creativity.


