Anodizing Steel: Techniques, Benefits, and Applications

What is anodizing steel? In this article we'll uncover this process, weigh its pros and cons, and discover how it transforms steel across various sectors.
Introduction
Anodizing steel is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish. Anodizing can protect steel from a variety of corrosive environments and make steel more wear-resistant.
Anodized steel is commonly used in various applications, including automotive industry, electronics and more.
For more information, view Unionfab’s metal post-process options.
Understanding Anodizing Steel
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the surface of a metal into a protective oxide layer. This layer, called anodic oxide, is harder, more durable, and more corrosion-resistant than the underlying metal.
Anodizing can be applied to various metals, including aluminum, titanium, magnesium, and steel.
Why is Steel Anodized?
Steel is anodized to protect itself from rust and enhance its overall performance. The resulting benefits include improved corrosion resistance, increased durability, potential aesthetic improvements, and some level of electrical insulation.
These advantages make anodized steel a valuable material choice for various applications across different industries.
How Anodizing Works on Steel?
Pre-Anodizing Preparations
Surface Cleaning: Remove grease, dirt, and contaminants to ensure a good oxide layer forms..
Surface Roughening (optional) : Sandblasting or grit blasting can increase surface area for better oxide adhesion (if needed).
Surface Etching (optional) : A chemical dip removes a thin layer of steel for improved oxide adhesion (if necessary).
Process Overview
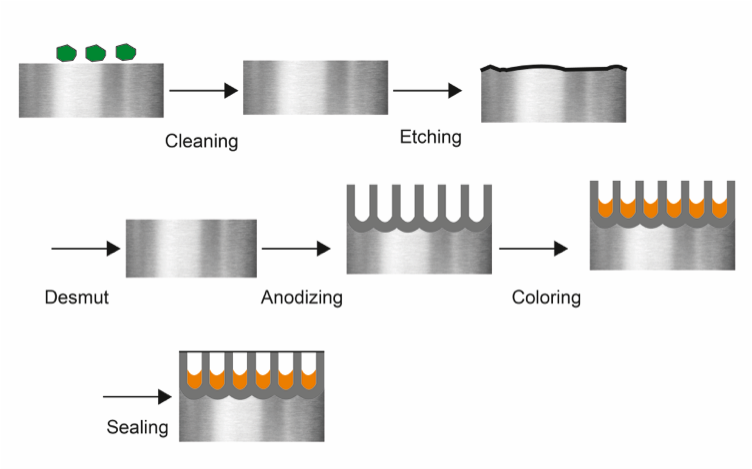
Cleaning and Pretreatment: The steel surface is thoroughly cleaned and pretreated to remove any contaminants and ensure a uniform oxide layer.
Electrolytic Bath: The steel is submerged in an electrolytic bath containing an acidic solution, typically sulfuric acid.
Direct Current: A direct current is passed through the bath, making the steel the anode (positive electrode).
Oxide Formation: Oxygen ions in the electrolyte migrate towards the anode and react with the steel surface, forming the anodic oxide layer.
Sealing: After anodizing, the oxide layer is often sealed in hot water or a chemical solution to improve its durability and corrosion resistance.
Chemical Reactions
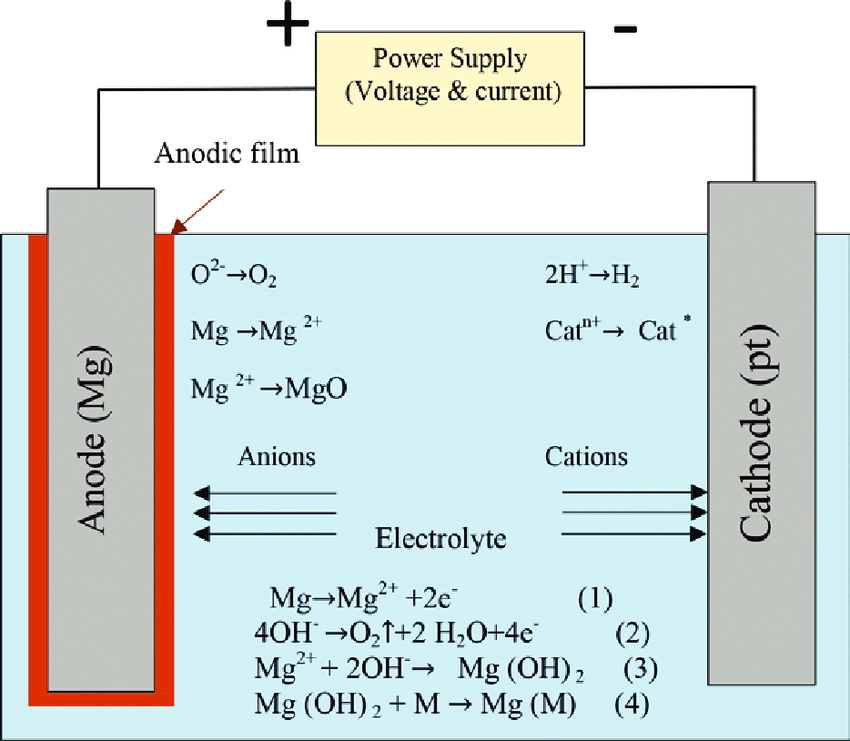
Anode (Steel): Iron atoms lose electrons, becoming ferrous ions (Fe²⁺) that enter the electrolyte.
Cathode: Hydrogen ions (H⁺) gain electrons and form hydrogen gas (H₂) bubbles.
Overall, iron ions react with water to form a protective iron oxide layer (like magnetite, Fe₃O₄) on the steel surface. This layer fights rust and enhances durability.

Techniques of Anodizing Steel
Methods of Anodizing
Method | Oxide Layer Thickness | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Sulfuric Acid Anodizing | 0.5-2 mm | General purpose, decorative, electrical components |
Hardcoat Anodizing | 25-50 mm | Wear parts, tooling, machinery components |
Chromic Acid Anodizing | 0.5-2 mm | Similar to SAA, but with better color options |
Oxalic Acid Anodizing | 0.5-2 mm | Similar to SAA, but more environmentally friendly |
Phosphoric Acid Anodizing | 0.5-2 mm | Similar to SAA, but with a more matte finish |
Pros and Cons of Anodizing Steel
Pros
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: The primary benefit. Anodizing creates a stable oxide layer that acts as a barrier against rust and other forms of corrosion. This extends the lifespan of steel exposed to moisture or harsh environments.
Improved Durability: The anodizing process hardens the steel surface, making it more resistant to scratches, abrasions, and wear and tear.
Aesthetic Options: Compared with bare steel, anodizing can create a black oxide layer or even other colors, potentially eliminating the need for additional painting or coating.
Electrical Insulation Properties: The oxide layer formed during anodizing provides some electrical insulation,which can be beneficial in specific applications.
Cons
Potential for Hydrogen Embrittlement: If not properly controlled, the anodizing process can introduce hydrogen into the steel, which can make it brittle and susceptible to cracking.
Dimensional Changes: The anodizing process can cause slight changes in the dimensions of the steel parts.
Color Limitations: The natural color of anodized steel is typically a dull gray or black. Color options are limited compared to other finishes.
Increased Cost: Anodizing adds an additional cost to the manufacturing process.
Environmental Concerns: Some anodizing processes use hazardous chemicals, which can pose environmental risks.
Applications of Anodized Steel
Anodized steel finds uses in various industries due to its properties:
Architecture: Corrosion resistance and aesthetics make it ideal for building facades, railings, and cladding.
Automotive: Wheels, trim, and some engine components benefit from wear resistance and corrosion protection.
Aerospace: Lightweight and durable, it's used in some aerospace components.
Consumer Goods: Tools, hardware, and cutlery can be anodized for better wear and appearance.
Medical Equipment: Corrosion resistance and biocompatibility make it suitable for certain medical instruments.
Electronics (limited): Some components might utilize its slight electrical insulation properties.
Conclusion
Anodizing steel offers a unique set of advantages. The resulting oxide layer significantly improves corrosion resistance and durability, while also offering some aesthetic options and electrical insulation properties. When strategically applied, anodizing steel can be a valuable tool.
Ready to bring your parts to life with expert finishing? Explore our wide range of metal finishing services designed to elevate your projects. Whether you need anodizing, polishing, or custom finishes, our team is ready to assist you.
Seamlessly Add Anodizing to Your Quote
At Unionfab, we make it easy to include anodizing in your manufacturing projects.
How to Add Anodizing in Our Quoting System
Click “Get Instant Quote” on our website toolbar or here.
Upload your 3D model or edit an existing project.
Select the item you want to customize and click “Edit Item.”
Choose Anodizing from the finishing dropdown menu and click “Apply.”
Need more detailed instructions? Check out our Step-by-Step Guide for a comprehensive walkthrough!
Unionfab offers much more than just finishing services. As a leading 3D printing and manufacturing company, we specialize in providing end-to-end solutions—from prototyping to production, ensuring your projects are completed with precision and quality.
Whether you need advanced 3D printing, CNC machining, or finishing services, we are your one-stop shop for all manufacturing needs. Contact us today to unlock the full potential of your designs!


