On-Demand Manufacturing: How Production is Transformed
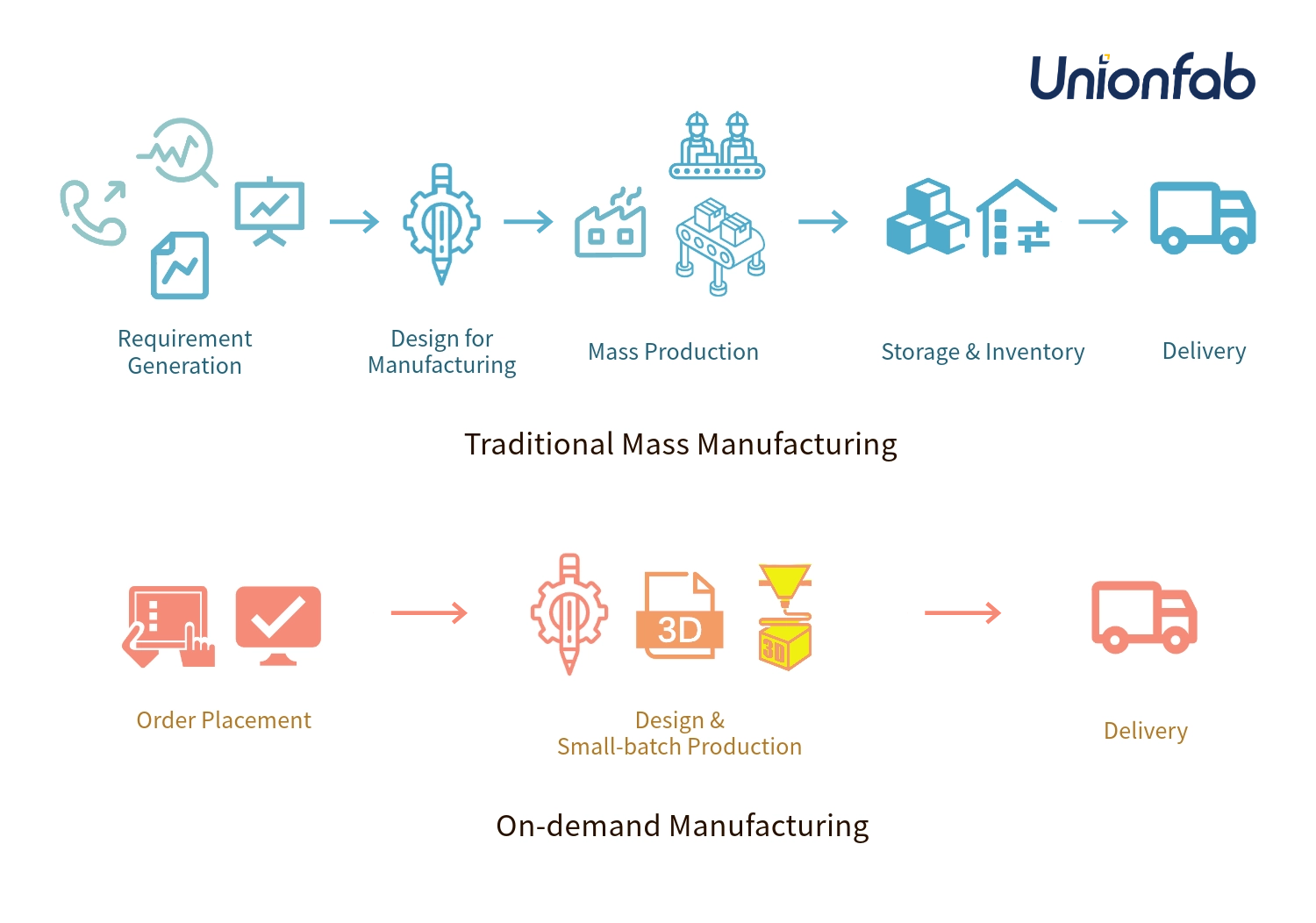
On-demand manufacturing now enable flexible, customized production in small batches closer to the end user. Techniques like 3D printing, CNC machining, injection molding and vacuum casting provides advantages over mass production.
Introduction to On-Demand Manufacturing
On-demand manufacturing, or manufacturing on demand (MOD), is a method of manufacturing in which goods are only produced when they are required – in contrast to mass production. It refers to making products digitally and physically closer to the point of consumption, utilizing flexible, distributed production systems rather than centralized mass production.
While standardized, one-size-fits-all products were once acceptable, consumers now demand precise customization and versions tailored to their unique needs not feasible through mass manufacturing. To remain competitive, companies must meet this demand for specialized variations through more nimble, responsive production models.
On-demand systems address this need by enabling customized, versatile manufacturing in smaller batches. Products can be adapted quickly if customer desires change. This represents a major shift away from high-volume manufacturing toward flexible, low-volume production driven by consumption patterns in real time.
Differences from Traditional Mass Production
Centralization vs. Distribution
Mass Production: Traditional mass production prioritizes high-volume production in order to benefit from economies of scale. Production takes place in large, centralized factories built specifically for standardized, high-volume production, minimizing unit costs and thus maximizing productivity.
On-Demand Manufacturing: In contrast, on-demand manufacturing adopts a more distributed model oriented towards flexible, specialized low-volume production. Manufacturing occurs locally using flexible systems situated closer to the end user. This enables quick responsiveness to changing customer demands.
Volume and Standardization vs. Small batches and Customization


Mass Production: Mass production optimizes for high volumes and economies of scale, often resulting in standardized, identical products.
On-Demand Manufacturing: On-demand manufacturing prioritizes customization and specialization. Variations and tailored solutions are easy to produce in low batches.
Inventory Management

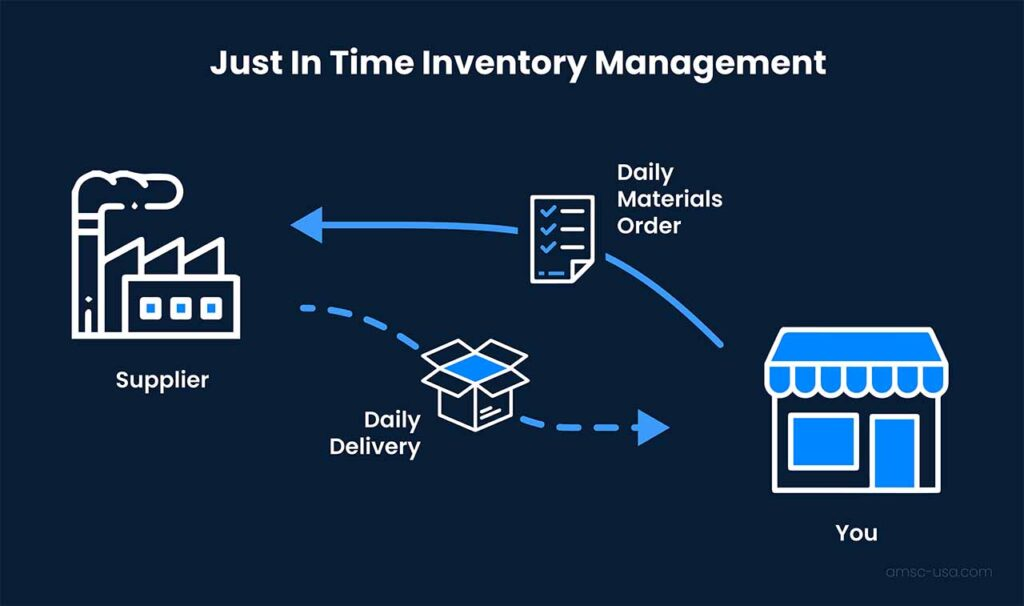
Mass Production: Mass production often involves maintaining significant inventories to meet anticipated demand.
On-Demand Manufacturing: On-demand manufacturing reduces the reliance on extensive inventories, emphasizing just-in-time (JIT) delivery models where products are produced in response to actual orders, minimizing waste and surplus inventory.
Advantages of On-Demand Manufacturing
Benefits for manufacturers:
Agility to Customized Demand - Producing to order allows quick responses to changing customer preferences. Short lead times enable meeting specialized requests profitability.
Reduced Lead Times - No waiting for large production runs. Digital manufacturing technologies like 3D printing can produce and deliver in days versus weeks/months for traditional manufacturing.
Reduced Minimum Orders and Waste - On-demand avoids upfront mass production of standardized parts that may go unsold resulting in excess inventory. Batches closely match confirmed orders.
Easier Mass Customization - In on-demand manufacturing, particularly with techniques such as 3D printing and CNC machining, parts are digitally defined using CAD/CAM files. There is no need to produce new physical tooling for each variation, allowing for the efficient creation of derivative products.
Rapid Prototyping - Easy, fast design iterations optimize products more efficiently by getting feedback sooner from prototypes in customers’ hands, leading to faster Time to Market (TTM) and the ability to stay ahead of competitors.
Potential for New Revenue Streams - Businesses can explore new revenue streams by offering on-demand manufacturing services to other companies or individuals. This can include producing spare parts, custom components, or design services.
Lower Inventory Costs - Less capital tied up in maintaining large physical stockpiles with JIT digital inventories. Real-time production frees up finances for new opportunities.
On-Demand Manufacturing Techniques
3D Printing
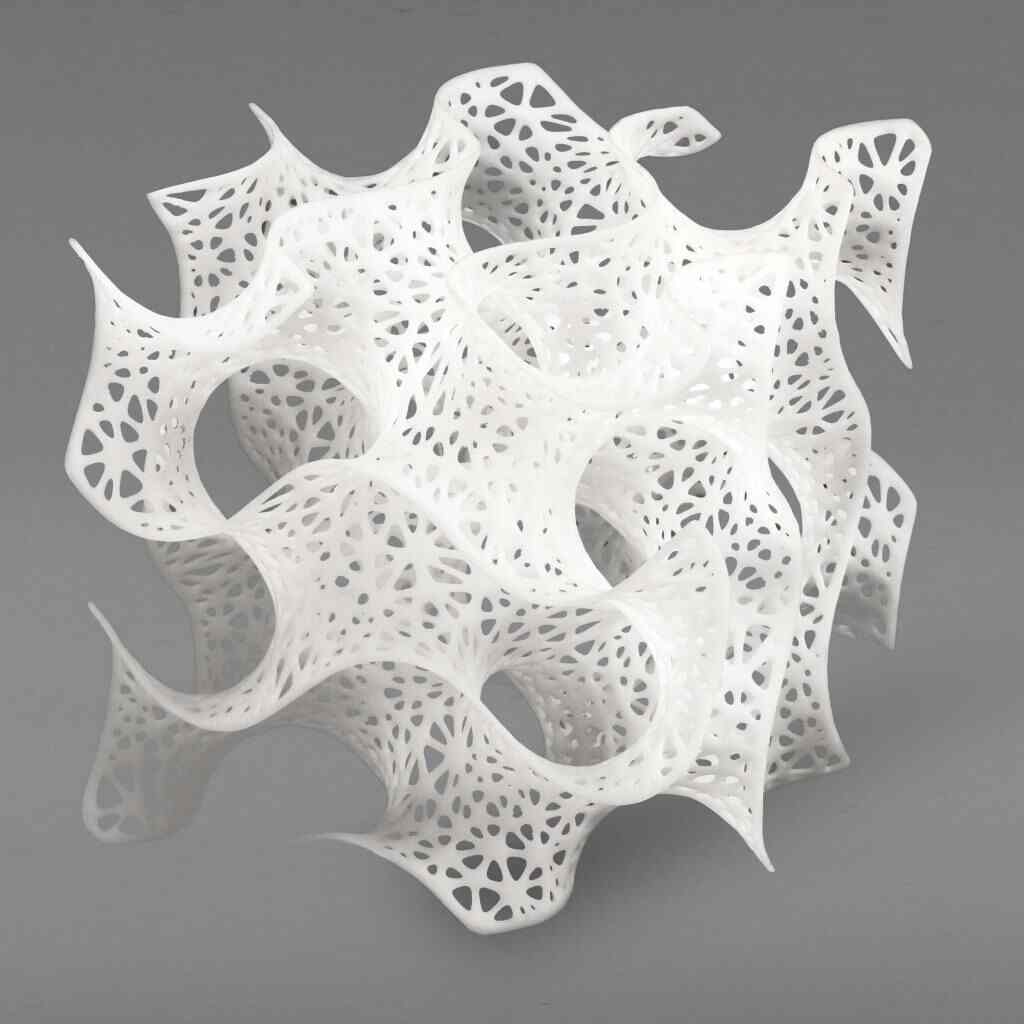

Additive manufacturing via 3D printing excels at producing low-volume customized components on demand. It allows complex geometries to be made without typical tooling constraints.
3D printing is well-suited for design prototyping and specialized/individualized parts in limited quantities. However, it may not be as cost-effective or efficient for high-volume production due to its layer-by-layer additive process.
CNC Machining
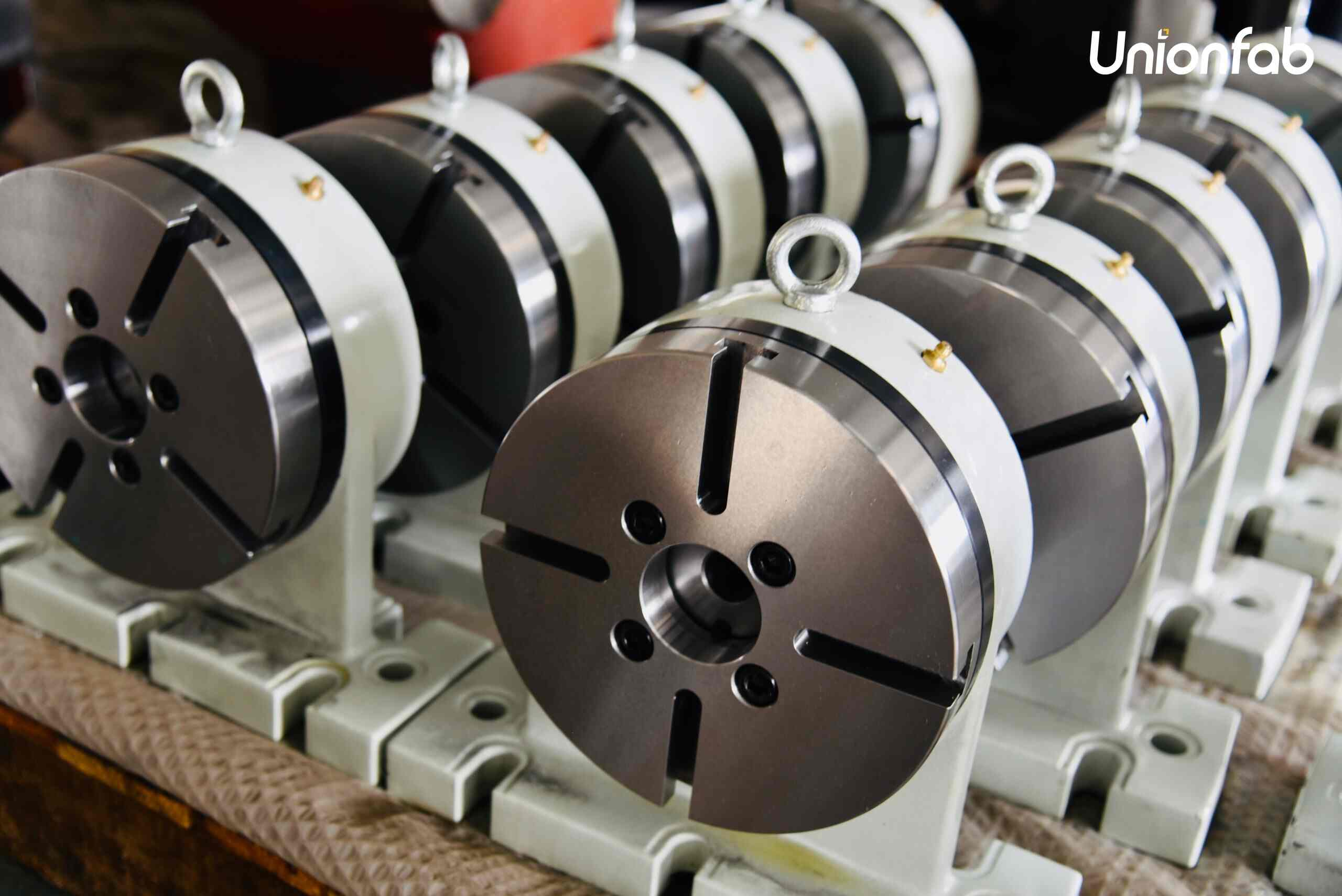
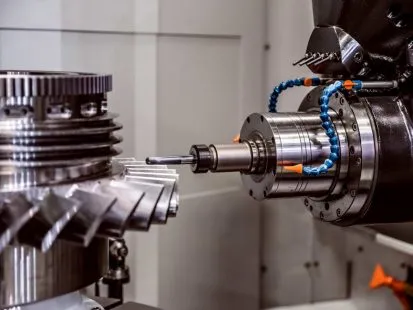

CNC (computer numerical control) machining is synonymous with precision. It excels in producing high-accuracy parts with tight tolerances.
This technique is ideal for industries where exact measurements and fine details are paramount, such as aerospace and medical devices.
Injection Molding
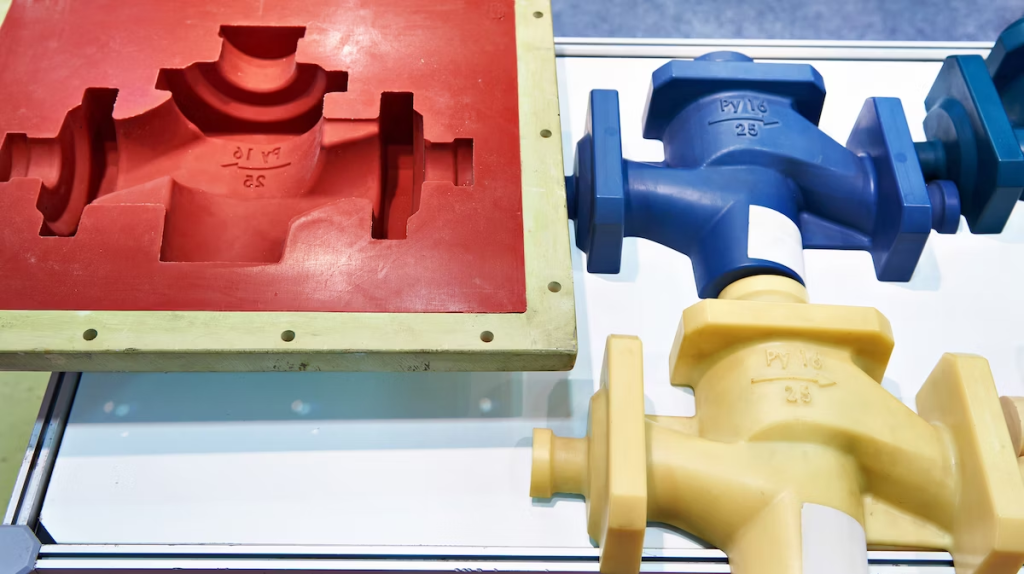
For higher volumes, injection molding molds allow mass-customized plastic or metal components to be produced scalably and cost-effectively.
While initial molds mean more startup costs, per-unit pricing drops significantly with large production quantities.
Vacuum Casting
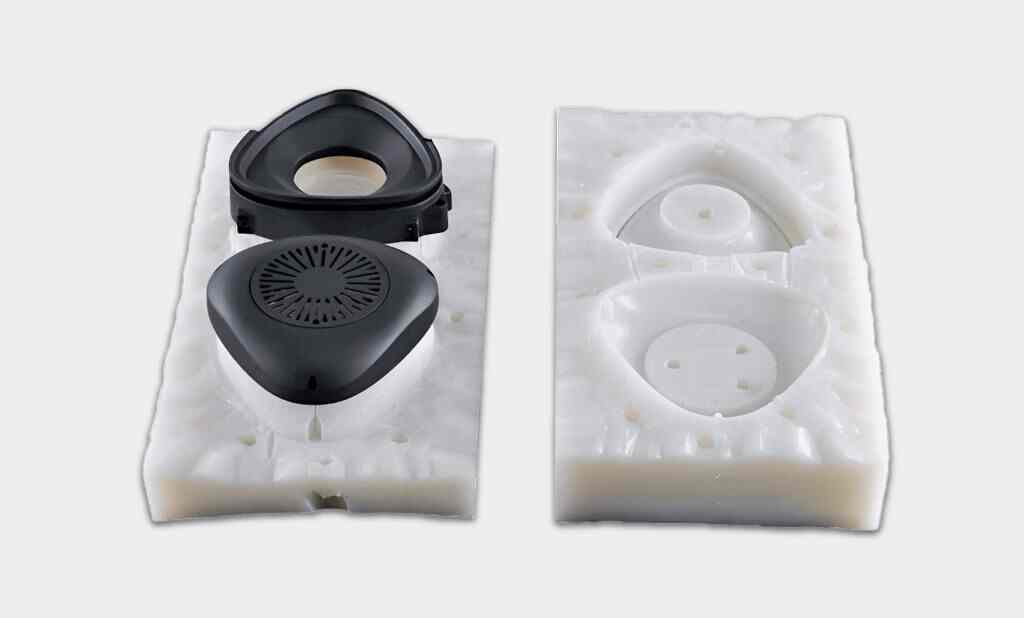

Vacuum casting provides an option for some materials like plastics to be reproduced in small batches with exceptional detail and surface finish.
It’s particularly cost-effective for low-volume production runs, offering an alternative to injection molding for smaller quantities.
Read this article to make a more informed comparison of these techniques and select the most suitable one for your project.
Challenges and Disadvantages
Higher Unit Costs - Production runs of one don’t benefit from scale economies as much as high-volume factories. Costs may be prohibitive until meeting minimum order quantities.
Supply Chain Complexity - Coordinating a global network of dispersed on-demand manufacturers is more intricate than single-site mass production facilities.
Technical Limitations on Sizes - 3D printing and CNC have maximum dimensions depending on machine size and material properties. Large-scale or oversized parts may pose challenges in terms of production.
Limited Material Selection - On-demand manufacturing, especially 3D printing, may offer a more limited selection of materials compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Skill and Expertise Requirements - Operating computer-integrated tools and digital design workflows requires knowledgeable technicians with expertise in areas such as CAD/CAM design, machine operation versus semi-skilled labor for traditional assembly lines.
Scalability Challenges - Scalability can be a challenge for certain methods, especially when transitioning from small-scale to large-scale production.
Will On-Demand Manufacturing Lead to Increased Supply Chain Complexity?
Distributed model of On-demand manufacturing can introduce challenges regarding supply chain complexity:
Production Network Complexity - A distributed model often means production facilities may be spread across multiple locations or even globally. Coordinating production, quality control, and logistics among these dispersed facilities can add complexity.
Logistics and Transportation - Coordinating the movement of raw materials, semi-finished products, and finished goods among multiple production sites and distribution centers can introduce logistical complexities. Managing transportation and minimizing shipping costs can be challenging.
Quality Control and Standardization - Ensuring consistent product quality across distributed manufacturing facilities may require stringent quality control measures and standardized processes, which can be complex to implement and maintain.
Supply Chain Visibility - Maintaining visibility across a distributed supply chain can be challenging. Real-time monitoring of inventory levels, production progress, and demand patterns require advanced data integration systems.
Digital Collaboration - Disparate on-demand manufacturing systems should seamlessly interface through consolidated IOT/IT platforms to synchronously share designs, track progress and enable collaboration.
Risk Management - Distributed networks with many single points of failure can be vulnerable to disruptions. Agile mitigation plans are needed to reduce delays from quality issues, supplier problems or geopolitical events impacting nodes.
To succeed in a distributed on-demand manufacturing model, businesses must invest in robust supply chain management strategies. The goal is building flexibility, visibility and collaborative mindsets to navigate risks.
As your trusted partner, Unionfab offer comprehensive solutions to overcome supply chain problems and unlock numerous benefits:
Transparency Through Our Platform
Our advanced order management platform offers comprehensive transparency throughout the production process, allowing you to closely monitor and manage every stage of your orders.
Quality Control and Refund Policy
Our partnership includes robust quality control measures that help you maintain consistent product standards. In the rare event of quality issues, our flexible refund policy ensures that you can address customer concerns promptly and effectively, safeguarding your reputation and customer trust.
Collaboration with Leading Delivery Companies
Partnering with industry leaders such as FedEx, UPS, and DHL, we guarantee punctual and secure deliveries of products to you.
Embark on your journey as an on-demand manufacturer by partnering with us! Feel free to contact our sales team for further information.

Conclusion
On-demand manufacturing stands as a transformative force that aligns perfectly with the needs of today’s dynamic market landscape. Its ability to respond swiftly to customer preferences, streamline production, and reduce waste resonates strongly in an era marked by customization, sustainability, and rapidly changing consumer demands.
Key Points Recap:
On-demand manufacturing represents a shift away from traditional mass production models, focusing on flexibility, customization, and efficiency.
Techniques such as 3D printing, CNC machining, vacuum casting, and injection molding underpin the versatility of on-demand manufacturing.
Advantages include agility, reduced lead times, minimized waste, rapid prototyping, and low inventory costs.
Challenges encompass higher unit costs for low volumes, supply chain complexities, technical limitations, material constraints, skill requirements, and scalability hurdles.


